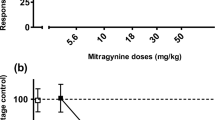
Abstract
Rationale
Mitragynine (MG) is the primary active alkaloid extracted from the leaves of Mitragyna speciosa or kratom and exhibits pharmacological activities mediated by opioid receptors. The plant has been traditionally used for its opium and psychostimulant-like effects to increase work efficiency or as a substitute in the self-treatment of opiate addiction.
Objectives
The present study was performed to investigate the discriminative stimulus effects of MG in rats. The pharmacological mechanism of MG action and its derivative, 7-hydroxymitragynine (7-HMG) with a specific focus on opioid receptor involvement was examined in rats trained to discriminate morphine from vehicle. In order to study the dual actions of MG, the effect of cocaine substitution to the MG discriminative stimulus was also performed in MG-trained rats.
Methods
Male Sprague Dawley rats were trained to discriminate MG from vehicle in a two-lever drug discrimination procedure under a tandem variable-interval (VI 60’) fixed-ratio (FR 10) schedule of food reinforcement.
Results
Rats acquired the MG discrimination (15.0 mg/kg, i.p.) which was similar to the acquisition of morphine discrimination (5.0 mg/kg, i.p.) in another group of rats. MG substituted fully to the morphine discriminative stimulus in a dose-dependent manner, suggesting pharmacological similarities between the two drugs. The administration of 7-HMG derivative in 3.0 mg/kg (i.p.) dose engendered full generalisation to the morphine discriminative stimulus. In addition, the MG stimulus also partially generalised to cocaine (10.0 mg/kg, i.p.) stimulus.
Conclusion
The present study demonstrates that the discriminative stimulus effect of MG possesses both opioid- and psychostimulant-like subjective effects.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmad K, Aziz Z (2012) Mitragyna speciosa use in the northern states of Malaysia: a cross-sectional study. J Ethnopharmacol 141:446–450
Apryani E, Hidayat MT, Moklas MAA, Fakurazi S, Farah Idayu N (2010) Effects of mitragynine from Mitragyna speciosa Korth leaves on working memory. J Ethnopharmacol 129:357–360
Assanangkornchai S, Muekthong A, Sam-Angsri N, Pattanasattayawong U, Takayama H (2007) The use of Mitragyna speciosa ("Krathom"), an addictive plant, in Thailand. Subst Use Misuse 42:2145–2157
Azizi J, Ismail S, Mordi MN, Ramanathan S, Said MI, Mansor SM (2010) In vitro and in vivo effects of three different Mitragyna speciosa korth leaf extracts on phase II drug metabolizing enzymes-glutathione transferases (GSTs). Molecules 15:432–441
Bartoletti M, Colantoni A, De Luca V, Gaiardi M (2010) Single and repeated baclofen treatment attenuates the discriminative stimulus effects of morphine in rats. Pharmacol, Biochem & Behav 97:279–283
Boyer EW, Babu KM, Adkins JE, McCurdy CR, Halpern JH (2008) Self-treatment of opioid withdrawal using kratom (Mitragyna speciosa korth). Addiction 103:1048–1050
Burkill IH (1935) A dictionary of the Economic Products of the Malay Peninsula. II: 1480-1483
Chan KB, Pakiam C, Rahim RA (2005) Psychoactive plant abuse: the identification of mitragynine in ketum and in ketum preparations. Bull Narc 57(1–2):249–256
Fakurazi S, Rahman SA, Hidayat MT, Ithnin H, Moklas MA, Arulselvan P (2013) The combination of mitragynine and morphine prevents the development of morphine tolerance in mice. Molecules (Basel, Switzerland) 18:666–681
Farah Idayu N, TaufikHidayat M, Moklas MAM, Sharida F, NurulRaudzah AR, Shamima AR, Apryani E (2011) Antidepressant-like effect of mitragynine isolated from Mitragyna speciosa Korth in mice model of depression. Phytomedicine 18(5):402–407
Grewal KS (1932a) Observations on the pharmacology of mitragynine. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 46:251–271
Grewal KS (1932b) The effect of mitragynine on man. Br J Med Psychol 12:41–58
Hassan Z, Muzaimi M, Navaratnam V, Yusoff NH, Suhaimi FW, Vadivelu R, Vicknasingam BK, Amato D, von Horsten S, Ismail NI, Jayabalan N, Hazim AI, Mansor SM, Muller CP (2013) From Kratom to mitragynine and its derivatives: physiological and behavioural effects related to use, abuse, and addiction. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 37:138–151
