Abstract
Rationale
The serotonergic system has been repeatedly linked to visual attention in general, but the effects of selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SSRI) on specific components of visual attention remain unknown. Changes in distinct perceptual and cognitive processes are not readily evident in most attention paradigms.
Objective
In this study, we isolate basic components of visual attention to investigate potential effects of longer-term SSRI administration on non-emotional aspects of visual attention in healthy males.
Methods
In a randomized double-blind placebo-controlled design, 32 young healthy males were tested on multiple attentional parameters, before and after a 3-week SSRI intervention with fluoxetine (40 mg daily) or placebo. Data were modeled with a computational theory of visual attention to derive independent estimates of five distinct components of visual attention.
Results
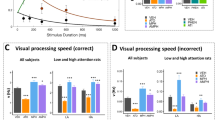
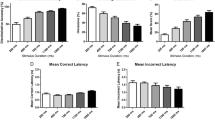
The SSRI intervention selectively and significantly lowered the threshold for conscious visual perception. Specifically, we demonstrate that this improvement does not stem from a general increase in the speed of visual processing, as previously suggested, but specifically from a change in the perceptual threshold.
Conclusions
The study provides a novel description of the attentional dynamics affected by SSRI, while supporting previous findings on attentional effects of SSRI. Furthermore, it accentuates the utility of employing accuracy-based measures of attentional performance when conducting psychopharmacological research.



Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
The models had 14 degrees of freedom (df): K, 5 df (the value reported is the expected K given a particular distribution of the probability that on a given trial, K = 1, 2,…, 6); C, 1 df; t0, 2 df (the perceptual threshold was assumed to be drawn trial-by-trial from a normal distribution with a given mean and standard deviation); windex, 5 df (one weight for each of the six locations under the restriction that the relative weights sum to 1); and α, 1 df.
References
Aghajanian GK, Sanders-Bush E (2002) Serotonin
Amado-Boccara I, Gougoulis N, Poirier Littre M, Galinowski A, Loo H (1995) Effects of antidepressants on cognitive functions: a review. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 19:479–493
Anderson IM, Del-Ben CM, Mckie S, Richardson P, Williams SR, Elliott R, Deakin JW (2007) Citalopram modulation of neuronal responses to aversive face emotions: a functional MRI study. Neuroreport 18:1351–1355
Bar-Haim Y, Lamy D, Pergamin L, Bakermans-Kranenburg MJ, Van Ijzendoorn MH (2007) Threat-related attentional bias in anxious and nonanxious individuals: a meta-analytic study. Psychol Bull 133:1–24
Bech P, Rasmussen N-A, Olsen LR, Noerholm V, Abildgaard W (2001) The sensitivity and specificity of the major depression inventory, using the present state examination as the index of diagnostic validity. J Affect Disord 66:159–164
Bigos KL, Pollock BG, Aizenstein HJ, Fisher PM, Bies RR, Hariri AR (2008) Acute 5-HT reuptake blockade potentiates human amygdala reactivity. Neuropsychopharmacology 33:3221–3225
Brunken WJ, Jin XT, Pis-Lopez AM (1993) The properties of the serotoninergic system in the retina. Prog Retin Res 12:75–99
Bundesen C (1990) A theory of visual attention. Psychol Rev 97:523–547
Bundesen C, Habekost T (2008) Principles of visual attention: linking mind and brain. Oxford University Press, Oxford
Campbell F, Gregory A (1960) Effect of size of pupil on visual acuity
Carli M, Samanin R (1992) Serotonin2 receptor agonists and serotonergic anorectic drugs affect rats’ performance differently in a five-choice serial reaction time task. Psychopharmacology 106:228–234
Carli M, Samanin R (2000) The 5-HT1A receptor agonist 8-OH-DPAT reduces rats’ accuracy of attentional performance and enhances impulsive responding in a five-choice serial reaction time task: role of presynaptic 5-HT1A receptors. Psychopharmacology 149:259–268
Charlier C, Pinto E, Ansseau M, Plomteux G (2000) Relationship between clinical effects, serum drug concentration, and concurrent drug interactions in depressed patients treated with citalopram, fluoxetine, clomipramine, paroxetine or venlafaxine. Hum Psychopharmacol Clin Exp 15:453–459
Del-Ben CM, Deakin JW, Mckie S, Delvai NA, Williams SR, Elliott R, Dolan M, Anderson IM (2005) The effect of citalopram pretreatment on neuronal responses to neuropsychological tasks in normal volunteers: an FMRI study. Neuropsychopharmacology 30:1724–1734
Derogatis LR (1975) Symptom checklist-90-revised (SCL-90-R). Minneapolis, MN: NCS Assessments.
