Abstract
Rationale
Orexinergic system is involved in reward processing and drug addiction.
Objectives
Here, we investigated the effect of intrahippocampal CA1 administration of orexin-2 receptor (OX2r) antagonist on the acquisition, expression, and extinction of morphine-induced place preference in rats.
Methods
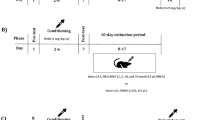
Conditioned place preference (CPP) was induced by subcutaneous injection of morphine (5 mg/kg) during a 3-day conditioning phase. Three experimental plots were designed; TCS OX2 29 as a selective antagonist of orexin-2 receptors (OX2rs) was dissolved in DMSO, prepared in solutions with different concentrations (1, 3, 10, and 30 nM), and was bilaterally microinjected into the CA1 and some neighboring regions (0.5 μl/side). Conditioning scores and locomotor activities were recorded during the test.
Results
Results demonstrate that intra-CA1 administration of the OX2r antagonist attenuates the induction of morphine CPP during the acquisition and expression phases. Effect of TCS OX2 29 on reduction of morphine CPP was dose-dependent and was more pronounced during the acquisition than the expression. Furthermore, higher concentrations of TCS OX2 29 facilitated the extinction of morphine-induced CPP and reduced extinction latency period. Nevertheless, administration of TCS OX2 29 solutions did not have any influence on locomotor activity of all phases.
Conclusions
Our findings suggest that OX2rs in the CA1 region of hippocampus are involved in the development of the acquisition and expression of morphine CPP. Moreover, blockade of OX2rs could facilitate extinction and may abrogate or extinguish the ability of drug-related cues, implying that the antagonist might be considered as a propitious therapeutic agent in suppressing drug-seeking behavior.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akbari E, Motamedi F, Naghdi N, Noorbakhshnia M (2008) The effect of antagonization of orexin 1 receptors in CA 1 and dentate gyrus regions on memory processing in passive avoidance task. Behav Brain Res 187:172–177. doi:10.1016/j.bbr.2007.09.019
Akbari E, Naghdi N, Motamedi F (2006) Functional inactivation of orexin 1 receptors in CA1 region impairs acquisition, consolidation and retrieval in Morris water maze task. Behav Brain Res 173:47–52. doi:10.1016/j.bbr.2006.05.028
Akirav I, Richter-Levin G (2002) Mechanisms of amygdala modulation of hippocampal plasticity. J Neurosci 22:9912–9921
Albertin SV, Mulder AB, Tabuchi E, Zugaro MB, Wiener SI (2000) Lesions of the medial shell of the nucleus accumbens impair rats in finding larger rewards, but spare reward-seeking behavior. Behav Brain Res 117:173–183. doi:10.1016/s0166-4328(00)00303-x
Bardo M, Bevins RA (2000) Conditioned place preference: what does it add to our preclinical understanding of drug reward? Psychopharmacology (Berl) 153:31–43. doi:10.1007/s002130000569
Black YD, Green-Jordan K, Eichenbaum HB, Kantak KM (2004) Hippocampal memory system function and the regulation of cocaine self-administration behavior in rats. Behav Brain Res 151:225–238. doi:10.1016/j.bbr.2003.08.020
Cammarota M, Bevilaqua LR, Barros DM, Vianna MR, Izquierdo LA, Medina JH, Izquierdo I (2005) Retrieval and the extinction of memory. Cell Mol Neurobiol 25:465–474. doi:10.1007/s10571-005-4009-z
Corrigall WA, Linseman MA (1988) Conditioned place preference produced by intra-hippocampal morphine. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 30:787–789. doi:10.1016/0091-3057(88)90100-1
Cutler DJ, Morris R, Sheridhar V, Wattam TA, Holmes S, Patel S, Arch JR, Wilson S, Buckingham RE, Evans ML (1999) Differential distribution of orexin-A and orexin-B immunoreactivity in the rat brain and spinal cord. Peptides 20:1455–1470. doi:10.1016/s0196-9781(99)00157-6
De Lecea L, Kilduff T, Peyron C, Gao X-B, Foye P, Danielson P, Fukuhara C, Battenberg E, Gautvik V, Fn B (1998) The hypocretins: hypothalamus-specific peptides with neuroexcitatory activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 95:322–327. doi:10.1073/pnas.95.1.322