Ishikawa H, Takayama H, Norio A (2002) Dimerization of indole derivatives with hypervalentiodines (III): a new entry for the concise total synthesis of rac- and meso-chimonanthines. Tetrahedron Lett 43:5637–5639
Janchawee B, Keawpradub N, Chittrakarn S, Prasettho S, Wararatananurak P, Sawangjareon K (2007) A high-performance liquid chromatographic method for determination of mitragynine in serum and its application to a pharmacokinetic study in rats. Biomed Chromatogr: BMC 21:176–183
Jansen KL, Prast CJ (1988) Ethnopharmacology of kratom and the Mitragyna alkaloids. J Ethnopharmacol 23:115–119
Macko E, Weisbach JA, Douglas B (1972) Some observations on the pharmacology of mitragynine. Arch Int de Pharmacodynamieet de Therapie 198:145–161
Matsumoto K, Mizowaki M, Suchitra T, Murakami Y, Takayama H, Sakai S, Aimi N, Watanabe H (1996a) Central antinociceptive effects of mitragynine in mice: contribution of descending noradrenergic and serotonergic systems. Eur J Pharmacol 317:75–81
Matsumoto K, Mizowaki M, Suchitra T, Takayama H, Sakai S, Aimi N, Watanabe H (1996b) Antinociceptive action of mitragynine in mice: evidence for the involvement of supraspinal opioid receptors. Life Sci 59:1149–1155
Matsumoto K, Horie S, Ishikawa H, Takayama H, Aimi N, Ponglux D, Watanabe K (2004) Antinociceptive effect of 7-hydroxymitragynine in mice: discovery of an orally active opioid analgesic from the Thai medicinal herb Mitragyna speciosa. Life Sci 74:2143–2155
Matsumoto K, Horie S, Takayama H, Ishikawa H, Aimi N, Ponglux D, Murayama T, Watanabe K (2005a) Antinociception, tolerance and withdrawal symptoms induced by 7-hydroxymitragynine, an alkaloid from the Thai medicinal herb Mitragyna speciosa. Life Sci 78:2–7
Matsumoto K, Yamamoto LT, Watanabe K, Yano S, Shan J, Pang PK, Ponglux D, Takayama H, Horie S (2005b) Inhibitory effect of mitragynine, an analgesic alkaloid from Thai herbal medicine, on neurogenic contraction of the vas deferens. Life Sci 78:187–194
Matsumoto K, Hatori Y, Murayama T, Tashima K, Wongseripipatana S, Misawa K, Kitajima M, Takayama H, Horie S (2006) Involvement of mu-opioid receptors in antinociception and inhibition of gastrointestinal transit induced by 7-hydroxymitragynine, isolated from Thai herbal medicine Mitragyna speciosa. Eur J Pharmacol 549:63–70
Negus SS, Mello NK (1999) Effects of kappa opioid agonists on the discriminative stimulus effects of cocaine in rhesus monkeys. Exp Clin Psychopharm 7:307–317
Norakanphadung P (1966) Pramuan Khuamru Ruang Yaseptit Hai Thot. Thanyarak Hospital, Bangkok
Overton DA (1988) Similarities and differences between behavioural control by drug-produced stimuli and by sensory stimuli. Psychopharmacology 4:176–198
Ponglux D, Wongseripipatana S, Takayama H, Kikuchi M, Kurihara M, Kitajima M, Aimi N, Sakai S (1994) A New Indole Alkaloid, 7 alpha-Hydroxy-7H-mitragynine, from Mitragyna speciosa in Thailand. Planta Med 60:580–581
Preston KL, Bigelow GE (1991) Subjective and discriminative effects of drugs. Behav Pharmacol 2:293–313
Reanmongkol W, Keaupradub N, Sawangjaroen K (2007) Effects of the extracts from Mitragyna speciosa korth. Leaves on analgesic and behavioral activities in experimental animals. J Sci Technol 29:39–48
Sabetghadam A, Ramanathan S, Mansor SM (2010) The evaluation of antinociceptive activity of alkaloid, methanolic, and aqueous extracts of Malaysian Mitragyna speciosa Korth leaves in rats. Pharmacogn Res 2:181–185
Sabetghadam A, Ramanathan S, Sasidharan S, Mansor SM (2013) Subchronic exposure to mitragynine, the principal alkaloid of Mitragyna speciosa, in rats. J Ethnopharmacol 146:815–823
Schmidt KT, Weinshenker D (2014) Adrenaline rush: the role of adrenergic receptors in stimulant-induced behaviors. Mol Pharmacol 85:640–650
Schuster CR, Fischman MW, Johanson CE (1981) Internal stimulus control and subjective effects of drugs. NIDA Res Monogr 37:116–129
Sevak RJ, Stoops WW, Hays LR, Rush CR (2009) Discriminative stimulus and subject-rated effects of methamphetamine, d-amphetamine, methylphenidate, and triazolam in methamphetamine-trained humans. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 328:1007–1018
Shamima AR, Fakurazi S, Hidayat MT, Hairuszah I, Moklas MA, Arulselvan P (2012) Antinociceptive action of isolated mitragynine from Mitragyna speciosa through activation of opioid receptor system. Int J Mol Sci 13:11427–11442
Shellard EJ (1974) The alkaloids of Mitragyna with special reference to those of Mitragyna speciosa, Korth. Bull Narc 26:41–55
