Abstract
Background
Although glutamate transmission via astrocytes has been proposed to contribute to the pathophysiology of depression, the precise mechanisms are unknown. Herein, we investigated the levels of glutamate transporter-1 (GLT-1) and glutamine synthetase (GS) of astrocytes in learned helplessness (LH) rats (an animal model of depression) and non-LH rats (an animal model of resilience).
Methods
We administered inescapable mild electric shock to rats and then discriminated the LH and non-LH rats by a post-shock test. Almost 55% of the rats acquired LH. We then measured the expressions of GLT-1 and GS in several brain regions of LH and non-LH rats by Western blot analysis.
Results
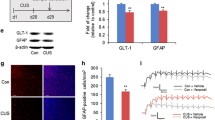
The levels of GLT-1 and GS in the CA-1, CA-3, dentate gyrus (DG), medial prefrontal cortex (mPF), and nucleus accumbens (NAc) of the LH group were significantly higher than those of the control group. The GS levels in the amygdala of the LH rats were significantly decreased compared to the controls. There were significant differences in GLT-1 and GS levels between the non-LH and LH rats in the CA-1 and CA-3.
Conclusions
These results suggest that the LH rats experienced up-regulations of GLT-1 and GS in the CA-1, CA-3, DG, mPF, and NAc and a down-regulation of GS in the amygdala. It is possible that the effects of the GLT-1 and GS levels on astrocytes in the CA-1 and CA-3 are critical for the differentiation of resilience from vulnerability.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Albrecht J, Sidoryk-Węgrzynowicz M, Zielińska M, Aschner M (2010) Roles of glutamine in neurotransmission. Neuron Glia Biol 6:263–276
Bernstein H-G, Meyer-Lotz G, Dobrowolny H et al (2015) Reduced density of glutamine synthetase immunoreactive astrocytes in different cortical areas in major depression but not in bipolar I disorder. Front Cell Neurosci 9:273
Charney DS (2004) Psychobiological mechanisms of resilience and vulnerability: implications for successful adaptation to extreme stress. Am J Psychiatry 161:195–216
Cheung NS, Pascoe CJ, Giardina SF, John CA, Beart PM (1998) Micromolar L-glutamate induces extensive apoptosis in an apoptotic-necrotic continuum of insult-dependent, excitotoxic injury in cultured cortical neurones. Neuropharmacology 37:1419–1429
Frodl T, Meisenzahl EM, Zetzsche T, Born C, Jäger M, Groll C, Bottlender R, Leinsinger G, Möller HJ (2003) Larger amygdala volumes in first depressive episode as compared to recurrent major depression and healthy control subjects. Biol Psychiatry 53:338–344
Godlewska B, Norbury R, Selvaraj S et al (2012) Short-term SSRI treatment normalises amygdala hyperactivity in depressed patients. Psychol Med 42:2609–2617
Goldwater DS, Pavlides C, Hunter RG, Bloss EB, Hof PR, McEwen BS, Morrison JH (2009) Structural and functional alterations to rat medial prefrontal cortex following chronic restraint stress and recovery. Neuroscience 164:798–808
Gruenbaum SE, Wang H, Zaveri HP, Tang AB, Lee TSW, Eid T, Dhaher R (2015) Inhibition of glutamine synthetase in the central nucleus of the amygdala induces anhedonic behavior and recurrent seizures in a rat model of mesial temporal lobe epilepsy. Epilepsy Behav 51:96–103
Hammen C (2005) Stress and depression. Annu Rev Clin Psychol 1:293–319
Hashimoto K, Sawa A, Iyo M (2007) Increased levels of glutamate in brains from patients with mood disorders. Biol Psychiatry 62:1310–1316
Hertz L (1979) Functional interactions between neurons and astrocytes I. Turnover and metabolism of putative amino acid transmitters. Prog Neurobiol 13:277–323
Iwata M, Shirayama Y, Ishida H, Kawahara R (2006) Hippocampal synapsin I, growth-associated protein-43, and microtubule-associated protein-2 immunoreactivity in learned helplessness rats and antidepressant-treated rats. Neuroscience 141:1301–1313
Iwata M, Shirayama Y, Ishida H, Hazama GI, Nakagome K (2011) Hippocampal astrocytes are necessary for antidepressant treatment of learned helplessness rats. Hippocampus 21:877–884
Jett JD, Bulin SE, Hatherall LC, McCartney CM, Morilak DA (2017) Deficits in cognitive flexibility induced by chronic unpredictable stress are associated with impaired glutamate neurotransmission in the rat medial prefrontal cortex. Neuroscience 346:284–297
