Abstract
Rationale
Benzodiazepines, such as diazepam, are anxiolytic-sedative drugs, used for the treatment of several different disorders. The pharmacological mechanism of action of benzodiazepines is well understood; however, it remains unclear which neural networks and systems are involved in translating these neurochemical actions into their therapeutic effects.
Objectives
The objective of this study was to investigate the effects of 7-day diazepam administration compared to placebo on resting-state functional connectivity in healthy adults independent of any task.
Methods
Thirty-four healthy participants were randomly assigned to receive either diazepam (N = 17) or placebo (15 mg daily for 7 days) and underwent resting-state functional magnetic resonance acquisition. Model-free data analysis was performed using independent component analysis and dual regression.
Results
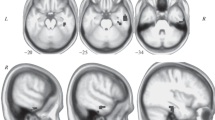
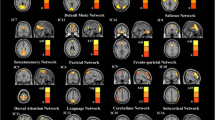
Consistent with previous research, 11 resting-state networks were identified. Increased connectivity in response to diazepam administration was found in the medial visual network and middle/inferior temporal network. Diazepam did not cause any decreases in functional connectivity.
Conclusions
Diazepam administration increases functional connectivity in areas of emotional processing independent of any task. Diazepam also enhanced functional connectivity in the medial visual system, which is a brain region rich in GABAA receptors, and shows high binding of GABAergic drugs. These increases in functional connectivity are characteristic of CNS depressants.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abadie P, Baron JC, Bisserbe JC, Boulenger JP, Rioux P, Travere JM, Barre L, Petit-Taboue MC, Zarifian E (1992) Central benzodiazepine receptors in human brain: estimation of regional Bmax and KD values with positron emission tomography. Eur J Pharmacol 213:107–115
Anteraper SA, Triantafyllou C, Sawyer AT, Hofmann SG, Gabrieli JD, Whitfield-Gabrieli S (2014) Hyper-connectivity of subcortical resting-state networks in social anxiety disorder. Brain connectivity.
Beckmann CF, Smith SM (2004) Probabilistic independent component analysis for functional magnetic resonance imaging. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 23:137–152
Beckmann C, Noble J, Smith S (2001) Investigating the intrinsic dimensionality of FMRI data for ICA. Seventh Int Conf on Functional Mapping of the Human Brain
Beckmann CF, DeLuca M, Devlin JT, Smith SM (2005) Investigations into resting-state connectivity using independent component analysis. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci 360:1001–1013
Beckmann CF, Mackay CE, Filippini N, Smith SM (2009) Group comparison of resting-state FMRI data using multi-subject ICA and dual regression 15th Annual Meeting of the Organization for Human Brain Mapping (OHBM), San Francisco, CA
Britz J, Van De Ville D, Michel CM (2010) BOLD correlates of EEG topography reveal rapid resting-state network dynamics. Neuroimage 52:1162–1170
Calhoun VD, Altschul D, McGinty V, Shih R, Scott D, Sears E, Pearlson GD (2004) Alcohol intoxication effects on visual perception: an fMRI study. Hum Brain Mapp 21:15–26
Chebib M, Johnston GA (1999) The ‘ABC’ of GABA receptors: a brief review. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol 26:937–940
Cole DM, Smith SM, Beckmann CF (2010) Advances and pitfalls in the analysis and interpretation of resting-state FMRI data. Front Syst Neurosci 4:8
Damoiseaux JS, Rombouts SA, Barkhof F, Scheltens P, Stam CJ, Smith SM, Beckmann CF (2006) Consistent resting-state networks across healthy subjects. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 103:13848–13853
Davis M, Whalen PJ (2001) The amygdala: vigilance and emotion. Mol Psychiatry 6:13–34
De Luca M, Beckmann CF, De Stefano N, Matthews PM, Smith SM (2006) fMRI resting state networks define distinct modes of long-distance interactions in the human brain. Neuroimage 29:1359–1367
Del-Ben CM, Ferreira CA, Sanchez TA, Alves-Neto WC, Guapo VG, de Araujo DB, Graeff FG (2012) Effects of diazepam on BOLD activation during the processing of aversive faces. J Psychopharmacol (Oxford, England) 26:443–451
Engel AK, Fries P, Singer W (2001) Dynamic predictions: oscillations and synchrony in top-down processing. Nat Rev Neurosci 2:704–716
Esposito F, Pignataro G, Di Renzo G, Spinali A, Paccone A, Tedeschi G, Annunziato L (2010) Alcohol increases spontaneous BOLD signal fluctuations in the visual network. Neuroimage 53:534–543
Eysenck HJ, Eysenck SBG (1975) Manual of the Eysenck Personality Questionnaire. Hodder and Stoughton, London
Feige B, Voderholzer U, Riemann D, Hohagen F, Berger M (1999) Independent sleep EEG slow-wave and spindle band dynamics associated with 4 weeks of continuous application of short-half-life hypnotics in healthy subjects. Clin Neurophysiol : Off J Int Fed Clin Neurophysiol 110:1965–1974