Singh D, Muller CP, Vicknasingam BK (2014) Kratom (Mitragyna speciosa) dependence, withdrawal symptoms and craving in regular users. Drug Alcohol Depend 139:132–137
Stolerman IP, Garcha HS (1989) Temporal factors in drug discrimination: experiments with nicotine. J Psychopharm (Oxford, England) 3:88–97
Stolerman IP, Naylor C, Elmer GI, Goldberg SR (1999) Discrimination and self-administration of nicotine by inbred strains of mice. Psychopharmacology 141:297–306
Stolt AC, Schroder H, Neurath H, Grecksch G, Hollt V, Meyer MR, Maurer HH, Ziebolz N, Havemann-Reinecke U, Becker A (2014) Behavioral and neurochemical characterization of kratom (Mitragyna speciosa) extract. Psychopharmacology 231:13–25
Su RB, Ren YH, Liu Y, Ding T, Lu XQ, Wu N, Liu ZM, Li J (2008) Agmatine inhibits morphine-induced drug discrimination in rats. Eur J Pharmacol 593:62–67
Suwanlert S (1975) A study of kratom eaters in Thailand. Bull Narc 27:21–27
Takayama H, Ishikawa H, Kurihara M, Kitajima M, Aimi N, Ponglux D, Koyama F, Matsumoto K, Moriyama T, Yamamoto LT, Watanabe K, Murayama T, Horie S (2002) Studies on the synthesis and opioid agonistic activities of mitragynine-related indole alkaloids: discovery of opioid agonists structurally different from other opioid ligands. J Med Chem 45:1949–1956
Takayama H (2004) Chemistry and pharmacology of analgesic indole alkaloids from the rubiaceous plant, Mitragyna speciosa. Chem Pharm Bull 52:916–928
Taufik Hidayat M, Apryani E, Nabishah BM, Moklas MAA, Sharida F, Farhan MA (2010) Determination of mitragynine bound opioid receptors. Adv in Med Dent Sci 3:65–70
Thongpradichote S, Matsumoto K, Tohda M, Takayama H, Aimi N, Sakai S, Watanabe H (1998) Identification of opioid receptor subtypes in antinociceptive actions of supraspinally-administered mitragynine in mice. Life Sci 62:1371–1378
Tsuchiya S, Miyashita S, Yamamoto M, Horie S, Sakai S, Aimi N, Takayama H, Watanabe K (2002) Effect of mitragynine, derived from Thai folk medicine, on gastric acid secretion through opioid receptor in anesthetized rats. Eur J Pharmacol 443:185–188
Utar Z, Majid MI, Adenan MI, Jamil MF, Lan TM (2011) Mitragynine inhibits the COX-2 mRNA expression and prostaglandin E (2) production induced by lipopolysaccharide in RAW264.7 macrophage cells. J Ethnopharmacol 136:75–82
Vicknasingam B, Narayanan S, Beng GT, Mansor SM (2010) The informal use of ketum (Mitragyna speciosa) for opioid withdrawal in the northern states of peninsular Malaysia and implications for drug substitution therapy. Int J Drug Policy 21:283–288
Ward J, Rosenbaum C, Hernon C, McCurdy CR, Boyer EW (2011) Herbal medicines for the management of opioid addiction: safe and effective alternatives to conventional pharmacotherapy? CNS Drugs 25:999–1007
Watanabe K, Yano S, Horie S, Yamamoto LT (1997) Inhibitory effect of mitragynine, an alkaloid with analgesic effect from Thai medicinal plant Mitragyna speciosa, on electrically stimulated contraction of isolated guinea-pig ileum through the opioid receptor. Life Sci 60:933–942
Wing VC, Shoaib M (2012) Translating the smoking cessation properties of the antidepressant nortriptyline using reinforcing, discriminative and aversive stimulus effects of nicotine in rats. Psychopharmacology 219:847–857
Wray L (1907) “Biak”: an opium substitute. J Fed Malay States Mus 2:53–54
Yamamoto LT, Horie S, Takayama H, Aimi N, Sakai S, Yano S, Shan J, Pang PK, Ponglux D, Watanabe K (1999) Opioid receptor agonistic characteristics of mitragynine pseudoindoxyl in comparison with mitragynine derived from Thai medicinal plant Mitragyna speciosa. Gen Pharmacol 33:73–78
Acknowledgments
This research received financial support from Higher Education Centre of Excellence (HiCoE) special funding (304/CDADAH/650527/K134), USM Research University Grant (RUT) [1001/CDADAH/855005], International Research Collaboration Fund (1002/CDADAH/910410) and MyBrain15 Scholarship from Ministry of Higher Education.
Conflict of interest
None
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Harun, N., Hassan, Z., Navaratnam, V. et al. Discriminative stimulus properties of mitragynine (kratom) in rats. Psychopharmacology 232, 2227–2238 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-015-3866-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-015-3866-5