Abstract
Rationale
Alcohol-dependent (AD) patients with a history of childhood maltreatment (CM) have shown a more severe clinical profile and a higher risk of relapse than those without CM. It was hypothesized that stress responsivity plays an important role in moderating the relationship between CM and AD. Surprisingly, systematic investigations about the stress responsivity in AD patients with CM are rare.
Objective
This study compared physiological and subjective stress responses in AD patients with and without CM as well as in healthy controls with and without CM.
Methods
A total of 130 participants performed the Trier Social Stress Test (TSST). Physiological stress reactivity related to the noradrenergic system was assessed by salivary alpha-amylase (sAA) activity. Subjective ratings of anxiety, nervousness, distress, and mood were rated on visual analogue scales.
Results
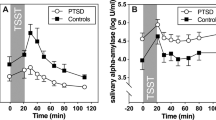
AD patients showed significantly lower stress-related sAA activity than healthy controls (p ≤ 0.024; z ≥ 1.97). A different pattern was found in the subjective ratings. In particular, anticipatory anxiety revealed a clear effect of CM (p ≤ 0.005; z ≥ 2.43) but no difference between AD patients and healthy controls (p > 0.05). After the TSST, distress ratings differed between AD patients with CM and AD patients without CM (p ≤ 0.009; z ≥ 2.61).
Conclusion
The discrepancy between physiological responsivity and subjective stress experiences may account for an increased inability to cope with stressful situations, which in turn might explain the enhanced risk of relapse in AD patients with a history of CM during early abstinence.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adinoff B, Martin PR, Bone GHA, Eckardt MJ, Roehrich L, George DT, Moss HB, Eskay R, Linnoila M, Gold PW (1990) Hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis functioning and cerebrospinal-fluid corticotropin releasing hormone and corticotropin levels in alcoholics after recent and long-term abstinence. Arch Gen Psychiat 47:325–330
Adinoff B, Junghanns K, Kiefer F, Krishnan-Sarin S (2005) Suppression of the HPA axis stress-response: implications for relapse. Alcoholism-Clinical and Experimental Research 29:1351–1355
Andrews J, Ali N, Pruessner JC (2013) Reflections on the interaction of psychogenic stress systems in humans: the stress coherence/compensation model. Psychoneuroendocrinology 38:947–961
Anthenelli RM (2012) Overview: stress and alcohol use disorders revisited. Alcohol Res-Curr Rev 34:386–390
Beck AT, Steer RA, Brown GK (1996) Beck depression inventory, 2nd edn. The Psychological Corporation, San Antonio, Manual
Bernstein DP, Fink L (1998) Childhood trauma questionnaire: a retrospective self-report manual. The Psychological Corporation, San Antonio, TX
Bernstein DP, Stein JA, Newcomb MD, Walker E, Pogge D, Ahluvalia T, Stokes J, Handelsman L, Medrano M, Desmond D, Zule W (2003) Development and validation of a brief screening version of the childhood trauma questionnaire. Child Abuse Negl 27:169–190
Blaine SK, Seo D, Sinha R (2015) Peripheral and prefrontal stress system markers and risk of relapse in alcoholism. Addiction biology
Blaine SK, Milivojevic V, Fox H, Sinha R (2016) Alcohol effects on stress pathways: impact on craving and relapse risk. Can J Psychiatr 61:145–153
Brady KT, Back SE (2012) Childhood trauma, posttraumatic stress disorder, and alcohol dependence. Alcohol Res-Curr Rev 34:408–413
De Bellis MD (2005) The psychobiology of neglect. Child Maltreatment 10:150–172
De Bellis MD, Zisk A (2014) The biological effects of childhood trauma. Child Adolesc Psychiatr Clin N Am 23(185–222):vii
De Bellis MD, Lefter L, Trickett PK, Putnam FW Jr (1994) Urinary catecholamine excretion in sexually abused girls. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry 33:320–327
Ditzen B, Ehlert U, Nater UM (2014) Associations between salivary alpha-amylase and catecholamines—a multilevel modeling approach. Biol Psychol 103:15–18
Ehrenreich H, Schuck J, Stender N, Pilz J, Gefeller O, Schilling L, Poser W, Kaw S (1997) Endocrine and hemodynamic effects of stress versus systemic CRF in alcoholics during early and medium term abstinence. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 21:1285–1293
Elliott JC, Stohl M, Wall MM, Keyes KM, Goodwin RD, Skodol AE, Krueger RF, Grant BF, Hasin DS (2014) The risk for persistent adult alcohol and nicotine dependence: the role of childhood maltreatment. Addiction 109:842–850
Enoch MA (2011) The role of early life stress as a predictor for alcohol and drug dependence. Psychopharmacology 214:17–31
