Abstract
Rationale
Extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK1/2) phosphorylation is critical for neuronal and behavioural functions; in particular, phosphorylated ERK1/2 (pERK1/2) expression in the nucleus accumbens (Acb) of the rat is stimulated by addictive drugs with the exception of morphine, which decreases accumbal ERK1/2 phosphorylation in the Sprague-Dawley and Wistar rats. The psychogenetically selected Roman low- (RLA) and high-avoidance (RHA) rats differ behaviourally and neurochemically in many responses to addictive drugs. In particular, morphine elicits a greater increment in locomotor activity and in dopamine transmission in the Acb of RHA vs RLA rats. However, the effects of morphine on place conditioning (conditioned place preference (CPP)) and ERK1/2 phosphorylation in the Roman lines remain unknown.
Objectives and methods
To characterize in the Roman lines the reinforcing properties of morphine (i.e. morphine-elicited CPP acquisition) and the relationship between these properties and its effects on ERK1/2 phosphorylation in the Acb, the behavioural effects of morphine were evaluated in a place-conditioning apparatus and ERK1/2 phosphorylation was assessed by immunohistochemistry in the shell and core subregions of the Acb of rats both acutely administered with morphine or undergoing conditioning.
Results
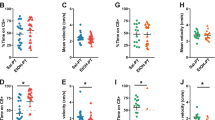
Morphine elicited CPP in both Roman lines and decreased pERK1/2 expression in the Acb of RLA but not RHA rats. Such decrease was prevented by conditioning.
Conclusions
These findings indicate that the selective breeding of the Roman lines has generated a divergence, in terms of morphine-elicited pERK1/2 expression but not of morphine-elicited CPP, between RLA and RHA rats and sustain the observation that changes in pERK1/2 expression in the Acb are not a requisite for the reinforcing effects of morphine.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Acquas E, Di Chiara G (1994) D1 receptor blockade stereospecifically impairs the acquisition of drug-conditioned place preference and place aversion. Behav Pharmacol 5(6):555–569
Acquas E, Carboni E, Leone P, Di Chiara G (1989) SCH 23390 blocks drug-conditioned place-preference and place-aversion: anhedonia (lack of reward) or apathy (lack of motivation) after dopamine-receptor blockade? Psychopharmacology 99(2):151–155
Acquas E, Pisanu A, Spiga S, Plumitallo A, Zernig G, Di Chiara G (2007) Differential effects of intravenous R,S-(±)-3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine (MDMA, ecstasy) and its S(+)- and R(−)-enantiomers on dopamine transmission and extracellular signal regulated kinase phosphorylation (pERK) in the rat nucleus accumbens shell and core. J Neurochem 102:121–132
Baars MY, Müller MJ, Gallhofer B, Netter P (2013) Relapse (number of detoxifications) in abstinent male alcohol-dependent patients as related to personality traits and types of tolerance to frustration. Neuropsychobiology 67:241–248
Belin D, Mar AC, Dalley JW, Robbins TW, Everitt BJ (2008) High impulsivity predicts the switch to compulsive cocaine-taking. Science 320:1352–1355
Beninger RJ, Gerdjikov T (2004) The role of signaling molecules in reward-related incentive learning. Neurotox Res 61:91–104
Berke JD, Hyman SE (2000) Addiction, dopamine, and the molecular mechanisms of memory. Neuron 25:515–532
Brami-Cherrier K, Valjent E, Hervé D, Darragh J, Corvol JC, Pages C, Arthur SJ, Girault JA, Caboche J (2005) Parsing molecular and behavioural effects of cocaine in mitogen- and stress-activated protein kinase-1-deficient mice. J Neurosci 25:11444–11454
Carr GD, Fibiger HC, Phillips AG (1989) Conditioned place preference as a measure of drug reward. In: Liebman J, Cooper S (eds) The neuropharmacological basis of reward. Oxford Science Publication, Clarendon Press, Oxford, pp 264–319
Ciccarelli A, Giustetto M (2014) Role of ERK signaling in activity-dependent modifications of histone proteins. Neuropharmacology 80:34–44
Colombo G, Lobina C, Carai MA, Gessa GL (2006) Phenotypic characterization of genetically selected Sardinian alcohol-preferring (sP) and -non-preferring (sNP) rats. Addict Biol 11:324–338
Coppens CM, de Boer SF, Steimer T, Koolhaas JM (2013) Correlated behavioural traits in rats of the Roman selection lines. Behav Genet 430:220–226
