Abstract
Rationale
Several studies have demonstrated a correlation between extracellular glutamate concentration in the mesolimbic reward pathway and alcohol craving. Extracellular glutamate concentration is regulated by several glutamate transporters. Glial glutamate transporter 1 (GLT1) is one of them that regulates the majority of extracellular glutamate concentration. In addition, cystine/glutamate antiporter (xCT) is another transporter that regulates extracellular glutamate.
Objectives
We focus in this study to determine the effects of ceftriaxone, β-lactam antibiotic, on glial proteins such as GLT1 isoforms, xCT, glutamate aspartate transporter (GLAST), and several associated signaling pathways as well as ethanol intake in P rats. Additionally, to examine the onset of signaling pathways associated with GLT1 upregulation following ceftriaxone treatment, we tested 2- versus 5-day daily dosing of ceftriaxone.
Results
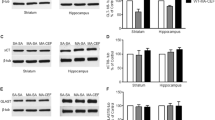
Ceftriaxone treatment (100 mg/kg), 2 and 5 days, resulted in about five fold reduction in ethanol intake by P rats. The reduction in ethanol intake was associated with significantly enhanced expression of GLT1, GLT1a, GLT1b, and xCT in the nucleus accumbens (NAc) and prefrontal cortex (PFC) of 5-day ceftriaxone-treated P rats. Two-day-treated P rats showed marked changes in expression of these glutamate transporters in the PFC but not in the NAc. Importantly, ceftriaxone-treated P rats (2 and 5 days) demonstrated enhanced phosphorylation of Akt and nuclear translocation of nuclear factor kappaB (NFκB) in the NAc and PFC compared to control animals.
Conclusions
These findings demonstrate that ceftriaxone treatment induced upregulation of GLT1, GLT1 isoforms, and xCT in association with activation of the Akt-NFκB signaling pathway.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abulseoud OA, Miller JD, Wu J, Choi DS, Holschneider DP (2012) Ceftriaxone upregulates the glutamate transporter in medial prefrontal cortex and blocks reinstatement of methamphetamine seeking in a condition place preference paradigm. Brain Res 1456:14–21
Alajaji M, Bowers MS, Knackstedt L, Damaj MI (2013) Effects of the beta-lactam antibiotic ceftriaxone on nicotine withdrawal and nicotine-induced reinstatement of preference in mice. Psychopharmacology 228:419–426
Alhaddad H, Das SC, Sari Y (2014a) Effects of ceftriaxone on ethanol intake: a possible role for xCT and GLT-1 isoforms modulation of glutamate levels in P rats. Psychopharmacology.
Alhaddad H, Kim NT, Aal-Aaboda M, Althobaiti YS, Leighton J, Boddu SH, Wei Y, Sari Y (2014b) Effects of MS-153 on chronic ethanol consumption and GLT1 modulation of glutamate levels in male alcohol-preferring rats. Front Behav Neurosci 8:366
Baker DA, McFarland K, Lake RW, Shen H, Tang XC, Toda S, Kalivas PW (2003a) Neuroadaptations in cystine-glutamate exchange underlie cocaine relapse. Nat Neurosci 6:743–749
Baker DA, McFarland K, Lake RW, Shen H, Toda S, Kalivas PW (2003b) N-acetyl cysteine-induced blockade of cocaine-induced reinstatement. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1003:349–351
Baker DA, Xi ZX, Shen H, Swanson CJ, Kalivas PW (2002) The origin and neuronal function of in vivo nonsynaptic glutamate. J Neurosci Off J Soc Neurosci 22:9134–9141
Barker JM, Torregrossa MM, Taylor JR (2012) Low prefrontal PSA-NCAM confers risk for alcoholism-related behavior. Nat Neurosci 15:1356–1358