Delamater AR (2004) Experimental extinction in Pavlovian conditioning: behavioural and neuroscience perspectives. Q J Exp Psychol Sect B 57:97–132. doi:10.1080/02724990344000097
Ferbinteanu J, McDonald R (2001) Dorsal/ventral hippocampus, fornix, and conditioned place preference. Hippocampus 11:187–200. doi:10.1002/hipo.1036
Flores Á, Valls-Comamala V, Costa G, Saravia R, Maldonado R, Berrendero F (2014) The hypocretin/orexin system mediates the extinction of fear memories. Neuropsychopharmacology 39:2732–2741. doi:10.1038/npp.2014.146
Harris GC, Aston-Jones G (2006) Arousal and reward: a dichotomy in orexin function. Trends Neurosci 29:571–577. doi:10.1016/j.tins.2006.08.002
Harris GC, Wimmer M, Aston-Jones G (2005) A role for lateral hypothalamic orexin neurons in reward seeking. Nature 437:556–559. doi:10.1038/nature04071
Harris GC, Wimmer M, Randall-Thompson JF, Aston-Jones G (2007) Lateral hypothalamic orexin neurons are critically involved in learning to associate an environment with morphine reward. Behav Brain Res 183:43–51. doi:10.1016/j.bbr.2007.05.025
Hunsaker MR, Tran GT, Kesner RP (2009) A behavioral analysis of the role of CA3 and CA1 subcortical efferents during classical fear conditioning. Behav Neurosci 123:624. doi:10.1037/a0015455
Hyman SE, Malenka RC, Nestler EJ (2006) Neural mechanisms of addiction: the role of reward-related learning and memory. Annu Rev Neurosci 29:565–598. doi:10.1146/annurev.neuro.29.051605.113009
Isokawa M (2012) Cellular signal mechanisms of reward-related plasticity in the hippocampus. Neural Plast 2012. doi:10.1155/2012/945373
Jay TM, Witter MP (1991) Distribution of hippocampal CA1 and subicular efferents in the prefrontal cortex of the rat studied by means of anterograde transport of Phaseolus vulgaris‐leucoagglutinin. J Comp Neurol 313:574–586. doi:10.1002/cne.903130404
Koob GF, Volkow ND (2010) Neurocircuitry of addiction. Neuropsychopharmacology 35:217–238. doi:10.1038/npp.2010.4
Lisman JE, Grace AA (2005) The hippocampal-VTA loop: controlling the entry of information into long-term memory. Neuron 46:703–713. doi:10.1016/j.neuron.2005.05.002
Liu F, Jiang H, Zhong W, Wu X, Luo J (2010) Changes in ensemble activity of hippocampus CA1 neurons induced by chronic morphine administration in freely behaving mice. Neuroscience 171:747–759. doi:10.1016/j.neuroscience.2010.09.052
Lu X-Y, Bagnol D, Burke S, Akil H, Watson SJ (2000) Differential distribution and regulation of OX1 and OX2 orexin/hypocretin receptor messenger RNA in the brain upon fasting. Horm Behav 37:335–344. doi:10.1006/hbeh.2000.1584
Luo AH, Tahsili-Fahadan P, Wise RA, Lupica CR, Aston-Jones G (2011) Linking context with reward: a functional circuit from hippocampal CA3 to ventral tegmental area. Science 333:353–357. doi:10.1126/science.1204622
Marcus JN, Aschkenasi CJ, Lee CE, Chemelli RM, Saper CB, Yanagisawa M, Elmquist JK (2001) Differential expression of orexin receptors 1 and 2 in the rat brain. J Comp Neurol 435:6–25. doi:10.1002/cne.1190
Meyers RA, Zavala AR, Neisewander JL (2003) Dorsal, but not ventral, hippocampal lesions disrupt cocaine place conditioning. Neuroreport 14:2127–2131. doi:10.1097/00001756-200311140-00023
Morris R, Garrud P, Rawlins J, O’Keefe J (1982) Place navigation impaired in rats with hippocampal lesions. Nature 297:681–683. doi:10.1038/297681a0
Nambu T, Sakurai T, Mizukami K, Hosoya Y, Yanagisawa M, Goto K (1999) Distribution of orexin neurons in the adult rat brain. Brain Res 827:243–260. doi:10.1016/s0006-8993(99)01336-0
Narita M, Nagumo Y, Hashimoto S, Narita M, Khotib J, Miyatake M, Sakurai T, Yanagisawa M, Nakamachi T, Shioda S (2006) Direct involvement of orexinergic systems in the activation of the mesolimbic dopamine pathway and related behaviors induced by morphine. J Neurosci 26:398–405. doi:10.1523/jneurosci.2761-05.2006
Nestler EJ (2001) Total recall—the memory of addiction. Science 292:2266–2267. doi:10.1126/science.1063024
Olmstead MC, Franklin KB (1997) The development of a conditioned place preference to morphine: effects of microinjections into various CNS sites. Behav Neurosci 111:1324. doi:10.1037/0735-7044.111.6.1324
