Abstract
Rationale
Gaboxadol is a selective agonist at γ-aminobutyric acidA (GABAA) receptors that contain α4-δ subunits, and it produces anxiolytic and sedative effects. Although adverse effects preclude its clinical use, its mechanism of action suggests that those receptors might provide novel therapeutic targets, particularly for modulators of those GABAA receptor subtypes, by retaining therapeutic effects of gaboxadol and not adverse effects.
Objectives
The current study compared discriminative stimulus effects of gaboxadol with those of modulators acting at GABAA receptors containing α4-δ subunits.
Materials
Eight rats discriminated 5.6 mg/kg gaboxadol from vehicle while responding under a fixed - ratio 10 schedule for food. Modulators acting at GABAA receptors containing α4-δ subunits (pregnanolone, ethanol, and flumazenil) and receptors that do not contain those subunits (midazolam) were studied alone; pregnanolone and ethanol were also combined with gaboxadol. In addition, gaboxadol was studied in separate groups discriminating 0.32 mg/kg midazolam, 3.2 mg/kg pregnanolone, or 0.75 g/kg ethanol from vehicle.
Results
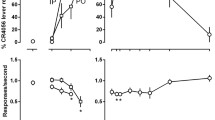
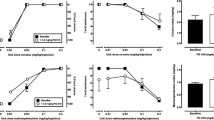
Gaboxadol produced ≥80 % gaboxadol-lever responding and did not alter rates. No other drug produced, on average, ≥80 % drug-lever responding up to doses that decreased rates, although 1.78 mg/kg midazolam produced 32 % gaboxadol-lever responding. Ethanol and pregnanolone did not enhance the effects of gaboxadol. Rats discriminating midazolam, pregnanolone, or ethanol from vehicle responded predominantly on the vehicle lever after receiving gaboxadol.
Conclusions
Drugs that modulate GABAA receptors containing α4-δ subunits neither mimicked nor enhanced the discriminative stimulus effects of gaboxadol, indicating that at least some effects of gaboxadol are not shared with modulators of that GABAA receptor subtype.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ator NA, Griffiths RR (1986) Discriminative stimulus effects of atypical anxiolytics in baboons and rats. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 237:393–403
Bai X, Gerak LR (2011) Comparing the discriminative stimuli produced by either the neuroactive steroid pregnanolone or the benzodiazepine midazolam in rats. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 214:427–435
Belelli D, Peden DR, Rosahl TW et al (2005) Extrasynaptic GABAA receptors of thalamocortical neurons: a molecular target for hypnotics. J Neurosci 25:11513–11520
Bianchi MT, Macdonald RL (2003) Neurosteroids shift partial agonist activation of GABAA receptor channels from low- to high-efficacy gating patterns. J Neurosci 23:10934–10943
Borghese CM, Stórustovu S, Ebert B et al (2006) The δ subunit of γ-aminobutyric acid type A receptors does not confer sensitivity to low concentrations of ethanol. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 316:1360–1368
Brickley SG, Mody I (2012) Extrasynaptic GABAA receptors: their function in the CNS and implications for disease. Neuron 73:23–34
Brown N, Kerby J, Bonnert TP et al (2002) Pharmacological characterization of a novel cell line expressing human α4β3δ GABAA receptors. Br J Pharmacol 136:965–974
Cope DW, Hughes SW, Crunelli V (2005) GABAA receptor-mediated tonic inhibition in thalamic neurons. J Neurosci 25:11553–11563
De Vry J, Slangen JL (1986) Effects of training dose on discrimination and cross-generalization of chlordiazepoxide, pentobarbital and ethanol in the rat. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 88:341–345
Deacon S, Staner L, Staner C et al (2007) Effect of short-term treatment with gaboxadol on sleep maintenance and initiation in patients with primary insomnia. Sleep 30:281–287
Drasbek KR, Jensen K (2006) THIP, a hypnotic and antinociceptive drug, enhances an extrasynaptic GABAA receptor-mediated conductance in mouse neocortex. Cereb Cortex 16:1134–1141
Engel SR, Purdy RH, Grant KA (2001) Characterization of discriminative stimulus effects of the neuroactive steroid pregnanolone. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 297:489–495
