Abstract
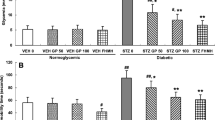
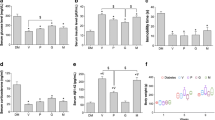
Depression is a chronic and progressive syndrome and commonly associated with several neuropsychiatric comorbidities, of which depression is the most studied. It has been demonstrated that statins also have anti-inflammatory and immunomodulatory properties, which being explored for potential benefits in depression. However, the role of statins in the treatment of diabetes-related depression has not been well examined. Herein, we investigated the effects of atorvastatin on depressive behaviors and neuroinflammation in streptozotocin-induced diabetic mice. Our data indicated that oral administration of atorvastatin at 10 or 20 mg/kg for 3 weeks markedly ameliorated diabetes-associated depressive behaviors reflected by better performance in sucrose preference test (SPT), tail suspension test (TST), and novelty-suppressed feeding test (NSFT). The study further showed that atrovastatin decreased the expression of nucleus NF-κB p65 expression and ameliorated neuroinflammatory responses in prefrontal cortex as evidenced by less Iba-1-positive cells and lower inflammatory mediators including IL-1β and TNF-α. As expected, atorvastatin-treated diabetic mice exhibited significant improvement of hyperlipidemia rather than hyperglycemia. These results suggest that atorvastatin has the potential to be employed as a therapy for diabetes-related depression.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Boku S, Nakagawa S, Toda H, Hishimoto A (2018) Neural basis of major depressive disorder: Beyond monoamines hypothesis. Psychiatry Clin Neurosci 72:3–12
Buchberger B, Huppertz H, Krabbe L, Lux B, Mattivi JT, Siafarikas A (2016) Symptoms of depression and anxiety in youth with type 1 diabetes: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Psychoneuroendocrinology 70:70–84
Datta G, Colasanti A, Rabiner EA, Gunn RN, Malik O, Ciccarelli O et al (2017) Neuroinflammation and its relationship to changes in brain volume and white matter lesions in multiple sclerosis. Brain. 140:2297–2938
Di Legge S, Koch G, Diomedi M, Stanzione P, Sallustio F (2012) Stroke prevention: managing modifiable risk factors. Stroke Res Treat 2012:391538
Du GT, Hu M, Mei ZL, Wang C, Liu GJ, Hu M, Long Y, Miao MX, Chang LJ, Hong H (2014) Telmisartan treatment ameliorates memory deficits in streptozotocin-induced diabetic mice via attenuating cerebral amyloidosis. J Pharmacol Sci 124:418–426
Durisko Z, Mulsant BH, Andrews PW (2015) An adaptationist perspective on the etiology of depression. J Affect Disord 172:315–323
ElBatsh MM (2015) Antidepressant-like effect of simvastatin in diabetic rats. Can J Physiol Pharmacol 93:649–656
Elsayed M, Banasr M, Duric V, Fournier NM, Licznerski P, Duman RS (2012) Antidepressant effects of fibroblast growth factor-2 in behavioral and cellular models of depression. Biol Psychiatry 72:258–265
Fang SC, Xie H, Chen F, Hu M, Long Y, Sun HB et al (2017) Simvastatin ameliorates memory impairment and neurotoxicity in streptozotocin-induced diabetic mice. Neuroscience. 355:200–211
Forman K, Vara E, García C, Kireev R, Cuesta S, Acuña-Castroviejo D et al (2016) Influence of aging and growth hormone on different members of the NFκB family and IκB expression in the heart from a murine model of senescence-accelerated aging. Exp Gerontol 73:114–120
Ghanizadeh A, Hedayati A (2013) Augmentation of fluoxetine with lovastatin for treating major depressive disorder, a randomized double-blind placebo controlled-clinical trial. Depress Anxiety 30:1084–1088
Ghodke RM, Tour N, Devi K (2012) Effects of statins and cholesterol on memory functions in mice. Metab Brain Dis 27:443–451
Golden SH, Lazo M, Carnethon M, Bertoni AG, Schreiner PJ, Diez Roux AV et al (2008) Examining a bidirectional association between depressive symptoms and diabetes. JAMA. 299:2751–2759
Gonzalez JS, Peyrot M, McCarl LA, Collins EM, Serpa L, Mimiaga MJ et al (2008) Depression and diabetes treatment nonadherence: a meta-analysis. Diabetes Care 31:2398–2403
Graeber MB (2010) Changing face of microglia. Science. 330:783–788