Corda MG, Piras G, Piludu MA, Giorgi O (2014) Differential effects of voluntary ethanol consumption on dopamine output in the nucleus accumbens shell of Roman high- and low-avoidance rats: a behavioural and brain microdialysis study. World J Neurosci 4:279–292
Crabbe JC, Belknap JK, Buck KJ (1994) Genetic animal models of alcohol and drug abuse. Science 264:1715–1723
Davis S, Laroche S (2006) Mitogen-activated protein kinase/extracellular regulated kinase signalling and memory stabilization: a review. Genes Brain Behav 5(Suppl 2):61–72
Di Chiara G, Bassareo V, Fenu S, De Luca MA, Spina L, Cadoni C, Acquas E, Carboni E, Valentini V, Lecca D (2004) Dopamine and drug addiction: the nucleus accumbens shell connection. Neuropharmacology 47:227–241
Driscoll P, Battig K (1982) Behavioural, emotional, and neurochemical profiles of rats selected for extreme differences in active, two-way avoidance performance. In: Lieblich I (ed) Genetics of the brain. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 95–123
Ersche KD, Simon Jones P, Williams GB, Smith DG, Bullmore ET, Robbins TW (2013) Distinctive personality traits and neural correlates associated with stimulant drug use versus familial risk of stimulant dependence. Biol Psychiatry 74:137–144
Fattore L, Piras G, Corda MG, Giorgi O (2009) The Roman high- and low-avoidance rat lines differ in the acquisition, maintenance, extinction, and reinstatement of intravenous cocaine self-administration. Neuropsychopharmacology 34:1091–1101
Fenu S, Spina L, Rivas E, Longoni R, Di Chiara G (2006) Morphine-conditioned single-trial place preference: role of nucleus accumbens shell dopamine receptors in acquisition, but not expression. Psychopharmacology 187(2):143–153
Fernàndez-Teruel A, Escorihuela RM, Castellano B, González B, Tobeña A (1997) Neonatal handling and environmental enrichment effects on emotionality, novelty/reward seeking, and age-related cognitive and hippocampal impairments: focus on the Roman rat lines. Behav Genet 27:513–526
Fernàndez-Teruel A, Driscoll P, Gil L, Aguilar R, Tobeña A, Escorihuela RM (2002a) Enduring effects of environmental enrichment on novelty seeking, saccharin and ethanol intake in two rat lines (RHA/Verh and RLA/Verh) differing in incentive-seeking behaviour. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 73(1):225–231
Fernàndez-Teruel A, Giménez-Llort L, Escorihuela RM, Gil L, Aguilar R, Steimer T, Tobeña A (2002b) Early-life handling stimulation and environmental enrichment: are some of their effects mediated by similar neural mechanisms? Pharmacol Biochem Behav 73(1):233–245
Flagel SB, Robinson TE, Clark JJ, Clinton SM, Watson SJ, Seeman P, Phillips PE, Akil H (2010) An animal model of genetic vulnerability to behavioural disinhibition and responsiveness to reward-related cues: implications for addiction. Neuropsychopharmacology 35:388–400
Funada M, Suzuki T, Narita M, Misawa M, Nagase H (1993) Blockade of morphine reward through the activation of kappa-opioid receptors in mice. Neuropharmacology 32:1315–1323
Gerdjikov TV, Ross GM, Beninger RJ (2004) Place preference induced by nucleus accumbens amphetamine is impaired by antagonists of ERK or p38 MAP kinases in rats. Behav Neurosci 118:740–750
Giorgi O, Orlandi M, Escorihuela RM, Driscoll P, Lecca D, Corda MG (1994) GABAergic and dopaminergic transmission in the brain of Roman high-avoidance and Roman low-avoidance rats. Brain Res 638(1–2):133–138
Giorgi O, Lecca D, Piras G, Driscoll P, Corda MG (2003) Dissociation between mesocortical dopamine release and fear-related behaviours in two psychogenetically selected lines of rats that differ in coping strategies to aversive conditions. Eur J Neurosci 17:2716–2726
Giorgi O, Piras G, Lecca D, Corda MG (2005) Differential activation of dopamine release in the nucleus accumbens core and shell after acute or repeated amphetamine injections: a comparative study in the Roman high- and low-avoidance rat lines. Neuroscience 135:987–998
Giorgi O, Piras G, Corda MG (2007) The psychogenetically selected Roman high- and low-avoidance rat lines: a model to study the individual vulnerability to drug addiction. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 31(1):148–163
Giorgi O, Corda MG, Sabariego M, Giugliano V, Piludu MA, Rosas M, Acquas E (2015) Differential effects of cocaine on extracellular signal-regulated kinase phosphorylation in nuclei of the extended amygdala and prefrontal cortex of psychogenetically selected Roman high- and low-avoidance rats. J Neurosci Res 93:714–721