Desimone R, Duncan J (1995) Neural mechanisms of selective visual attention. Annu Rev Neurosci 18:193–222
Dumont GJ, De Visser SJ, Cohen AF, Van Gerven JM, Biomarker Working Group of the German Association for Applied Human Pharmacology (2005) Biomarkers for the effects of selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) in healthy subjects. Br J Clin Pharmacol 59:495–510
Duncan J, Bundesen C, Olson A, Humphreys G, Chavda S, Shibuya H (1999) Systematic analysis of deficits in visual attention. J Exp Psychol Gen 128:450–478
Dyrholm M, Kyllingsbæk S, Espeseth T, Bundesen C (2011) Generalizing parametric models by introducing trial-by-trial parameter variability: the case of TVA. J Math Psychol 55:416–429
Eysel UT, Burandt U (1984) Fluorescent tube light evokes flicker responses in visual neurons. Vis Res 24:943–948
Fairweather D, Pozzo C, Kerr J, Lafferty S, Hindmarch I (1997) Citalopram compared to dothiepin and placebo: effects on cognitive function and psychomotor performance. Hum Psychopharmacol Clin Exp 12:119–126
Finke K, Dodds CM, Bublak P, Regenthal R, Baumann F, Manly T, Müller U (2010) Effects of modafinil and methylphenidate on visual attention capacity: a TVA-based study. Psychopharmacology 210:317–329
Fisher PM, Haahr ME, Jensen CG, Frokjaer VG, Siebner HR, Knudsen GM (2015) Fluctuations in [11C] SB207145 PET binding associated with change in threat-related amygdala reactivity in humans. Neuropsychopharmacology 40:1510–1518
Forsell Y (2005) The major depression inventory versus schedules for clinical assessment in neuropsychiatry in a population sample. Soc Psychiatry Psychiatr Epidemiol 40:209–213
Frisén L (1980) The neurology of visual acuity. Brain J Neurol 103:639–670
Gerdelat-Mas A, Loubinoux I, Tombari D, Rascol O, Chollet F, Simonetta-Moreau M (2005) Chronic administration of selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SSRI) paroxetine modulates human motor cortex excitability in healthy subjects. NeuroImage 27:314–322
Geyer MA (1995) Serotonergic functions in arousal and motor activity. Behav Brain Res 73:31–35
Gur M, Snodderly DM (1997) A dissociation between brain activity and perception: chromatically opponent cortical neurons signal chromatic flicker that is not perceived. Vis Res 37:377–382
Haahr M, Fisher P, Jensen C, Frokjaer V, Mc Mahon B, Madsen K, Baaré W, Lehel S, Norremolle A, Rabiner E (2014) Central 5-HT4 receptor binding as biomarker of serotonergic tonus in humans: a [11C]SB207145 PET study. Mol Psychiatry 19:427–432
Harmer CJ, Mackay CE, Reid CB, Cowen PJ, Goodwin GM (2006) Antidepressant drug treatment modifies the neural processing of nonconscious threat cues. Biol Psychiatry 59:816–820
Hart WM, Adler FH (1992) Adler’s physiology of the eye: clinical application. Mosby Inc
Hindmarch I (1987) Three antidepressants (amitriptyline, dothiepin, fluoxetine), with and without alcohol, compared with placebo on tests of psychomotor ability related to car driving. Hum Psychopharmacol Clin Exp 2:177–183
Hindmarch I (1995) The behavioural toxicity of the selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors. Int Clin Psychopharmacol 9:13–18
Hindmarch I, Bhatti J (1988) Psychopharmacological effects of sertraline in normal, healthy volunteers. Europ J Clin Pharmacol 35:221–223
Hindmarch I, Harrison C (1988) The effects of paroxetine and other antidepressants in combination with alcohol in psychomotor activity related to car driving. Hum Psychopharmacol Clin Exp 3:13–20
Jannuzzi G, Gatti G, Magni P, Spina E, Pacifici R, Zuccaro P, Torta R, Guarneri L, Perucca E (2002) Plasma concentrations of the enantiomers of fluoxetine and norfluoxetine: sources of variability and preliminary observations on relations with clinical response. Ther Drug Monit 24:616–627
Jensen CG, Vangkilde S, Frokjaer V, Hasselbalch SG (2012) Mindfulness training affects attention—or is it attentional effort? J Exp Psychol Gen 141:106–123
Jensen CG, Lansner J, Petersen A, Vangkilde SA, Ringkøbing SP, Frokjaer VG, Adamsen D, Knudsen GM, Denninger JW, Hasselbalch SG (2015) Open and calm—a randomized controlled trial evaluating a public stress reduction program in Denmark. BMC Public Health 15:1
Kerr J, Fairweather D, Mahendran R, Hindmarch I (1992) The effects of paroxetine, alone and in combination with alcohol on psychomotor performance and cognitive function in the elderly. Int Clin Psychopharmacol
Knorr U, Kessing LV (2010) The effect of selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors in healthy subjects. A systematic review. Nord J Psychiatry 64:153–163
Laroche RB, Morgan RE (2007) Adolescent fluoxetine exposure produces enduring, sex-specific alterations of visual discrimination and attention in rats. Neurotoxicol Teratol 29:96–107