Gragnoli C (2014) Hypothesis of the neuroendocrine cortisol pathway gene role in the comorbidity of depression, type 2 diabetes, and metabolic syndrome. Appl Clin Genet 7:43–53
Grey M, Whittemore R, Tamborlane W (2002) Depression in type 1 diabetes in children: natural history and correlates. J Psychosom Res 53:907–911
Harrison RW, Ashton CH (1994) Do cholesterol-lowering agents affect brain activity? A comparison of simvastatin, pravastatin, and placebo in healthy volunteers. Br J Clin Pharmacol 37:231–236
Hu P, Thinschmidt JS, Yan Y, Hazra S, Bhatwadekar A, Caballero S et al (2013) CNS inflammation and bone marrow neuropathy in type 1 diabetes. Am J Pathol 183:1608–1620
Jaiswal M, Schinske A, Pop-Busui R (2014) Lipids and lipid management in diabetes. Best Pract Res Clin Endocrinol Metab 28:325–338
Jeon SW, Kim YK (2017) Inflammation-induced depression: Its pathophysiology and therapeutic implications. J Neuroimmunol 313:92–98
Jia M, Li C, Zheng Y, Ding X, Chen M, Ding J, du R, Lu M, Hu G (2017) Leonurine exerts antidepressant-like effects in the chronic mild stress-induced depression model in mice by inhibiting neuroinflammation. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol 20:886–895
Krishnadas R, Cavanagh J (2012) Depression: an inflammation illness? J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 83:495–502
Kwon KJ, Lee EJ, Kim MK, Kim SY, Kim JN, Kim JO, Kim HJ, Kim HY, Han JS, Shin CY, Han SH (2015) Diabetes augments cognitive dysfunction in chronic cerebral hypoperfusion by increasing neuronal cell death: implication of cilostazol for diabetes mellitus-induced dementia. Neurobiol Dis 73:12–23
Lee YC, Lin CH, Wu RM, Lin MS, Lin JW, Chang CH, Lai MS (2013) Discontinuation of statin therapy associates with Parkinson disease: a population-based study. Neurology. 81:410–416
Lei Q, Peng WN, You H, Hu ZP, Lu W (2014) Statins in nervous system-associated diseases: angels or devils? Pharmazie. 69:448–454
Liao JK (2002) Beyond lipid lowering: the role of statins in vascular protection. Int J Cardiol 86:5–18
Lin JR, Fang SC, Tang SS, Hu M, Long Y, Ghosh A, Sun HB, Kong LY, Hong H (2017) Hippocampal CysLT1R knockdown or blockade represses LPS-induced depressive behaviors and neuroinflammatory response in mice. Acta Pharmacol Sin 38:477–487
Lloyd CE, Roy T, Nouwen A, Chauhan AM (2012) Epidemiology of depression in diabetes: international and cross-cultural issues. J Affect Disord 142(Suppl):S22–S29
Ludka FK, Zomkowski AD, Cunha MP, Dal-Cim T, Zeni AL, Rodrigues AL, Tasca CI (2013) Acute atorvastatin treatment exerts antidepressant-like effect in mice via the L-arginine-nitric oxide-cyclic guanosine monophosphate pathway and increases BDNF levels. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol 23:400–412
McAlister FA, Lawson FM, Teo KK, Armstrong PW (2001) Randomised trials of secondary prevention programmes in coronary heart disease: systematic review. Br Med J 323:957–962
Moher D, Liberati A, Tetzlaff J, Altman DG (2009) Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analysis: the PRISMA statement. Br Med J 339:b2535
Muldoon MF (1994) Injury, death, and cholesterol. Ann Intern Med 121:719–720
Nimmerjahn A, Kirchhoff F, Helmchen F (2005) Resting microglia cells are highly dynamic surveillants of brain parenchyma in vivo. Science. 308:1314–1318
O’Neil A, Sanna L, Redlich C, Sanderson K, Jacka F, Williams LJ et al (2012) The impact of statins on psychological wellbeing: a systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Med 10:154
Parsaik AK, Singh B, Murad MH, Singh K, Mascarenhas SS, Williams MD et al (2014) Statins use and risk of depression: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Affect Disord 160:62–67
Pickup JC (2004) Inflammation and activated innate immunity in the pathogenesis of type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care 27:813–823
Redlich C, Berk M, Williams LJ, Sundquist J, Sundquist K, Li X (2014) Stain use and risk of depression: a Swedish national cohort study. BMC Psychiatry 14:348
Renshaw PF, Parsegian A, Yang CK, Novero A, Yoon SJ, Lyoo IK et al (2009) Lovastatin potentiates the antidepressant efficacy of fluoxetine in rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 92:88–92