Girault JA, Valjent E, Caboche J, Herve D (2007) ERK2: a logical AND gate critical for druginduced plasticity? Curr Opin Pharmacol 7:77–85
Glover EM, Davis M (2008) Anxiolytic-like effects of morphine and buprenorphine in the rat model of fear-potentiated startle: tolerance, cross-tolerance, and blockade by naloxone. Psychopharmacology 198(2):167–180
Guitart-Masip M, Johanson B, Fernández-Teruel A, Tobeña A, Giménez-Llort (2008) Divergent effect of the selective D3 receptor agonist PD-128,907 on locomotor activity in Roman high- and low-avoidance rats: relationship to NGFI-A gene expression in the Calleja islands. Psychopharmacology 196:39–49
Ibba F, Vinci S, Spiga S, Peana AT, Assaretti AR, Spina L, Longoni R, Acquas E (2009) Ethanol-induced extracellular signal regulated kinase: role of dopamine D1 receptors. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 33:858–867
Kapur JN, Sahoo PK, Wong KC (1985) A new method for gray-level picture thresholding using the entropy of the histogram. Comput Vis Graph Image Process 29:273–285
Kennedy BC, Panksepp JB, Runckel PA, Lahvis GP (2012) Social influences on morphine-conditioned place preference in adolescent BALB/cJ and C57BL/6J mice. Psychopharmacology 219(3):923–932
Koob GF (2006) The neurobiology of addiction: a neuroadaptational view relevant for diagnosis. Addiction 101(Suppl 1):23–30
Koob GF, Le Moal M (2001) Drug addiction, dysregulation of reward, and allostasis. Neuropsychopharmacology 24:97–129
Lazega D, Driscoll P, Frischknecht HR, Siegfreid B, Waser PG (1986) Opiate receptor binding and behavioural effects of morphine in RHA/Verh and RLA/Verh rats. NIDA Res Monogr 75:485–488
Lecca D, Piras G, Driscoll P, Giorgi O, Corda MG (2004) A differential activation of dopamine output in the shell and core of the nucleus accumbens is associated with the motor responses to addictive drugs: a brain dialysis study in Roman high- and low-avoidance rats. Neuropharmacology 46:688–699
Leone P, Di Chiara G (1987) Blockade of D-1 receptors by SCH 23390 antagonizes morphine- and amphetamine-induced place preference conditioning. Eur J Pharmacol 135(2):251–254
Marotta R, Fenu S, Scheggi S, Vinci S, Rosas M, Falqui A, Gambarana C, De Montis MG, Acquas E (2014) Acquisition and expression of conditioned taste aversion differentially affects extracellular signal regulated kinase and glutamate receptor phosphorylation in rat prefrontal cortex and nucleus accumbens. Front Behav Neurosci 8:153
Molander AC, Mar A, Norbury A, Steventon S, Moreno M, Caprioli D, Theobald DEH, Belin D, Everitt BJ, Robbins TW, Dalley JW (2011) High impulsivity predicting vulnerability to cocaine addiction in rats: some relationship with novelty preference but not novelty reactivity, anxiety or stress. Psychopharmacology 215:721–731
Moreno M, Cardona D, Gomez MJ, Sanchez-Santed F, Tobena A, Fernàndez-Teruel A, Campa L, Sunol C, Escarabajal MD, Torres C, Flores P (2010) Impulsivity characterization in the Roman high- andlow-avoidance rat strains: behavioural and neurochemical differences. Neuropsychopharmacology 35:1198–1208
Mucha RF, van der Kooy D, O'Shaughnessy M, Bucenieks P (1982) Drug reinforcement studied by the use of place conditioning in rat. Brain Res 243(1):91–105
Nestler EJ (2001) Molecular neurobiology of addiction. Am J Addict 10:201–217
Paxinos G, Watson C (1998) The rat brain in stereotaxic coordinates. Academic Press, Sydney
Peana AT, Giugliano V, Rosas M, Sabariego M, Acquas E (2013) Effects of L-cysteine on reinstatement of ethanol-seeking behaviour and on reinstatement-elicited extracellular signal-regulated kinase phosphorylation in the rat nucleus accumbens shell. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 37(Suppl 1):E329–E337
Rosas M, Zaru A, Sabariego M, Giugliano V, Carboni E, Colombo G, Acquas E (2014) Differential sensitivity of ethanol-elicited ERK phosphorylation in nucleus accumbens of Sardinian alcohol-preferring and -non preferring rats. Alcohol 48:471–476
Rosas M, Porru S, Fenu S, Ruiu S, Peana AT, Papale A, Brambilla R, Di Chiara G, Acquas E (2016) Role of nucleus accumbens μ opioid receptors in the effects of morphine on ERK1/2 phosphorylation. Psychopharmacology 233(15–16):2943–2954
Salzmann J, Marie-Claire C, Le Guen S, Roques BP, Noble F (2003) Importance of ERK activation in behavioural and biochemical effects induced by MDMA in mice. Br J Pharmacol 140:831–828