John CS, Sypek EI, Carlezon WA, Cohen BM, Öngür D, Bechtholt AJ (2015) Blockade of the GLT-1 transporter in the central nucleus of the amygdala induces both anxiety and depressive-like symptoms. Neuropsychopharmacology 40:1700–1708
Kim R, Healey KL, Sepulveda-Orengo MT, Reissner KJ (2018) Astroglial correlates of neuropsychiatric disease: from astrocytopathy to astrogliosis. Prog Neuro-Psychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 87:126–146
Kohen R, Kirov S, Navaja G et al (2005) Gene expression profiling in the hippocampus of learned helpless and nonhelpless rats. Pharmacogenomics J 5:278–291
Lakshminarasimhan H, Chattarji S (2012) Stress leads to contrasting effects on the levels of brain derived neurotrophic factor in the hippocampus and amygdala. PLoS One 7:e30481
Licinio J, Wong M (2011) Advances in depression research: 2011. Mol Psychiatry 16:686–687. https://doi.org/10.1038/mp.2011.74
Machado-Vieira R, Manji HK, Zarate CA (2009) The role of the tripartite glutamatergic synapse in the pathophysiology and therapeutics of mood disorders. Neuroscientist 15:525–539
Magariños AM, Deslandes A, McEwen BS (1999) Effects of antidepressants and benzodiazepine treatments on the dendritic structure of CA3 pyramidal neurons after chronic stress. Eur J Pharmacol 371:113–122
Miguel-Hidalgo JJ, Waltzer R, Whittom AA, Austin MC, Rajkowska G, Stockmeier CA (2010) Glial and glutamatergic markers in depression, alcoholism, and their comorbidity. J Affect Disord 127:230–240
Mitani H, Shirayama Y, Yamada T, Maeda K, Ashby CR Jr, Kawahara R (2006) Correlation between plasma levels of glutamate, alanine and serine with severity of depression. Prog Neuro-Psychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 30:1155–1158
Muneoka K, Shirayama Y, Horio M, Iyo M, Hashimoto K (2013) Differential levels of brain amino acids in rat models presenting learned helplessness or non-learned helplessness. Psychopharmacology 229:63–71
Obrenovitch TP, Urenjak J (1997) Altered glutamatergic transmission in neurological disorders: from high extracellular glutamate to excessive synaptic efficacy. Prog Neurobiol 51:39–87
Odeon MM, Andreu M, Yamauchi L, Grosman M, Acosta GB (2015) Chronic postnatal stress induces voluntary alcohol intake and modifies glutamate transporters in adolescent rats. Stress 18:427–434
Sanacora G, Rothman DL, Mason G et al (2003) Clinical studies implementing glutamate neurotransmission in mood disorders. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1003:292–308
Sanacora G, Zarate CA, Krystal JH, Manji HK (2008) Targeting the glutamatergic system to develop novel, improved therapeutics for mood disorders. Nat Rev Drug Discov 7:426–437
Selye H (1985) The nature of stress. Basal Facts 7:3–11
Sheline YI, Wang PW, Gado MH, Csernansky JG, Vannier MW (1996) Hippocampal atrophy in recurrent major depression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 93:3908–3913
Shirayama Y, Chaki S (2006) Neurochemistry of the nucleus accumbens and its relevance to depression and antidepressant action in rodents. Curr Neuropharmacol 4:277–291
Shirayama Y, Hashimoto K (2017) Effects of a single bilateral infusion of R-ketamine in the rat brain regions of a learned helplessness model of depression. Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci 267:177–182
Shirayama Y, Chen AC-H, Nakagawa S et al (2002) Brain-derived neurotrophic factor produces antidepressant effects in behavioral models of depression. J Neurosci 22:3251–3261. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.22-08-03251.2002
Shirayama Y, Yang C, J-c Z et al (2015) Alterations in brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) and its precursor proBDNF in the brain regions of a learned helplessness rat model and the antidepressant effects of a TrkB agonist and antagonist. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol 25:2449–2458
Smalheiser NR, Lugli G, Rizavi HS, Zhang H, Torvik VI, Pandey GN, Davis JM, Dwivedi Y (2011) MicroRNA expression in rat brain exposed to repeated inescapable shock: differential alterations in learned helplessness vs. non-learned helplessness. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol 14:1315–1325