Bauer J, Pedersen A, Scherbaum N, Bening J, Patschke J, Kugel H, Heindel W, Arolt V, Ohrmann P (2013) Craving in alcohol-dependent patients after detoxification is related to glutamatergic dysfunction in the nucleus accumbens and the anterior cingulate cortex. Neuropsychopharmacol Off Publ Am Coll Neuropsychopharmacol 38:1401–1408
Berger UV, DeSilva TM, Chen W, Rosenberg PA (2005) Cellular and subcellular mRNA localization of glutamate transporter isoforms GLT1a and GLT1b in rat brain by in situ hybridization. J Comp Neurol 492:78–89
Bridges R, Lutgen V, Lobner D, Baker DA (2012) Thinking outside the cleft to understand synaptic activity: contribution of the cystine-glutamate antiporter (system x(c)(-)) to normal and pathological glutamatergic signaling. Pharmacol Rev 64:780–802
Chen T, Zhang D, Dragomir A, Kobayashi K, Akay Y, Akay M (2011) Investigating the influence of PFC transection and nicotine on dynamics of AMPA and NMDA receptors of VTA dopaminergic neurons. J Neuroeng Rehabil 8:58
Chen W, Aoki C, Mahadomrongkul V, Gruber CE, Wang GJ, Blitzblau R, Irwin N, Rosenberg PA (2002) Expression of a variant form of the glutamate transporter GLT1 in neuronal cultures and in neurons and astrocytes in the rat brain. J Neurosci Off J Soc Neurosci 22:2142–2152
Chen W, Mahadomrongkul V, Berger UV, Bassan M, DeSilva T, Tanaka K, Irwin N, Aoki C, Rosenberg PA (2004) The glutamate transporter GLT1a is expressed in excitatory axon terminals of mature hippocampal neurons. J Neurosci Off J Soc Neurosci 24:1136–1148
Costin BN, Wolen AR, Fitting S, Shelton KL, Miles MF (2013) Role of adrenal glucocorticoid signaling in prefrontal cortex gene expression and acute behavioral responses to ethanol. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 37:57–66
Dan HC, Cooper MJ, Cogswell PC, Duncan JA, Ting JP, Baldwin AS (2008) Akt-dependent regulation of NF-{kappa}B is controlled by mTOR and Raptor in association with IKK. Genes Dev 22:1490–1500
Danbolt NC (2001) Glutamate uptake. Prog Neurobiol 65:1–105
Dong Y, Nasif FJ, Tsui JJ, Ju WY, Cooper DC, Hu XT, Malenka RC, White FJ (2005) Cocaine-induced plasticity of intrinsic membrane properties in prefrontal cortex pyramidal neurons: adaptations in potassium currents. J Neurosci Off J Soc Neurosci 25:936–940
Echeverry-Alzate V, Tuda-Arizcun M, Buhler KM, Santos A, Gine E, Olmos P, Gorriti MA, Huertas E, Rodriguez de Fonseca F, Lopez-Moreno JA (2012) Cocaine reverses the naltrexone-induced reduction in operant ethanol self-administration: the effects on immediate-early gene expression in the rat prefrontal cortex. Neuropharmacology 63:927–935
Gendreau S, Voswinkel S, Torres-Salazar D, Lang N, Heidtmann H, Detro-Dassen S, Schmalzing G, Hidalgo P, Fahlke C (2004) A trimeric quaternary structure is conserved in bacterial and human glutamate transporters. J Biol Chem 279:39505–39512
Ghosh M, Yang Y, Rothstein JD, Robinson MB (2011) Nuclear factor-kappaB contributes to neuron-dependent induction of glutamate transporter-1 expression in astrocytes. J Neurosci Off J Soc Neurosci 31:9159–9169
Goldstein RZ, Volkow ND (2011) Dysfunction of the prefrontal cortex in addiction: neuroimaging findings and clinical implications. Nat Rev Neurosci 12:652–669
Gonzalez-Gonzalez IM, Garcia-Tardon N, Gimenez C, Zafra F (2009) Splice variants of the glutamate transporter GLT1 form hetero-oligomers that interact with PSD-95 and NMDA receptors. J Neurochem 110:264–274
Griffin WC, Haun HL, Hazelbaker CL, Ramachandra VS, Becker HC (2013) Increased extracellular glutamate in the nucleus accumbens promotes excessive ethanol drinking in ethanol dependent mice. Neuropsychopharmacol Off Publ Am Coll Neuropsychopharmacol.