Sanna F, Corda MG, Melis MR, Piludu MA, Giorgi O, Argiolas A (2014) Male Roman high- and low- avoidance rats show different patterns of copulatory behaviour: comparison with Sprague Dawley rats. Physiol Behav 127:27–36
Scheggi S, Crociani A, De Montis MG, Tagliamonte A, Gambarana C (2009) Dopamine D1 receptor-dependent modifications in the dopamine and cAMP-regulated phosphoprotein of Mr 32 kDa phosphorylation pattern in striatal areas of morphine-sensitized rats. Neuroscience 163(2):627–639
Selcher JC, Nekrasova T, Paylor R, Landreth GE, Sweatt JD (2001) Mice lacking the ERK1 isoform of MAP kinase are unimpaired in emotional learning. Learn Mem 8(1):11–19
Shippemberg TS, Herz A (1987) Place preference conditioning reveals the involvement of D1-dopamine receptors in the motivational properties of mu- and kappa-opioid agonists. Brain Res 436(1):169–172
Solecki W, Turek A, Kubik J, Przewlocki R (2009) Motivational effects of opiates in conditioned place preference and aversion paradigm—a study in three inbred strains of mice. Psychopharmacology 207:245–255
Spina L, Longoni R, Vinci S, Ibba F, Peana AT, Muggironi G, Spiga S, Acquas E (2010) Role of dopamine D1 receptors and extracellular signal regulated kinase in the motivational properties of acetaldehyde as assessed by place preference conditioning. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 34(4):607–616
Stansfield KH, Kirstein CL (2007) Chronic cocaine or ethanol exposure during adolescence alters novelty-related behaviours in adulthood. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 86(4):637–642
Steimer T, Driscoll P (2003) Divergent stress responses and coping styles in psychogenetically selected Roman high-(RHA) and low-(RLA) avoidance rats: behavioural, neuroendocrine and developmental aspects. Stress 6:87–100
Steimer T, Driscoll P (2005) Inter-individual vs line/strain differences in psychogenetically selected Roman High-(RHA) and Low-(RLA) Avoidance rats: neuroendocrine and behavioural aspects. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 29(1):99–112
Suzuki T, Tsuda M, Funada M, Misawa M (1995) Blockade of morphine-induced place preference by diazepam in mice. Eur J Pharmacol 280:327–330
Tzschentke TM (2007) Measuring reward with the conditioned place preference (CPP) paradigm: update of the last decade. Addict Biol 12:227–462
Valjent E, Corvol JC, Pages C, Besson MJ, Maldonado R, Caboche J (2000) Involvement of the extracellular signal-regulated kinase cascade for cocaine-rewarding properties. J Neurosci 20:8701–8709
Valjent E, Pages C, Rogard M, Besson MJ, Maldonado R, Caboche J (2001) Delta 9- tetrahydrocannabinol-induced MAPK/ERK and Elk-1 activation in vivo depends on dopaminergic transmission. Eur J Neurosci 14:342–352
Valjent E, Pagès C, Hervé D, Girault JA, Caboche J (2004) Addictive and non-addictive drugs induce distinct and specific patterns of ERK activation in mouse brain. Eur J Neurosci 19:1826–1836
Verheul R, van den Brink W (2000) The role of personality pathology in the etiology and treatment of substance use disorders. Curr Opin Psychiatry 13:163–169
Zarrindast MR, Rostami P, Zarei M, Roohbakhsh A (2005) Intracerebroventricular effects of histaminergic agents on morphine-induced anxiolysis in the elevated plus-maze in rats. Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol 97(5):276–281
Zhai H, Li Y, Wang X, Lu L (2008) Drug-induced alterations in the extracellular signal regulated kinase (ERK) signalling pathway: implications for reinforcement and reinstatement. Cell Mol Neurobiol 28:157–172
Zhang L, Lou D, Jiao H, Zhang D, Wang X, Xia Y, Zhang J, Xu M (2004) Cocaine-induced intracellular signaling and gene expression are oppositely regulated by the dopamine D1 and D3 receptors. J Neurosci 24:3344–3354
Funding
This study was supported by funds from MIUR (Ministero dell’Istruzione, Università e Ricerca, PRIN), Regione Autonoma della Sardegna (RAS) (L.R. 7/2007, CRP2_537), Fondazione Banco di Sardegna (Sassari, Italy) and from the University of Cagliari to EA and by grants from MIUR to OG and MGC and from RAS (L.R. 7/2007, CRP-59842) to OG.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rosas, M., Porru, S., Sabariego, M. et al. Effects of morphine on place conditioning and ERK1/2 phosphorylation in the nucleus accumbens of psychogenetically selected Roman low- and high-avoidance rats. Psychopharmacology 235, 59–69 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-017-4740-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-017-4740-4