Lingjaerde O, Ahlfors U, Bech P, Dencker S, Elgen K (1987) The UKU side effect rating scale: a new comprehensive rating scale for psychotropic drugs and a cross-sectional study of side effects in neuroleptic-treated patients. Acta Psychiatr Scand 76:1–100
Loubinoux I, Pariente J, Boulanouar K, Carel C, Manelfe C, Rascol O, Celsis P, Chollet F (2002) A single dose of the serotonin neurotransmission agonist paroxetine enhances motor output: double-blind, placebo-controlled, fMRI study in healthy subjects. NeuroImage 15:26–36
Loubinoux I, Tombari D, Pariente J, Gerdelat-Mas A, Franceries X, Cassol E, Rascol O, Pastor J, Chollet F (2005) Modulation of behavior and cortical motor activity in healthy subjects by a chronic administration of a serotonin enhancer. NeuroImage 27:299–313
Macoveanu J, Fisher PM, Haahr ME, Frokjaer VG, Knudsen GM, Siebner HR (2014) Effects of selective serotonin reuptake inhibition on neural activity related to risky decisions and monetary rewards in healthy males. NeuroImage 99:434–442
Mariño J, Schummers J, Lyon DC, Schwabe L, Beck O, Wiesing P, Obermayer K, Sur M (2005) Invariant computations in local cortical networks with balanced excitation and inhibition. Nat Neurosci 8:194–201
Mccormick D, Wang Z (1991) Serotonin and noradrenaline excite GABAergic neurones of the guinea-pig and cat nucleus reticularis thalami. J Physiol 442:235–255
Monckton JE, Mccormick DA (2002) Neuromodulatory role of serotonin in the ferret thalamus. J Neurophysiol 87:2124–2136
Moreau AW, Amar M, Callebert J, Fossier P (2013) Serotonergic modulation of LTP at excitatory and inhibitory synapses in the developing rat visual cortex. Neuroscience 238:148–158
Nardella A, Rocchi L, Conte A, Bologna M, Suppa A, Berardelli A (2014) Inferior parietal lobule encodes visual temporal resolution processes contributing to the critical flicker frequency threshold in humans
Nathan P, Sitaram G, Stough C, Silberstein R, Sali A (2000) Serotonin, noradrenaline and cognitive function: a preliminary investigation of the acute pharmacodynamic effects of a serotonin versus a serotonin and noradrenaline reuptake inhibitor. Behav Pharmacol 11:639–642
Nord M, Finnema SJ, Halldin C, Farde L (2013) Effect of a single dose of escitalopram on serotonin concentration in the non-human and human primate brain. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol 1–10
Pape H-C, Mccormick DA (1989) Noradrenaline and serotonin selectively modulate thalamic burst firing by enhancing a hyperpolarization-activated cation current. Nature 340:715–718
Parrott A (1982) Critical flicker fusion thresholds and their relationship to other measures of alertness. Pharmacopsychiatry 15:39–43
Schmitt JA, Riedel WJ, Vuurman EF, Kruizinga M, Ramaekers JG (2002) Modulation of the critical flicker fusion effects of serotonin reuptake inhibitors by concomitant pupillary changes. Psychopharmacology 160:381–386
Shibuya H, Bundesen C (1988) Visual selection from multielement displays: measuring and modeling effects of exposure duration. J Exp Psychol Hum Percept Perform 14:591–600
Steriade M, Llinás RR (1988) The functional states of the thalamus and the associated neuronal interplay. Physiol Rev 68:649–742
Vangkilde S, Bundesen C, Coull JT (2011) Prompt but inefficient: nicotine differentially modulates discrete components of attention. Psychopharmacology 218:667–680
Wells EF, Bernstein GM, Scott BW, Bennett PJ, Mendelson JR (2001) Critical flicker frequency responses in visual cortex. Exp Brain Res 139:106–110
Who, W.H.O (1993) The ICD-10 classification of mental and behavioural disorders: diagnostic criteria for research
Winstanley CA, Chudasama Y, Dalley JW, Theobald DE, Glennon JC, Robbins TW (2003) Intra-prefrontal 8-OH-DPAT and M100907 improve visuospatial attention and decrease impulsivity on the five-choice serial reaction time task in rats. Psychopharmacology 167:304–314
Funding
The project was funded by a center grant from the Lundbeck Foundation to Center for Integrated Molecular Brain Imaging (Cimbi, www.cimbi.dk). JL is supported by a grant from the Lundbeck Foundation: Attention, impulsivity, and monoamines: from psychological functions to molecular mechanisms.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Signe Vangkilde and Gitte M. Knudsen shared last authorship
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lansner, J., Jensen, C.G., Petersen, A. et al. Three weeks of SSRI administration enhances the visual perceptual threshold - a randomized placebo-controlled study. Psychopharmacology 236, 1759–1769 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-018-5158-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-018-5158-3