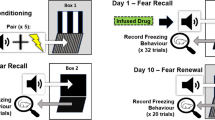
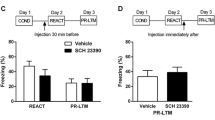
Abstract
There is much evidence suggesting that the mesoamygdala dopaminergic (DAergic) system plays a crucial role in the formation and expression of fear conditioning, with both D1 and D2 receptors being involved. In addition, cannabinoid CB1 receptor (CB1R) signaling modulates DAergic pathways. The present study sought to determine the involvement of basolateral amygdala (BLA) dopamine receptors in arachidonylcyclopropylamide (ACPA)-induced fear learning deficits. Context- and tone-dependent fear conditioning in adult male NMRI mice was evaluated. Pre-training intraperitoneal administration of ACPA (0.1 mg/kg) decreased the percentage of freezing in context- or tone-dependent fear conditioning, suggesting an acquisition impairment. Pre-training intra-BLA microinjection of a subthreshold dose of SKF38393 (D1-like receptor agonist), SCH23390 (D1-like receptor antagonist), quinpirole (D2-like receptor agonist), or sulpiride (D2-like receptor antagonist) did not alter the context-dependent fear learning deficit induced by ACPA, while SKF38393 or quinpirole restored ACPA effect on tone-dependent fear learning. Moreover, SKF38393 (1 μg/mouse), SCH23390 (0.04 and 0.08 μg/mouse), or quinpirole (0.1 μg/mouse) all impaired context-dependent fear learning. It is concluded that D1 or D2 dopamine (DA) receptor activation restores tone- but not context-dependent fear learning deficit induced by CB1 activation using ACPA.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abraham AD, Neve KA, Lattal KM (2014) Dopamine and extinction: a convergence of theory with fear and reward circuitry. Neurobiol Learn Mem 108:65–77
Akirav I (2011) The role of cannabinoids in modulating emotional and non-emotional memory processes in the hippocampus. Front Behav Neurosci 5:34
Arenos JD, Musty RE, Bucci DJ (2006) Blockade of cannabinoid CB1 receptors alters contextual learning and memory. Eur J Pharmacol 539:177–83
Bissiere S, Humeau Y, Luthi A (2003) Dopamine gates LTP induction in lateral amygdala by suppressing feedforward inhibition. Nat Neurosci 6:587–92
Blair HT, Schafe GE, Bauer EP, Rodrigues SM, LeDoux JE (2001) Synaptic plasticity in the lateral amygdala: a cellular hypothesis of fear conditioning. Learn Mem 8:229–42
Brandao ML, Troncoso AC, de Souza Silva MA, Huston JP (2003) The relevance of neuronal substrates of defense in the midbrain tectum to anxiety and stress: empirical and conceptual considerations. Eur J Pharmacol 463:225–33
Brandao ML, Borelli KG, Nobre MJ, Santos JM, Albrechet-Souza L, Oliveira AR, Martinez RC (2005) Gabaergic regulation of the neural organization of fear in the midbrain tectum. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 29:1299–311
Carvalho JD, de Oliveira AR, da Silva RC, Brandao ML (2009) A comparative study on the effects of the benzodiazepine midazolam and the dopamine agents, apomorphine and sulpiride, on rat behavior in the two-way avoidance test. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 92:351–6
Chegini HR, Nasehi M, Zarrindast MR (2014) Differential role of the basolateral amygdala 5-HT3 and 5-HT4 serotonin receptors upon ACPA-induced anxiolytic-like behaviors and emotional memory deficit in mice. Behav Brain Res 261:114–26
Coco ML, Kuhn CM, Ely TD, Kilts CD (1992) Selective activation of mesoamygdaloid dopamine neurons by conditioned stress: attenuation by diazepam. Brain Res 590:39–47
de la Mora MP, Gallegos-Cari A, Arizmendi-Garcia Y, Marcellino D, Fuxe K (2010) Role of dopamine receptor mechanisms in the amygdaloid modulation of fear and anxiety: structural and functional analysis. Prog Neurobiol 90:198–216
de Oliveira AR, Reimer AE, Brandao ML (2006) Dopamine D2 receptor mechanisms in the expression of conditioned fear. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 84:102–11
de Oliveira AR, Reimer AE, de Macedo CE, de Carvalho MC, Silva MA, Brandao ML (2011) Conditioned fear is modulated by D2 receptor pathway connecting the ventral tegmental area and basolateral amygdala. Neurobiol Learn Mem 95:37–45
Fernandez-Ruiz J, Hernandez M, Ramos JA (2010) Cannabinoid-dopamine interaction in the pathophysiology and treatment of CNS disorders. CNS Neurosci Ther 16:e72–91
Freund TF, Katona I, Piomelli D (2003) Role of endogenous cannabinoids in synaptic signaling. Physiol Rev 83:1017–66