Holmseth S, Scott HA, Real K, Lehre KP, Leergaard TB, Bjaalie JG, Danbolt NC (2009) The concentrations and distributions of three C-terminal variants of the GLT1 (EAAT2; slc1a2) glutamate transporter protein in rat brain tissue suggest differential regulation. Neuroscience 162:1055–1071
Ji YF, Xu SM, Zhu J, Wang XX, Shen Y (2011) Insulin increases glutamate transporter GLT1 in cultured astrocytes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 405:691–696
Kalivas PW (1993) Neurotransmitter regulation of dopamine neurons in the ventral tegmental area. Brain Res Brain Res Rev 18:75–113
Kapasova Z, Szumlinski KK (2008) Strain differences in alcohol-induced neurochemical plasticity: a role for accumbens glutamate in alcohol intake. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 32:617–631
Kau KS, Madayag A, Mantsch JR, Grier MD, Abdulhameed O, Baker DA (2008) Blunted cystine-glutamate antiporter function in the nucleus accumbens promotes cocaine-induced drug seeking. Neuroscience 155:530–537
Kerns RT, Ravindranathan A, Hassan S, Cage MP, York T, Sikela JM, Williams RW, Miles MF (2005) Ethanol-responsive brain region expression networks: implications for behavioral responses to acute ethanol in DBA/2J versus C57BL/6J mice. J Neurosci Off J Soc Neurosci 25:2255–2266
Knackstedt LA, LaRowe S, Mardikian P, Malcolm R, Upadhyaya H, Hedden S, Markou A, Kalivas PW (2009) The role of cystine-glutamate exchange in nicotine dependence in rats and humans. Biol Psychiatry 65:841–845
Knackstedt LA, Melendez RI, Kalivas PW (2010) Ceftriaxone restores glutamate homeostasis and prevents relapse to cocaine seeking. Biol Psychiatry 67:81–84
Lee SG, Su ZZ, Emdad L, Gupta P, Sarkar D, Borjabad A, Volsky DJ, Fisher PB (2008) Mechanism of ceftriaxone induction of excitatory amino acid transporter-2 expression and glutamate uptake in primary human astrocytes. J Biol Chem 283:13116–13123
Lewerenz J, Albrecht P, Tien ML, Henke N, Karumbayaram S, Kornblum HI, Wiedau-Pazos M, Schubert D, Maher P, Methner A (2009) Induction of Nrf2 and xCT are involved in the action of the neuroprotective antibiotic ceftriaxone in vitro. J Neurochem 111:332–343
Li LB, Toan SV, Zelenaia O, Watson DJ, Wolfe JH, Rothstein JD, Robinson MB (2006) Regulation of astrocytic glutamate transporter expression by Akt: evidence for a selective transcriptional effect on the GLT-1/EAAT2 subtype. J Neurochem 97:759–771
Li Y, Hu XT, Berney TG, Vartanian AJ, Stine CD, Wolf ME, White FJ (1999) Both glutamate receptor antagonists and prefrontal cortex lesions prevent induction of cocaine sensitization and associated neuroadaptations. Synapse 34:169–180
Madayag A, Lobner D, Kau KS, Mantsch JR, Abdulhameed O, Hearing M, Grier MD, Baker DA (2007) Repeated N-acetylcysteine administration alters plasticity-dependent effects of cocaine. J Neurosci 27:13968–13976
Madrid LV, Mayo MW, Reuther JY, Baldwin AS Jr (2001) Akt stimulates the transactivation potential of the RelA/p65 Subunit of NF-kappa B through utilization of the Ikappa B kinase and activation of the mitogen-activated protein kinase p38. J Biol Chem 276:18934–18940
Maragakis NJ, Dykes-Hoberg M, Rothstein JD (2004) Altered expression of the glutamate transporter EAAT2b in neurological disease. Ann Neurol 55:469–477
McBean GJ (2002) Cerebral cystine uptake: a tale of two transporters. Trends Pharmacol Sci 23:299–302