Feder A, Nestler EJ, Charney DS (2009) Psychobiology and molecular genetics of resilience. Nat Rev Neurosci 10:446–457
Fitzgerald PJ (2012) Neurodrinking: is alcohol a substrate in a novel, endogenous synthetic pathway for norepinephrine? Med Hypotheses 78:760–762
Fitzgerald PJ (2013) Elevated norepinephrine may be a unifying etiological factor in the abuse of a broad range of substances: alcohol, nicotine, marijuana, heroin, cocaine, and caffeine. Substance abuse : research and treatment 7:171–183
Hasin DS, Grant BF (2015) The National Epidemiologic Survey on Alcohol and Related Conditions (NESARC) waves 1 and 2: review and summary of findings. Soc Psych Psych Epid 50:1609–1640
Heim C, Newport DJ, Heit S, Graham YP, Wilcox M, Bonsall R, Miller AH, Nemeroff CB (2000) Pituitary-adrenal and autonomic responses to stress in women after sexual and physical abuse in childhood. Jama-J Am Med Assoc 284:592–597
Hostinar CE, Gunnar MR (2013) The developmental effects of early life stress: an overview of current theoretical frameworks. Curr Dir Psychol Sci 22:400–406
Ingjaldsson JT, Laberg JC, Thayer JF (2003) Reduced heart rate variability in chronic alcohol abuse: relationship with negative mood, chronic thought suppression, and compulsive drinking. Biol Psychiatry 54:1427–1436
Ireland MA, Vandongen R, Davidson L, Beilin LJ, Rouse IL (1984) Acute effects of moderate alcohol-consumption on blood-pressure and plasma catecholamines. Clin Sci 66:643–648
Junghanns K, Backhaus J, Tietz U, Lange W, Bernzen J, Wetterling T, Rink L, Driessen M (2003) Impaired serum cortisol stress response is a predictor of early relapse. Alcohol Alcohol 38:189–193
Kahkohen S (2004) Mechanisms of cardiovascular dysregulation during alcohol withdrawal. Prog Neuro-Psychoph 28:937–941
Karpyak VM, Romanowicz M, Schmidt JE, Lewis KA, Bostwick JM (2014) Characteristics of heart rate variability in alcohol-dependent subjects and nondependent chronic alcohol users. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 38:9–26
Kelbaek H, Floistrup S, Gjorup T, Christensen NJ, Hartling OJ, Godtfredsen J (1988) Central and peripheral haemodynamic changes after alcohol ingestion. Alcohol Alcohol 23:211–216
Keyes KM, Hatzenbuehler ML, Hasin DS (2011) Stressful life experiences, alcohol consumption, and alcohol use disorders: the epidemiologic evidence for four main types of stressors. Psychopharmacology 218:1–17
Kirschbaum C, Pirke KM, Hellhammer DH (1993) The ‘Trier Social Stress Test’—a tool for investigating psychobiological stress responses in a laboratory setting. Neuropsychobiology 28:76–81
Klinitzke G, Romppel M, Hauser W, Brahler E, Glaesmer H (2012) The German version of the childhood trauma questionnaire (CTQ): psychometric characteristics in a representative sample of the general population. Psychother Psychosom Med Psychol 62:47–51
Koob GF (2009) Brain stress systems in the amygdala and addiction. Brain Res 1293:61–75
Koob GF, Le Moal M (2001) Drug addiction, dysregulation of reward, and allostasis. Neuropsychopharmacology 24:97–129
Lijffijt M, Hu K, Swann AC (2014) Stress modulates illness-course of substance use disorders: a translational review. Frontiers in psychiatry 5:83
Maier H, Born IA, Veith S, Adler D, Seitz HK (1986) The effect of chronic ethanol consumption on salivary-gland morphology and function in the rat. Alcoholism-Clinical and Experimental Research 10:425–427
Nater UM, Rohleder N, Gaab J, Berger S, Jud A, Kirschbaum C, Ehlert U (2005) Human salivary alpha-amylase reactivity in a psychosocial stress paradigm. International journal of psychophysiology : official journal of the International Organization of Psychophysiology 55:333–342
Nater UM, Rohleder N, Schlotz W, Ehlert U, Kirschbaum C (2007) Determinants of the diurnal course of salivary alpha-amylase. Psychoneuroendocrinology 32:392–401
Otte C, Neylan TC, Pole N, Metzler T, Best S, Henn-Haase C, Yehuda R, Marmar CR (2005) Association between childhood trauma and catecholamine response to psychological stress in police academy recruits. Biol Psychiatry 57:27–32
Patkar AA, Gopalakrishnan R, Naik PC, Murray HW, Vergare MJ, Marsden CA (2003) Changes in plasma noradrenaline and serotonin levels and craving during alcohol withdrawal. Alcohol Alcohol 38:224–231
Quintana DS, McGregor IS, Guastella AJ, Malhi GS, Kemp AH (2013) A meta-analysis on the impact of alcohol dependence on short-term resting-state heart rate variability: implications for cardiovascular risk. Alcoholism-Clinical and Experimental Research 37:E23–E29