Greba Q, Kokkinidis L (2000) Peripheral and intraamygdalar administration of the dopamine D1 receptor antagonist SCH 23390 blocks fear-potentiated startle but not shock reactivity or the shock sensitization of acoustic startle. Behav Neurosci 114:262–72
Greba Q, Gifkins A, Kokkinidis L (2001) Inhibition of amygdaloid dopamine D2 receptors impairs emotional learning measured with fear-potentiated startle. Brain Res 899:218–26
Guarraci FA, Frohardt RJ, Kapp BS (1999a) Amygdaloid D1 dopamine receptor involvement in Pavlovian fear conditioning. Brain Res 827:28–40
Guarraci FA, Frohardt RJ, Young SL, Kapp BS (1999b) A functional role for dopamine transmission in the amygdala during conditioned fear. Ann N Y Acad Sci 877:732–6
Guarraci FA, Frohardt RJ, Falls WA, Kapp BS (2000) The effects of intra-amygdaloid infusions of a D2 dopamine receptor antagonist on Pavlovian fear conditioning. Behav Neurosci 114:647–51
Herman JP, Figueiredo H, Mueller NK, Ulrich-Lai Y, Ostrander MM, Choi DC, Cullinan WE (2003) Central mechanisms of stress integration: hierarchical circuitry controlling hypothalamo-pituitary-adrenocortical responsiveness. Front Neuroendocrinol 24:151–80
Inglis FM, Moghaddam B (1999) Dopaminergic innervation of the amygdala is highly responsive to stress. J Neurochem 72:1088–94
Inoue T, Izumi T, Maki Y, Muraki I, Koyama T (2000) Effect of the dopamine D(1/5) antagonist SCH 23390 on the acquisition of conditioned fear. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 66:573–8
Jacob W, Yassouridis A, Marsicano G, Monory K, Lutz B, Wotjak CT (2009) Endocannabinoids render exploratory behaviour largely independent of the test aversiveness: role of glutamatergic transmission. Genes Brain Behav 8:685–98
Kalivas PW, McFarland K (2003) Brain circuitry and the reinstatement of cocaine-seeking behavior. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 168:44–56
Kamprath K, Plendl W, Marsicano G, Deussing JM, Wurst W, Lutz B, Wotjak CT (2009) Endocannabinoids mediate acute fear adaptation via glutamatergic neurons independently of corticotropin-releasing hormone signaling. Genes Brain Behav 8:203–11
Kebabian JW, Calne DB (1979) Multiple receptors for dopamine. Nature 277:93–6
Lalumiere RT, Nguyen LT, McGaugh JL (2004) Post-training intrabasolateral amygdala infusions of dopamine modulate consolidation of inhibitory avoidance memory: involvement of noradrenergic and cholinergic systems. Eur J Neurosci 20:2804–10
Laviolette SR, Grace AA (2006) The roles of cannabinoid and dopamine receptor systems in neural emotional learning circuits: implications for schizophrenia and addiction. Cell Mol Life Sci 63:1597–613
LeDoux JE (2000) Emotion circuits in the brain. Annu Rev Neurosci 23:155–84
Leonard SK, Anderson CM, Lachowicz JE, Schulz DW, Kilts CD, Mailman RB (2003) Amygdaloid D1 receptors are not linked to stimulation of adenylate cyclase. Synapse 50:320–33
Marsicano G, Lutz B (1999) Expression of the cannabinoid receptor CB1 in distinct neuronal subpopulations in the adult mouse forebrain. Eur J Neurosci 11:4213–25
Martin AB, Fernandez-Espejo E, Ferrer B, Gorriti MA, Bilbao A, Navarro M, Rodriguez de Fonseca F, Moratalla R (2008) Expression and function of CB1 receptor in the rat striatum: localization and effects on D1 and D2 dopamine receptor-mediated motor behaviors. Neuropsychopharmacology 33:1667–79
Meador-Woodruff JH, Mansour A, Healy DJ, Kuehn R, Zhou QY, Bunzow JR, Akil H, Civelli O, Watson SJ Jr (1991) Comparison of the distributions of D1 and D2 dopamine receptor mRNAs in rat brain. Neuropsychopharmacology 5:231–42
Millan MJ (2003) The neurobiology and control of anxious states. Prog Neurobiol 70:83–244
Millan MJ, Newman-Tancredi A, Quentric Y, Cussac D (2001) The “selective” dopamine D1 receptor antagonist, SCH23390, is a potent and high efficacy agonist at cloned human serotonin2C receptors. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 156:58–62
Moreira FA, Wotjak CT (2010) Cannabinoids and anxiety. Curr Top Behav Neurosci 2:429–50
Ouyang M, Young MB, Lestini MM, Schutsky K, Thomas SA (2012) Redundant catecholamine signaling consolidates fear memory via phospholipase C. J Neurosci 32:1932–41
Paxinos G, Franklin KBJ (2001) The mouse brain in stereotaxic coordinates, 2nd edn. Academic.