Eppolito AK, Kodeih HR, Gerak LR (2014) Using drug combinations to assess potential contributions of non-GABAA receptors in the discriminative stimulus effects of the neuroactive steroid pregnanolone in rats. Physiol Behav 137:33–41
Gerak LR, France CP (2014) Discriminative stimulus effects of pregnanolone in rhesus monkeys. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 231:181–190
Grant KA, Colombo G (1993) Pharmacological analysis of the mixed discriminative stimulus effects of ethanol. Alcohol Alcohol Suppl 2:445–449
Grech DM, Balster RL (1994) Discriminative stimulus effects of presynaptic GABA agonists in pentobarbital-trained rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 47:5–11
Hajak G, Hedner J, Eglin M et al (2009) A 2-week efficacy and safety study of gaboxadol and zolpidem using electronic diaries in primary insomnia outpatients. Sleep Med 10:705–712
Hanchar HJ, Chutsrinopkun P, Meera P et al (2006) Ethanol potently and competitively inhibits binding of the alcohol antagonist Ro15-4513 to α4/6β3δ GABAA receptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci 103:8546–8551
Hoehn-Saric R (1983) Effects of THIP on chronic anxiety. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 80:338–341
Jia F, Pignataro L, Schofield CM et al (2005) An extrasynaptic GABAA receptor mediates tonic inhibition in thalamic VB neurons. J Neurophysiol 94:4491–4501
Jin Z, Bazov I, Kononenko O et al (2012) Selective changes of GABAA channel subunit mRNAs in the hippocampus and orbitofrontal cortex but not in prefrontal cortex of human alcoholics. Front Cell Neurosci 5:30
Jones HE, Balster RL (1998) Muscimol-like discriminative stimulus effects of GABA agonists in rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 59:319–326
Klempan TA, Sequeira A, Canetti L et al (2007) Altered expression of genes involved in ATP biosynthesis and GABAergic neurotransmission in the ventral prefrontal cortex of suicides with and without major depression. Mol Psychiatry 14:175–189
Knoflach F, Benke D, Wang Y et al (1996) Pharmacological modulation of the diazepam-insensitive recombinant gamma-aminobutyric acidA receptors α4β2γ3 and α6β2γ2. Mol Pharmacol 50:1253–1261
Korpi ER, Mihalek RM, Sinkkonen ST et al (2002) Altered receptor subtypes in the forebrain of GABAA receptor δ subunit-deficient mice: recruitment of γ2 subunits. Neuroscience 109:733–743
Lankford DA, Corser BC, Zheng Y-P et al (2008) Effect of gaboxadol on sleep in adult and elderly patients with primary insomnia: results from two randomized, placebo-controlled, 30-night polysomnography studies. Sleep 31:1359–1370
Lelas S, Gerak LR, France CP (2000) Antagonism of the discriminative stimulus effects of positive γ-aminobutyric acidA modulators in rhesus monkeys discriminating midazolam. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 294:902–908
McDonald LM, Sheppard WF, Staveley SM et al (2007) Gaboxadol, a selective extrasynaptic GABA(A) agonist, does not generalise to other sleep-enhancing drugs: a rat drug discrimination study. Neuropharmacology 52:844–853
McDonald LM, Sheppard WF, Staveley SM et al (2008) Discriminative stimulus effects of tiagabine and related GABAergic drugs in rats. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 197:591–600
McMahon LR, France CP (2005) Combined discriminative stimulus effects of midazolam with other positive GABAA modulators and GABAA receptor agonists in rhesus monkeys. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 178:400–409
Meera P, Wallner M, Otis TS (2011) Molecular basis for the high THIP/gaboxadol sensitivity of extrasynaptic GABA(A) receptors. J Neurophysiol 106:2057–2064
Merali Z, Du L, Hrdina P et al (2004) Dysregulation in the suicide brain: mRNA expression of corticotropin-releasing hormone receptors and GABAA receptor subunits in frontal cortical brain region. J Neurosci 24:1478–1485
Michelsen S, Sánchez C, Ebert B (2007) Lack of generalisation between the GABAA receptor agonist, gaboxadol, and allosteric modulators of the benzodiazepine binding site in the rat drug discrimination procedure. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 193:151–157