Schäfer I, Pawils S, Driessen M, Härter M, Hillemacher T, Klein M, Muehlhan M, Ravens-Sieberer U, Schäfer M, Scherbaum N, Schneider B, Thomasius R, Wiedemann K, Wegscheider K, Barnow S (2017) Understanding the role of childhood abuse and neglect as a cause and consequence of substance abuse: the German CANSAS-Network. Eur J Psychotraumatol (EJPT). doi:10.1080/20008198.2017.1304114
Schumacher S, Kirschbaum C, Fydrich T, Strohle A (2013) Is salivary alpha-amylase an indicator of autonomic nervous system dysregulations in mental disorders?—a review of preliminary findings and the interactions with cortisol. Psychoneuroendocrinology 38:729–743
Sinha R, Fox HC, Hong KA, Bergquist K, Bhagwagar Z, Siedlarz KM (2009) Enhanced negative emotion and alcohol craving, and altered physiological responses following stress and cue exposure in alcohol dependent individuals. Neuropsychopharmacology 34:1198–1208
Sinha R, Fox HC, Hong KIA, Hansen J, Tuit K, Kreek MJ (2011) Effects of adrenal sensitivity, stress- and cue-induced craving, and anxiety on subsequent alcohol relapse and treatment outcomes. Arch Gen Psychiat 68:942–952
Skoluda N, Strahler J, Schlotz W, Niederberger L, Marques S, Fischer S, Thoma MV, Spoerri C, Ehlert U, Nater UM (2015) Intra-individual psychological and physiological responses to acute laboratory stressors of different intensity. Psychoneuroendocrinology 51:227–236
Skrondal A, Rabe-Hesketh S (2004) Generalized latent variable modeling: multilevel, longitudinal, and structural equation models. CRC Press
Spaak J, Tomlinson G, McGowan CL, Soleas GJ, Morris BL, Picton P, Notarius CF, Floras JS (2010) Dose-related effects of red wine and alcohol on heart rate variability. Am J Physiol-Heart C 298:H2226–H2231
Starcke K, van Holst RJ, van den Brink W, Veltman DJ, Goudriaan AE (2013) Physiological and endocrine reactions to psychosocial stress in alcohol use disorders: duration of abstinence matters. Alcoholism-Clinical and Experimental Research 37:1343–1350
Sullivan JT, Sykora K, Schneiderman J, Naranjo CA, Sellers EM (1989) Assessment of alcohol withdrawal—the revised Clinical Institute Withdrawal Assessment for Alcohol scale (CIWA-Ar). Brit J Addict 84:1353–1357
Watts-English T, Fortson BL, Gibler N, Hooper SR, De Bellis MD (2006) The psychobiology of maltreatment in childhood. J Soc Issues 62:717–736
Wilcox CE, Pommy JM, Adinoff B (2016) Neural circuitry of impaired emotion regulation in substance use disorders. Am J Psychiat: appiajp201515060710
Wittchen H-U, Zaudig M, Fydrich T (1997) Strukturiertes Klinisches Interview für DSM-IV. [Structured Clinical Interview for DSM-IV]. Göttingen, Hogrefe
Wood AM, White IR, Hillsdon M, Carpenter J (2005) Comparison of imputation and modelling methods in the analysis of a physical activity trial with missing outcomes. Int J Epidemiol 34:89–99
Yang H, Devous MD, Briggs RW, Spence JS, Xiao H, Kreyling N, Adinoff B (2013) Altered neural processing of threat in alcohol-dependent men. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 37:2029–2038
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by the German Federal Ministry of Education and Research (Bundesministerium für Bildung und Forschung): Grant No. 01KR1203A. We would like to thank Kirsten Huwald, Sandra Schwentesius, and Iris Remmlinger-Marten for their lab assistance.
CANSAS study group: Schäfer I. (coordinator), Barnow S., Bullinger M., Driessen M., Härter M., Hiller P., Hillemacher T., Klein M., Muhtz C., Muehlhan M., Ravens-Sieberer U., Scherbaum N., Thomasius R., M. Schäfer, Schneider B., Wegscheider K., and Pawils S.
Authors’ contribution
MM is responsible for the study concept and design, conducted the statistical analyses, and wrote the paper. AH performed the data acquisition and contributed substantially to the interpretation of the data, MH guided the statistical analyses and contributed substantially to the interpretation of the data, KW performed the biochemical analyses and contributed substantially to the interpretation of the data, SB contributed substantially to the interpretation of the data, IS is the principal investigator, responsible for the study design, and contributed substantially to the interpretation of the data. All authors approved the final version of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Consortia
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Muehlhan, M., Höcker, A., Höfler, M. et al. Stress-related salivary alpha-amylase (sAA) activity in alcohol dependent patients with and without a history of childhood maltreatment. Psychopharmacology 234, 1901–1909 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-017-4595-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-017-4595-8