Abstract
Aim
Indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase 1 (IDO) is responsible for the progression of the kynurenine pathway, which has been implicated in the pathophysiology of inflammation-induced depression. It has been reported that asperosaponin VI (ASA VI) could play a neuroprotective role through anti-inflammatory and antioxidant. In this study, we examined the antidepressant effect of ASA VI in lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-treated mice and further explored its molecular mechanism by looking into the microglial kynurenine pathway.
Methods
To generate the model, LPS (0.83 mg/kg) was administered intraperitoneally to mice. The mice received ASA VI (10 mg/kg, 20 mg/kg, 40 mg/kg, and 80 mg/kg, i.p.) 30 min before LPS injection. Depressive-like behaviors were evaluated based on the duration of immobility in the forced swim test. Microglial activation and inflammatory cytokines were detected by immunohistochemistry, real-time PCR, and ELISA. The TLR4/NF-κB signaling pathway and the expression of IDO, GluA2, and CamKIIβ were also measured by western blotting.
Results
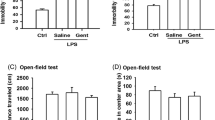
ASA VI exhibited significant antidepressant activity in the presence of LPS on immobility and latency times in the forced swim test. The LPS-induced activation of microglia and inflammatory response were inhibited by ASA VI, which showed a dose-dependent pattern. TLR4/NF-κB signaling pathway also was suppressed by ASA VI in the hippocampus and prefrontal cortex of LPS-treated mice. Furthermore, ASA VI inhibited the increase in IDO protein expression and normalized the aberrant glutamate transmission in the hippocampus and prefrontal cortex caused by LPS administration.
Conclusion
Our results propose a promising antidepressant effect for ASA VI possibly through the downregulation of IDO expression and normalization of the aberrant glutamate transmission. This remedying effect of ASA VI could be attributed to suppress microglia-mediated neuroinflammatory response via inhibiting the TLR4/NF-κB signaling pathway.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agudelo LZ, Femenia T, Orhan F, Porsmyr-Palmertz M, Goiny M, Martinez-Redondo V, Correia JC, Izadi M, Bhat M, Schuppe-Koistinen I, Pettersson AT, Ferreira DMS, Krook A, Barres R, Zierath JR, Erhardt S, Lindskog M, Ruas JL (2014) Skeletal muscle PGC-1alpha1 modulates kynurenine metabolism and mediates resilience to stress-induced depression. Cell 159:33–45
Al-Harbi KS (2012) Treatment-resistant depression: therapeutic trends, challenges, and future directions. Patient Prefer Adherence 6:369–388
Brites D, Fernandes A (2015) Neuroinflammation and depression: microglia activation, extracellular microvesicles and microRNA dysregulation. Front Cell Neurosci 9:476
Corona AW, Norden DM, Skendelas JP, Huang Y, O’Connor JC, Lawson M, Dantzer R, Kelley KW, Godbout JP (2013) Indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase inhibition attenuates lipopolysaccharide induced persistent microglial activation and depressive-like complications in fractalkine receptor (CX(3)CR1)-deficient mice. Brain Behav Immun 31:134–142
Dantzer R, O’Connor JC, Freund GG, Johnson RW, Kelley KW (2008) From inflammation to sickness and depression: when the immune system subjugates the brain. Nat Rev Neurosci 9:46–56
Du HX, Chen XG, Zhang L, Liu Y, Zhan CS, Chen J, Zhang Y, Yu ZQ, Zhang J, Yang HY, Zhong K, Liang CZ (2019) Microglial activation and neurobiological alterations in experimental autoimmune prostatitis-induced depressive-like behavior in mice. Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat 15:2231–2245
Duman RS, Aghajanian GK (2012) Synaptic dysfunction in depression: potential therapeutic targets. Science 338:68–72
Frick LR, Williams K, Pittenger C (2013) Microglial dysregulation in psychiatric disease. Clin Dev Immunol 2013:608654
Ginhoux F, Greter M, Leboeuf M, Nandi S, See P, Gokhan S, Mehler MF, Conway SJ, Ng LG, Stanley ER, Samokhvalov IM, Merad M (2010) Fate mapping analysis reveals that adult microglia derive from primitive macrophages. Science 330:841–845
Guo DK, Zhu Y, Sun HY, Xu XY, Zhang S, Hao ZB, Wang GH, Mu CC, Ren HG (2019) Pharmacological activation of REV-ERBalpha represses LPS-induced microglial activation through the NF-kappaB pathway. Acta Pharmacol Sin 40:26–34