Mihalek RM, Banerjee PK, Korpi ER et al (1999) Attenuated sensitivity to neuroactive steroids in γ-aminobutyrate type A receptor delta subunit knockout mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci 96:12905–12910
Mihalek RM, Bowers BJ, Wehner JM et al (2001) GABAA-receptor δ subunit knockout mice have multiple defects in behavioral responses to ethanol. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 25:1708–1718
Mitchell EA, Herd MB, Gunn BG et al (2008) Neurosteroid modulation of GABAA receptors: molecular determinants and significance in health and disease. Neurochem Int 52:588–595
Nielsen EB, Suzdak PD, Andersen KE et al (1991) Characterization of tiagabine (NO-328), a new potent and selective GABA uptake inhibitor. Eur J Pharmacol 196:257–266
Olsen RW, Sieghart W (2008) International Union of Pharmacology. LXX. Subtypes of gamma-aminobutyric acid(A) receptors: classification on the basis of subunit composition, pharmacology, and function. Update. Pharmacol Rev 60:243–260
Olsen RW, Sieghart W (2009) GABAA receptors: subtypes provide diversity of function and pharmacology. Neuropharmacology 56:141–148
Olsen RW, Hanchar HJ, Meera P, Wallner M (2007) GABAA receptor subtypes: the “one glass of wine” receptors. Alcohol Fayettev N 41:201–209
Peng Z, Hauer B, Mihalek RM et al (2002) GABA(A) receptor changes in delta subunit-deficient mice: altered expression of alpha4 and gamma2 subunits in the forebrain. J Comp Neurol 446:179–197
Roth T, Lines C, Vandormael K et al (2010) Effect of gaboxadol on patient-reported measures of sleep and waking function in patients with primary insomnia: results from two randomized, controlled, 3-month studies. J Clin Sleep Med JCSM Off Publ Am Acad Sleep Med 6:30–39
Rowlett JK, Spealman RD, Lelas S (1999) Discriminative stimulus effects of zolpidem in squirrel monkeys: comparison with conventional benzodiazepines and sedative-hypnotics. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 291:1233–1241
Vashchinkina E, Manner AK, Vekovischeva O et al (2014) Neurosteroid agonist at GABAA receptor induces persistent neuroplasticity in VTA dopamine neurons. Neuropsychopharmacology 39:727–737
Wallner M, Hanchar HJ, Olsen RW (2003) Ethanol enhances α4β3δ and α6β3δ γ-aminobutyric acid type A receptors at low concentrations known to affect humans. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 100:15218–15223
Wallner M, Hanchar HJ, Olsen RW (2006) Low-dose alcohol actions on α4β3δ GABAA receptors are reversed by the behavioral alcohol antagonist Ro15-4513. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 103:8540–8545
Walsh JK, Deacon S, Dijk D-J, Lundahl J (2007) The selective extrasynaptic GABAA agonist, gaboxadol, improves traditional hypnotic efficacy measures and enhances slow wave activity in a model of transient insomnia. Sleep 30:593–602
Walsh JK, Snyder E, Hall J et al (2008) Slow wave sleep enhancement with gaboxadol reduces daytime sleepiness during sleep restriction. Sleep 31:659–672
Whissell PD, Lecker I, Wang D-S et al (2015) Altered expression of δGABAA receptors in health and disease. Neuropharmacology 88:24–35
Wong G, Skolnick P, Katz JL, Witkin JM (1993) Transduction of a discriminative stimulus through a diazepam-insensitive gamma-aminobutyric acidA receptor. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 266:570–576
Acknowledgments
These studies were supported by US Public Health Service Grant DA017240. The authors wish to thank T. Bentley, A. Hernandez, A. Mensah, and C. Moreno for their excellent technical assistance. This work is dedicated to the memory of Dr Steven R. Goldberg, a mentor and a friend.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
The content is solely the responsibility of the authors and does not necessarily represent the official views of the National Institute on Drug Abuse or the National Institutes of Health.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zanettini, C., Pressly, J.D., Ibarra, M.H. et al. Comparing the discriminative stimulus effects of modulators of GABAA receptors containing α4-δ subunits with those of gaboxadol in rats. Psychopharmacology 233, 2005–2013 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-016-4243-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-016-4243-8