Son H, Baek JH, Go BS, Jung DH, Sontakke SB, Chung HJ, Lee DH, Roh GS, Kang SS, Cho GJ, Choi WS, Lee DK, Kim HJ (2018) Glutamine has antidepressive effects through increments of glutamate and glutamine levels and glutamatergic activity in the medial prefrontal cortex. Neuropharmacology 143:143–152
Taneja M, Salim S, Saha K, Happe HK, Qutna N, Petty F, Bylund DB, Eikenburg DC (2011) Differential effects of inescapable stress on locus coeruleus GRK3, alpha2-adrenoceptor and CRF1 receptor levels in learned helpless and non-helpless rats: a potential link to stress resilience. Behav Brain Res 221:25–33
Torp R, Danbolt N, Babaie E et al (1994) Differential expression of two glial glutamate transporters in the rat brain: an in situ hybridization study. Eur J Neurosci 6:936–942
Veeraiah P, Noronha JM, Maitra S, Bagga P, Khandelwal N, Chakravarty S, Kumar A, Patel AB (2014) Dysfunctional glutamatergic and γ-aminobutyric acidergic activities in prefrontal cortex of mice in social defeat model of depression. Biol Psychiatry 76:231–238
Vyas A, Mitra R, Rao BS et al (2002) Chronic stress induces contrasting patterns of dendritic remodeling in hippocampal and amygdaloid neurons. J Neurosci 22:6810–6818
Willner P (1986) Validation criteria for animal models of human mental disorders: learned helplessness as a paradigm case. Prog Neuro-Psychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 10:677–690
Willoughby JO, Mackenzie L, Broberg M, Thoren AE, Medvedev A, Sims NR, Nilsson M (2003) Fluorocitrate-mediated astroglial dysfunction causes seizures. J Neurosci Res 74:160–166
Wood SK, Walker HE, Valentino RJ, Bhatnagar S (2010) Individual differences in reactivity to social stress predict susceptibility and resilience to a depressive phenotype: role of corticotropin-releasing factor. Endocrinology 151:1795–1805
Yang C, Shirayama Y, Zhang JC, Ren Q, Hashimoto K (2015a) Peripheral interleukin-6 promotes resilience versus susceptibility to inescapable electric stress. Acta Neuropsychiatr 27:312–316
Yang C, Shirayama Y, Zhang JC et al (2015b) Regional differences in brain-derived neurotrophic factor levels and dendritic spine density confer resilience to inescapable stress. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol 18:121
Zazpe A, Artaiz I, Labeaga L, Lucero ML, Orjales A (2007) Reversal of learned helplessness by selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors in rats is not dependent on 5-HT availability. Neuropharmacology 52:975–984
Zhang K, Fujita Y, Chang L, Qu Y, Pu Y, Wang S, Shirayama Y, Hashimoto K (2019) Abnormal composition of gut microbiota is associated with resilience versus susceptibility to inescapable electric stress. Transl Psychiatry 9:231
Zhao J, Verwer R, Van Wamelen D et al (2016) Prefrontal changes in the glutamate-glutamine cycle and neuronal/glial glutamate transporters in depression with and without suicide. J Psychiatr Res 82:8–15
Zhu X, Ye G, Wang Z, Luo J, Hao X (2017) Sub-anesthetic doses of ketamine exert antidepressant-like effects and upregulate the expression of glutamate transporters in the hippocampus of rats. Neurosci Lett 639:132–137
Zink M, Vollmayr B, Gebicke-Haerter P et al (2010) Reduced expression of glutamate transporters vGluT1, EAAT2 and EAAT4 in learned helpless rats, an animal model of depression. Neuropharmacology 58:465–473
Acknowledgments
We thank Miwako Nakamura (Chiba University Graduate School of Medicine) for her technical support with the general experiments.
Funding
This research received no specific grant from any funding agency or commercial or not-for-profit sectors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceived and designed the experiments: K.Y., Y.O., M.K., H.K., M.N., Y.S., M.I. Performed the experiments: K.Y., Y.O., M.K., M.N. Analyzed the data: K.Y., Y.O., M.K. Wrote the paper: K.Y., Y.O., M.K., Y.S. Supervised the research: Y.S., M.I.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yoshino, K., Oda, Y., Kimura, M. et al. The alterations of glutamate transporter 1 and glutamine synthetase in the rat brain of a learned helplessness model of depression. Psychopharmacology 237, 2547–2553 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-020-05555-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-020-05555-3