Pezze MA, Feldon J (2004) Mesolimbic dopaminergic pathways in fear conditioning. Prog Neurobiol 74:301–20
Pickel VM, Colago EE, Mania I, Molosh AI, Rainnie DG (2006) Dopamine D1 receptors co-distribute with N-methyl-D-aspartic acid type-1 subunits and modulate synaptically-evoked N-methyl-D-aspartic acid currents in rat basolateral amygdala. Neuroscience 142:671–90
Piomelli D (2003) The molecular logic of endocannabinoid signalling. Nat Rev Neurosci 4:873–84
Reis FL, Masson S, de Oliveira AR, Brandao ML (2004) Dopaminergic mechanisms in the conditioned and unconditioned fear as assessed by the two-way avoidance and light switch-off tests. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 79:359–65
Repa JC, Muller J, Apergis J, Desrochers TM, Zhou Y, LeDoux JE (2001) Two different lateral amygdala cell populations contribute to the initiation and storage of memory. Nat Neurosci 4:724–31
Rogan MT, Staubli UV, LeDoux JE (1997) Fear conditioning induces associative long-term potentiation in the amygdala. Nature 390:604–7
Rosenkranz JA, Grace AA (2001) Dopamine attenuates prefrontal cortical suppression of sensory inputs to the basolateral amygdala of rats. J Neurosci 21:4090–103
Rosenkranz JA, Grace AA (2003) Affective conditioning in the basolateral amygdala of anesthetized rats is modulated by dopamine and prefrontal cortical inputs. Ann N Y Acad Sci 985:488–91
Sah P, Lopez De Armentia M (2003) Excitatory synaptic transmission in the lateral and central amygdala. Ann N Y Acad Sci 985:67–77
See RE, Fuchs RA, Ledford CC, McLaughlin J (2003) Drug addiction, relapse, and the amygdala. Ann N Y Acad Sci 985:294–307
Shin LM, Liberzon I (2010) The neurocircuitry of fear, stress, and anxiety disorders. Neuropsychopharmacology 35:169–91
Suzuki A, Josselyn SA, Frankland PW, Masushige S, Silva AJ, Kida S (2004) Memory reconsolidation and extinction have distinct temporal and biochemical signatures. J Neurosci 24:4787–95
Tan H, Lauzon NM, Bishop SF, Bechard MA, Laviolette SR (2010) Integrated cannabinoid CB1 receptor transmission within the amygdala-prefrontal cortical pathway modulates neuronal plasticity and emotional memory encoding. Cereb Cortex 20:1486–96
Urban JD, Clarke WP, von Zastrow M, Nichols DE, Kobilka B, Weinstein H, Javitch JA, Roth BL, Christopoulos A, Sexton PM, Miller KJ, Spedding M, Mailman RB (2007) Functional selectivity and classical concepts of quantitative pharmacology. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 320:1–13
Vallone D, Picetti R, Borrelli E (2000) Structure and function of dopamine receptors. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 24:125–32
Woodward RM, Panicker MM, Miledi R (1992) Actions of dopamine and dopaminergic drugs on cloned serotonin receptors expressed in Xenopus oocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 89:4708–12
Yokoyama M, Suzuki E, Sato T, Maruta S, Watanabe S, Miyaoka H (2005) Amygdalic levels of dopamine and serotonin rise upon exposure to conditioned fear stress without elevation of glutamate. Neurosci Lett 379:37–41
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to thank the Iran National Science Foundation (INSF) for providing financial support to this project.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Highlights
• I.p. administration of ACPA impaired both context- and tone-dependent fear memories.
• SKF38393, SCH23390, or quinpirole (intra-BLA) only impaired context-dependent fear memory.
• SKF38393 or quinpirole restored ACPA-induced tone-dependent fear learning deficit.
• Intra-BLA infusion of the drugs did not alter ACPA-induced context-dependent memory deficit.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nasehi, M., Hajian, M., Ebrahimi-Ghiri, M. et al. Role of the basolateral amygdala dopamine receptors in arachidonylcyclopropylamide-induced fear learning deficits. Psychopharmacology 233, 213–224 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-015-4096-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-015-4096-6