Melendez RI, Hicks MP, Cagle SS, Kalivas PW (2005) Ethanol exposure decreases glutamate uptake in the nucleus accumbens. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 29:326–333
Melone M, Bellesi M, Conti F (2009) Synaptic localization of GLT-1a in the rat somatic sensory cortex. Glia 57:108–117
Miller BR, Dorner JL, Shou M, Sari Y, Barton SJ, Sengelaub DR, Kennedy RT, Rebec GV (2008) Up-regulation of GLT1 expression increases glutamate uptake and attenuates the Huntington’s disease phenotype in the R6/2 mouse. Neuroscience 153:329–337
Moran MM, Melendez R, Baker D, Kalivas PW, Seamans JK (2003) Cystine/glutamate antiporter regulation of vesicular glutamate release. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1003:445–447
Ozes ON, Mayo LD, Gustin JA, Pfeffer SR, Pfeffer LM, Donner DB (1999) NF-kappaB activation by tumour necrosis factor requires the Akt serine-threonine kinase. Nature 401:82–85
Paxinos G, Watson C (2007) The rat brain in stereotaxic coordinates, 6th edn. Academic Press, New York
Pines G, Danbolt NC, Bjoras M, Zhang Y, Bendahan A, Eide L, Koepsell H, Storm-Mathisen J, Seeberg E, Kanner BI (1992) Cloning and expression of a rat brain L-glutamate transporter. Nature 360:464–467
Qrunfleh AM, Alazizi A, Sari Y (2013) Ceftriaxone, a beta-lactam antibiotic, attenuates relapse-like ethanol-drinking behavior in alcohol-preferring rats. J Psychopharmacol 27:541–549
Rao PS, Sari Y (2014a) Effects of ceftriaxone on chronic ethanol consumption: a potential role for xCT and GLT1 modulation of glutamate levels in male P rats. J Mol Neurosci 54(1):71–77
Rao PSS, Sari Y (2014b) Effectiveness of ceftriaxone treatment in preventing relapse-like drinking behavior following long-term ethanol dependence in P rats. J Addict Res Ther 5:183
Rasmussen B, Unterwald EM, Rawls SM (2011) Glutamate transporter subtype 1 (GLT-1) activator ceftriaxone attenuates amphetamine-induced hyperactivity and behavioral sensitization in rats. Drug Alcohol Depend 118:484–488
Rauen T, Wiessner M, Sullivan R, Lee A, Pow DV (2004) A new GLT1 splice variant: cloning and immunolocalization of GLT1c in the mammalian retina and brain. Neurochem Int 45:1095–1106
Reye P, Sullivan R, Scott H, Pow DV (2002) Distribution of two splice variants of the glutamate transporter GLT-1 in rat brain and pituitary. Glia 38:246–255
Rodd-Henricks ZA, Bell RL, Kuc KA, Murphy JM, McBride WJ, Lumeng L, Li TK (2001) Effects of concurrent access to multiple ethanol concentrations and repeated deprivations on alcohol intake of alcohol-preferring rats. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 25:1140–1150
Rothstein JD, Patel S, Regan MR, Haenggeli C, Huang YH, Bergles DE, Jin L, Dykes Hoberg M, Vidensky S, Chung DS, Toan SV, Bruijn LI, Su ZZ, Gupta P, Fisher PB (2005) Beta-lactam antibiotics offer neuroprotection by increasing glutamate transporter expression. Nature 433:73–77
Sari Y, Bell RL, Zhou FC (2006) Effects of chronic alcohol and repeated deprivations on dopamine D1 and D2 receptor levels in the extended amygdala of inbred alcohol-preferring rats. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 30:46–56
Sari Y, Franklin KM, Alazizi A, Rao PS, Bell RL (2013a) Effects of ceftriaxone on the acquisition and maintenance of ethanol drinking in peri-adolescent and adult female alcohol-preferring (P) rats. Neuroscience 241:229–238