Reus GZ, Fries GR, Stertz L, Badawy M, Passos IC, Barichello T et al (2015) The role of inflammation and microglial activation in the pathophysiology of psychiatric disorders. Neuroscience. 300:141–154
Salagre E, Fernandes BS, Dodd S, Brownstein DJ, Berk M (2016) Statins for the treatment of depression: a meta-analysis of randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trials. J Affect Disord 200:235–242
Shyamsundar M, McKeown ST, O’Kane CM, Craig TR, Brown V, Thickett DR et al (2009) Simvastatin decreases lipopolysaccharide-induced pulmonary inflammation in healthy volunteers. Am J Respir Cirt Care Med 179:1107–1114
Sild M, Ruthazer ES, Booij L (2017) Major depressive disorder and anxiety disorders from the glial perspective: etiological mechanisms, intervention and monitoring. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 83:474–488
Steiner J, Walter M, Gos T, Guillemin GJ, Bernstein HG, Sarnyai Z et al (2011) Severe depression is associated with increased microglial quinolinic acid in subregions of the anterior cingulate gyrus: evidence for an immune-modulated glutamatergic neurotransmission? J Neuroinflammation 8:94
Taguchi A (2009) Vascular factors in diabetes and Alzheimer’s disease. J Alzheimers Dis:859–864
Tennant KG, Lindsley SR, Kirigiti MA, True C, Kievit P (2019) Central and peripheral administration of fibroblast growth factor 1 improves pancreatic islet insulin secretion in diabetic mouse models. Diabetes 68:1462–1472
Vargas R, Rincon J, Pedreanez A, Viera N, Hernandez-Fonseca JP, Pena C, Mosquera J (2012) Role of angiotensin II in the brain inflammatory events during experimental diabetes in rats. Brain Res 1453:64–76
Wake H, Moorhouse AJ, Jinno S, Kohsaka S, Nabekura J (2009) Resting microglia directly monitor the functional state of synapses in vivo and determine the fate of ischemic terminals. J Neurosci 29:3974–3980
Walker ER, McGee RE, Druss BG (2015) Mortality in mental disorders and global disease burden implications: a systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA Psychiatry 72:334–341
Wang C, Yang XM, Zhuo YY, Zhou H, Lin HB, Cheng YF et al (2012) The phosphodiesterase-4 inhibitor rolipram reverses Aβ-induced cognitive impairment and neuroinflammatory and apoptotic responses in rats. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol 15:749–766
Xin LM, Chen L, Ji ZP, Zhang SY, Wang J, Liu YH et al (2015) Risk factors for anxiety in major depressive disorder patients. Clin Psychopharmacol Neurosci 13:263–268
Yu XB, Dong RR, Wang H, Lin JR, An YQ, Du Y et al (2016) Knockdown of hippocampal cysteinyl leukotriene receptor 1 prevents depressive behavior and neuroinflammation induced by chronic mild stress in mice. Psychopharmacology. 233:1739–1749
Yu XB, Zhang HN, Dai Y, Zhou ZY, Xu RA, Hu LF (2019) Simvastatin prevents and ameliorates depressive behaviors via neuroinflammatory regulation in mice. J Affect Disord 245:939–949
Zanoveli JM, Morais HD, Dias IC, Schreiber AK, Souza CP, Cunha JM (2016) Depression associated with diabetes: from pathophysiology to treatment. Curr Diabetes Rev 12:165–178
Zhang X, Tao Y, Wang J, Garcia-Mata R, Markovic-Plese S (2013) Simvastatin inhibits secretion of Th17-polarizing cytokines and antigen presentation by DCs in patients with relapsing remitting multiple sclerosis. Eur J Immunol 43:281–289
Zhao G, Yu YM, Kaneki M, Bonab AA, Tompkins RG, Fischman AJ (2015) Simvastatin reduces burn injury-induced splenic apoptosis via downregulation of the TNF-α/NF-κB pathway. Ann Surg 261:1006–1012
Funding
This work was supported by grants from the Science Foundation of the Zhejiang Pharmaceutical Association (2018ZYY43 to Zhang. HN, 2017ZYY20 to Yu. XB) and the Science Foundation of Wenzhou (S20100050 to Liang. J)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hai-Na, Z., Xu-Ben, Y., Cong-Rong, T. et al. Atorvastatin ameliorates depressive behaviors and neuroinflammatory in streptozotocin-induced diabetic mice. Psychopharmacology 237, 695–705 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-019-05406-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-019-05406-w