Paxinos G, Watson C (2007) The rat brain in stereotaxic coordinates, 6th edn. Elsevier-Academic Press, Waltham, Massachusetts, USA
Peyron C, Tighe DK, Van Den Pol AN, De Lecea L, Heller HC, Sutcliffe JG, Kilduff TS (1998) Neurons containing hypocretin (orexin) project to multiple neuronal systems. J Neurosci 18:9996–10015. doi:10.1.1.335.5389
Quirk GJ, Mueller D (2008) Neural mechanisms of extinction learning and retrieval. Neuropsychopharmacology 33:56–72. doi:10.1038/sj.npp.1301555
Rashidy-Pour A, Moradi M, Fatahi Z, Haghparast A, Haghparast A (2015) Role of intra-hippocampal orexin 1 and orexin 2 receptors in conditioned place preference induced by chemical stimulation of the lateral hypothalamus. Behav Brain Res 279:106–111. doi:10.1016/j.bbr.2014.10.051
Rezayof A, Razavi S, Haeri-Rohani A, Rassouli Y, Zarrindast M-R (2007) GABA A receptors of hippocampal CA1 regions are involved in the acquisition and expression of morphine-induced place preference. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol 17:24–31. doi:10.1016/j.euroneuro.2006.02.003
Rezayof A, Zatali H, Haeri-Rohani A, Zarrindast M-R (2006) Dorsal hippocampal muscarinic and nicotinic receptors are involved in mediating morphine reward. Behav Brain Res 166:281–290. doi:10.1016/j.bbr.2005.08.010
Riahi E, Khodagholi F, Haghparast A (2013) Role of dorsal hippocampal orexin-1 receptors in associating morphine reward with contextual stimuli. Behav Pharmacol 24:237–248. doi:10.1097/fbp.0b013e3283635ee9
Risold P, Swanson L (1997) Chemoarchitecture of the rat lateral septal nucleus. Brain Res Rev 24:91–113. doi:10.1016/s0165-0173(97)00008-8
Sakurai T, Amemiya A, Ishii M, Matsuzaki I, Chemelli RM, Tanaka H, Williams SC, Richardson JA, Kozlowski GP, Wilson S (1998) Orexins and orexin receptors: a family of hypothalamic neuropeptides and G protein-coupled receptors that regulate feeding behavior. Cell 92:573–585. doi:10.1016/s0092-8674(00)80949-6
Sartor GC, Aston-Jones GS (2012) A septal-hypothalamic pathway drives orexin neurons, which is necessary for conditioned cocaine preference. J Neurosci 32:4623–4631. doi:10.1523/jneurosci.4561-11.2012
Sharf R, Sarhan M, DiLeone RJ (2010) Role of orexin/hypocretin in dependence and addiction. Brain Res 1314:130–138. doi:10.1016/j.brainres.2009.08.028
Trivedi P, Yu H, MacNeil DJ, Van der Ploeg L, Guan X-M (1998) Distribution of orexin receptor mRNA in the rat brain. FEBS Lett 438:71–75. doi:10.1016/s0014-5793(98)01266-6
Wang WS, Chen ZG, Liu WT, Chi ZQ, He L, Liu JG (2015) Dorsal hippocampal NMDA receptor blockade impairs extinction of naloxone‐precipitated conditioned place aversion in acute morphine‐treated rats by suppressing ERK and CREB phosphorylation in the basolateral amygdala. Br J Pharmacol 172:482–491. doi:10.1111/bph.12671
Wolf ME (2002) Addiction: making the connection between behavioral changes and neuronal plasticity in specific pathways. Mol Interv 2:146. doi:10.1124/mi.2.3.146
Yang L, Zou B, Xiong X, Pascual C, Xie J, Malik A, Xie J, Sakurai T, Xie XS (2013) Hypocretin/orexin neurons contribute to hippocampus-dependent social memory and synaptic plasticity in mice. J Neurosci 33:5275–5284. doi:10.1523/jneurosci.3200-12.2013
Zarrindast M-R, Massoudi R, Sepehri H, Rezayof A (2006) Involvement of GABA B receptors of the dorsal hippocampus on the acquisition and expression of morphine-induced place preference in rats. Physiol Behav 87:31–38. doi:10.1016/j.physbeh.2005.08.041
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the grant (88-1039-A) from the Neuroscience Research Center of Shahid Beheshti University of Medical Sciences, Tehran, Iran.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(DOC 108 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sadeghi, B., Ezzatpanah, S. & Haghparast, A. Effects of dorsal hippocampal orexin-2 receptor antagonism on the acquisition, expression, and extinction of morphine-induced place preference in rats. Psychopharmacology 233, 2329–2341 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-016-4280-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-016-4280-3