Hanisch UK, Kettenmann H (2007) Microglia: active sensor and versatile effector cells in the normal and pathologic brain. Nat Neurosci 10:1387–1394
Hashmi AM, Butt Z, Umair M (2013) Is depression an inflammatory condition? A review of available evidence. J Pak Med Assoc 63:899–906
Hemmati S, Sadeghi MA, Mohammad Jafari R, Yousefi-Manesh H, Dehpour AR (2019) The antidepressant effects of GM-CSF are mediated by the reduction of TLR4/NF-kB-induced IDO expression. 16, 117
Jiang J, Jian Q, Jing M, Zhang Z, Zhang G, Shan L, Yu P, Wang Y, Xu L (2019) The novel N-methyl-d-aspartate receptor antagonist MN-08 ameliorates lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury in mice. Int Immunopharmacol 66:109–118
Jung YS, Park JH, Kim H, Kim SY, Hwang JY, Hong KW, Bae SS, Choi BT, Lee SW, Shin HK (2016) Probucol inhibits LPS-induced microglia activation and ameliorates brain ischemic injury in normal and hyperlipidemic mice. Acta Pharmacol Sin 37:1031–1044
Ke K, Li Q, Yang X, Xie Z, Wang Y, Shi J, Chi L, Xu W, Hu L, Shi H (2016) Asperosaponin VI promotes bone marrow stromal cell osteogenic differentiation through the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway in an osteoporosis model. Sci Rep 6:35233
Kohler O, Krogh J, Mors O, Benros ME (2016) Inflammation in depression and the potential for anti-inflammatory treatment. Curr Neuropharmacol 14:732–742
Kubicova L, Hadacek F, Chobot V (2013) Quinolinic acid: neurotoxin or oxidative stress modulator? Int J Mol Sci 14:21328–21338
Leal RB, Lopes MW (2018) Amygdala levels of the GluA1 subunit of glutamate receptors and its phosphorylation state at serine 845 in the anterior hippocampus are biomarkers of ictal fear but not anxiety
Lee JS, Song JH, Sohn NW, Shin JW (2013) Inhibitory effects of ginsenoside Rb1 on neuroinflammation following systemic lipopolysaccharide treatment in mice. Phytother Res 27:1270–1276
Martinez JA, Milagro FI, Claycombe KJ, Schalinske KL (2014) Epigenetics in adipose tissue, obesity, weight loss, and diabetes. Adv Nutr 5:71–81
O’Connor JC, Andre C, Wang Y, Lawson MA, Szegedi SS, Lestage J, Castanon N, Kelley KW, Dantzer R (2009a) Interferon-gamma and tumor necrosis factor-alpha mediate the upregulation of indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase and the induction of depressive-like behavior in mice in response to bacillus Calmette-Guerin. J Neurosci 29:4200–4209
O’Connor JC, Lawson MA, Andre C, Moreau M, Lestage J, Castanon N, Kelley KW, Dantzer R (2009b) Lipopolysaccharide-induced depressive-like behavior is mediated by indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase activation in mice. Mol Psychiatry 14:511–522
Ogyu K, Kubo K, Noda Y, Iwata Y, Tsugawa S, Omura Y, Wada M, Tarumi R, Plitman E, Moriguchi S, Miyazaki T, Uchida H, Graff-Guerrero A, Mimura M, Nakajima S (2018) Kynurenine pathway in depression: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 90:16–25
Oxenkrug GF (2010) Tryptophan kynurenine metabolism as a common mediator of genetic and environmental impacts in major depressive disorder: the serotonin hypothesis revisited 40 years later. Isr J Psychiatry Relat Sci 47:56–63
Pan N, Lu LY, Li M, Wang GH, Sun FY, Sun HS, Wen XJ, Cheng JD, Chen JW, Pang JY, Liu J, Guan YY, Zhao LY, Chen WL, Wang GL (2017) Xyloketal B alleviates cerebral infarction and neurologic deficits in a mouse stroke model by suppressing the ROS/TLR4/NF-kappaB inflammatory signaling pathway. Acta Pharmacol Sin 38:1236–1247
Rajabi M, Mohaddes G, Farajdokht F, Nayebi Rad S, Mesgari M, Babri S (2018) Impact of loganin on pro-inflammatory cytokines and depression- and anxiety-like behaviors in male diabetic rats. Physiol Int 105:199–209
Savitz J (2017) Role of kynurenine metabolism pathway activation in major depressive disorders. Curr Top Behav Neurosci 31:249–267
Schwarcz R, Stone TW (2017) The kynurenine pathway and the brain: challenges, controversies and promises. Neuropharmacology 112:237–247
Schwarcz R, Bruno JP, Muchowski PJ, Wu HQ (2012) Kynurenines in the mammalian brain: when physiology meets pathology. Nat Rev Neurosci 13:465–477
Song L, Wang S, Duan X, Liu X, Li Z, Nie L, Chu G (2014) Chromatographic fingerprint combined with content of asperosaponin VI and antioxidant activity for quality evaluation of wine-fried Dipsaci Radix. Nat Prod Commun 9:773–778