Sari Y, Prieto AL, Barton SJ, Miller BR, Rebec GV (2010) Ceftriaxone-induced up-regulation of cortical and striatal GLT1 in the R6/2 model of Huntington’s disease. J Biomed Sci 17:62
Sari Y, Sakai M, Weedman JM, Rebec GV, Bell RL (2011) Ceftriaxone, a beta-lactam antibiotic, reduces ethanol consumption in alcohol-preferring rats. Alcohol Alcohol 46:239–246
Sari Y, Smith KD, Ali PK, Rebec GV (2009) Upregulation of GLT1 attenuates cue-induced reinstatement of cocaine-seeking behavior in rats. J Neurosci Off J Soc Neurosci 29:9239–9243
Sari Y, Sreemantula SN (2012) Neuroimmunophilin GPI-1046 reduces ethanol consumption in part through activation of GLT1 in alcohol-preferring rats. Neuroscience 227:327–335
Sari Y, Sreemantula SN, Lee MR, Choi DS (2013b) Ceftriaxone treatment affects the levels of GLT1 and ENT1 as well as ethanol intake in alcohol-preferring rats. J Mol Neurosci MN 51:779–787
Schmitt A, Asan E, Lesch KP, Kugler P (2002) A splice variant of glutamate transporter GLT1/EAAT2 expressed in neurons: cloning and localization in rat nervous system. Neuroscience 109:45–61
Seo D, Lacadie CM, Tuit K, Hong KI, Constable RT, Sinha R (2013) Disrupted ventromedial prefrontal function, alcohol craving, and subsequent relapse risk. JAMA Psychiatr 70:727–739
Sondheimer I, Knackstedt LA (2011) Ceftriaxone prevents the induction of cocaine sensitization and produces enduring attenuation of cue- and cocaine-primed reinstatement of cocaine-seeking. Behav Brain Res 225:252–258
Tong ZY, Overton PG, Clark D (1995) Chronic administration of (+)-amphetamine alters the reactivity of midbrain dopaminergic neurons to prefrontal cortex stimulation in the rat. Brain Res 674:63–74
Trantham-Davidson H, LaLumiere RT, Reissner KJ, Kalivas PW, Knackstedt LA (2012) Ceftriaxone normalizes nucleus accumbens synaptic transmission, glutamate transport, and export following cocaine self-administration and extinction training. J Neurosci Off J Soc Neurosci 32:12406–12410
Vetreno RP, Qin L, Crews FT (2013) Increased receptor for advanced glycation end product expression in the human alcoholic prefrontal cortex is linked to adolescent drinking. Neurobiol Dis 59:52–62
Yang Y, Gozen O, Watkins A, Lorenzini I, Lepore A, Gao Y, Vidensky S, Brennan J, Poulsen D, Won Park J, Li Jeon N, Robinson MB, Rothstein JD (2009) Presynaptic regulation of astroglial excitatory neurotransmitter transporter GLT1. Neuron 61:880–894
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by Award Number R01AA019458 (Y.S.) from the National Institutes on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism. The authors thank Dr. Jeffery Rothstein from Johns Hopkins University and Dr. Paul Rosenberg from Harvard Medical School for proving our laboratory with GLT1a and GLT1b, respectively. The authors would like to thank Charisse Montgomery for editing this manuscript.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rao, P.S.S., Saternos, H., Goodwani, S. et al. Effects of ceftriaxone on GLT1 isoforms, xCT and associated signaling pathways in P rats exposed to ethanol. Psychopharmacology 232, 2333–2342 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-015-3868-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-015-3868-3