Subramaniapillai M, McIntyre RS (2017) A review of the neurobiology of obesity and the available pharmacotherapies. CNS Spectr 22:29–38
Walker AK, Budac DP, Bisulco S, Lee AW, Smith RA, Beenders B, Kelley KW, Dantzer R (2013) NMDA receptor blockade by ketamine abrogates lipopolysaccharide-induced depressive-like behavior in C57BL/6J mice. Neuropsychopharmacology 38:1609–1616
Wang Y, Lawson MA, Dantzer R, Kelley KW (2010a) LPS-induced indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase is regulated in an interferon-gamma-independent manner by a JNK signaling pathway in primary murine microglia. Brain Behav Immun 24:201–209
Wang Y, Lawson MA, Kelley KW, Dantzer R (2010b) Primary murine microglia are resistant to nitric oxide inhibition of indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase. Brain Behav Immun 24:1249–1253
Wang Y, Shen J, Yang X, Jin Y, Yang Z, Wang R, Zhang F, Linhardt RJ (2018) Akebia saponin D reverses corticosterone hypersecretion in an Alzheimer’s disease rat model. Biomed Pharmacother 107:219–225
Yan Y, Wang YL, Su Z, Zhang Y, Guo SX, Liu AJ, Wang CH, Sun FJ, Yang J (2014) Effect of oxytocin on the behavioral activity in the behavioral despair depression rat model. Neuropeptides 48:83–89
Yang S, Zhang W, Xuan LL, Han FF, Lv YL, Wan ZR, Liu H, Ren LL, Gong LL, Liu LH (2019) Akebia Saponin D inhibits the formation of atherosclerosis in ApoE(-/-) mice by attenuating oxidative stress-induced apoptosis in endothelial cells. Atherosclerosis 285:23–30
Yirmiya R, Rimmerman N, Reshef R (2015) Depression as a microglial disease. Trends Neurosci 38:637–658
Yu X, Wang LN, Du QM, Ma L, Chen L, You R, Liu L, Ling JJ, Yang ZL, Ji H (2012) Akebia Saponin D attenuates amyloid beta-induced cognitive deficits and inflammatory response in rats: involvement of Akt/NF-kappaB pathway. Behav Brain Res 235:200–209
Zhang JQ, Wu XH, Feng Y, Xie XF, Fan YH, Yan S, Zhao QY, Peng C, You ZL (2016) Salvianolic acid B ameliorates depressive-like behaviors in chronic mild stress-treated mice: involvement of the neuroinflammatory pathway. Acta Pharmacol Sin 37:1141–1153
Zhang J, Xie X, Tang M, Zhang J, Zhang B, Zhao Q, Han Y, Yan W, Peng C, You Z (2017) Salvianolic acid B promotes microglial M2-polarization and rescues neurogenesis in stress-exposed mice. Brain Behav Immun 66:111–124
Zhang L, Zhang J, You Z (2018) Switching of the microglial activation phenotype is a possible treatment for depression disorder. Front Cell Neurosci 12:306
Zhang W, Xue K, Gao Y, Huai Y, Wang W, Miao Z, Dang K, Jiang S, Qian A (2019) Systems pharmacology dissection of action mechanisms of Dipsaci Radix for osteoporosis. Life Sci 235:116820
Zhu M, Liu M, Guo QL, Zhu CQ, Guo JC (2018) Prolonged DADLE exposure epigenetically promotes Bcl-2 expression and elicits neuroprotection in primary rat cortical neurons via the PI3K/Akt/NF-kappaB pathway. Acta Pharmacol Sin 39:1582–1589
Acknowledgments
We thank Professor Lanping Guo at the Resource Center of the Chinese Academy of Traditional Chinese Medicine for giving us guidance on the experiment and writing. We are grateful to Jun Yu for help in revising the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81860675), Guizhou Science and Technology Plan Project ([2019]5611), and Department of Science and Technology of Guizhou High-level Innovative Talents ([2018]5638).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
JQZ, SNY, and TZ designed the conceptual idea for this study and wrote the manuscript. SNY, YHL, CHX, and CL performed the experiments and analyzed these data. CGY and WKJ contributed new analytical tools and reagents. All the authors participated in the discussion and approved the manuscript as submitted.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Table S1
(DOCX 16 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, J., Yi, S., Li, Y. et al. The antidepressant effects of asperosaponin VI are mediated by the suppression of microglial activation and reduction of TLR4/NF-κB-induced IDO expression. Psychopharmacology 237, 2531–2545 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-020-05553-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-020-05553-5