Filippini N, MacIntosh BJ, Hough MG, Goodwin GM, Frisoni GB, Smith SM, Matthews PM, Beckmann CF, Mackay CE (2009) Distinct patterns of brain activity in young carriers of the APOE-epsilon4 allele. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 106:7209–7214
First MB, Spitzer RL, Gibbon M, Williams JBW (1997) User’s guide for the structured clinical interview for DSM-IV axis I disorders SCID-I: clinician version. American Psychiatric Press
Fisahn A, Pike FG, Buhl EH, Paulsen O (1998) Cholinergic induction of network oscillations at 40 Hz in the hippocampus in vitro. Nature 394:186–189
Flodin P, Gospic K, Petrovic P, Fransson P (2012) Effects of L-dopa and oxazepam on resting-state functional magnetic resonance imaging connectivity: a randomized, cross-sectional placebo study. Brain Connect 2:246–253
Fornito A, Bullmore ET (2010) What can spontaneous fluctuations of the blood oxygenation-level-dependent signal tell us about psychiatric disorders? Curr Opin Psychiatry 23:239–249
Goldman RI, Stern JM, Engel J Jr, Cohen MS (2002) Simultaneous EEG and fMRI of the alpha rhythm. Neuroreport 13:2487–2492
Greenblatt DJ, Allen MD, Harmatz JS, Shader RI (1980) Diazepam disposition determinants. Clin Pharmacol Ther 27:301–312
Greenblatt DJ, Shader RI, Divoll M, Harmatz JS (1981) Benzodiazepines: a summary of pharmacokinetic properties. Br J Clin Pharmacol 11(Suppl 1):11S–16S
Greicius MD, Kiviniemi V, Tervonen O, Vainionpaa V, Alahuhta S, Reiss AL, Menon V (2008) Persistent default-mode network connectivity during light sedation. Hum Brain Mapp 29:839–847
Hahn A, Stein P, Windischberger C, Weissenbacher A, Spindelegger C, Moser E, Kasper S, Lanzenberger R (2011) Reduced resting-state functional connectivity between amygdala and orbitofrontal cortex in social anxiety disorder. Neuroimage 56:881–889
Hall SD, Barnes GR, Furlong PL, Seri S, Hillebrand A (2010) Neuronal network pharmacodynamics of GABAergic modulation in the human cortex determined using pharmaco-magnetoencephalography. Hum Brain Mapp 31:581–594
Honey G, Bullmore E (2004) Human pharmacological MRI. Trends Pharmacol Sci 25:366–374
Jenkinson M, Beckmann CF, Behrens TE, Woolrich MW, Smith SM (2012) FSL. Neuroimage 62:782–790
Jensen O, Goel P, Kopell N, Pohja M, Hari R, Ermentrout B (2005) On the human sensorimotor-cortex beta rhythm: sources and modeling. Neuroimage 26:347–355
Kiviniemi VJ, Haanpaa H, Kantola JH, Jauhiainen J, Vainionpaa V, Alahuhta S, Tervonen O (2005) Midazolam sedation increases fluctuation and synchrony of the resting brain BOLD signal. Magn Reson Imaging 23:531–537
Laird AR, Fox PM, Eickhoff SB, Turner JA, Ray KL, McKay DR, Glahn DC, Beckmann CF, Smith SM, Fox PT (2011) Behavioral interpretations of intrinsic connectivity networks. J Cogn Neurosci 23:4022–4037
Levin JM, Ross MH, Mendelson JH, Kaufman MJ, Lange N, Maas LC, Mello NK, Cohen BM, Renshaw PF (1998) Reduction in BOLD fMRI response to primary visual stimulation following alcohol ingestion. Psychiatry Res 82:135–146
Li SJ, Biswal B, Li Z, Risinger R, Rainey C, Cho JK, Salmeron BJ, Stein EA (2000) Cocaine administration decreases functional connectivity in human primary visual and motor cortex as detected by functional MRI. Magn Reson Med : Off J Soc Magn Reson Med / Soc Magn Reson Med 43:45–51
Licata SC, Lowen SB, Trksak GH, Maclean RR, Lukas SE (2011) Zolpidem reduces the blood oxygen level-dependent signal during visual system stimulation. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 35:1645–1652
Licata SC, Nickerson LD, Lowen SB, Trksak GH, Maclean RR, Lukas SE (2013) The hypnotic zolpidem increases the synchrony of BOLD signal fluctuations in widespread brain networks during a resting paradigm. Neuroimage 70:211–222
Link CG, Leigh TJ, Fell GL (1991) Effects of granisetron and lorazepam, alone and in combination, on the EEG of human volunteers. Br J Clin Pharmacol 31:93–97
Mackey AP, Miller Singley AT, Bunge SA (2013) Intensive reasoning training alters patterns of brain connectivity at rest. J Neurosci : Off J Soc Neurosci 33:4796–4803
Mandelli M, Tognoni G, Garattini S (1978) Clinical pharmacokinetics of diazepam. Clin Pharmacokinet 3:72–91
Mantini D, Perrucci MG, Del Gratta C, Romani GL, Corbetta M (2007) Electrophysiological signatures of resting state networks in the human brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 104:13170–13175
Margulies DS, Bottger J, Long X, Lv Y, Kelly C, Schafer A, Goldhahn D, Abbushi A, Milham MP, Lohmann G, Villringer A (2010) Resting developments: a review of fMRI post-processing methodologies for spontaneous brain activity. MAGMA (New York, NY) 23:289–307
Mohler H (2012) The GABA system in anxiety and depression and its therapeutic potential. Neuropharmacology 62:42–53
Paulus MP, Feinstein JS, Castillo G, Simmons AN, Stein MB (2005) Dose-dependent decrease of activation in bilateral amygdala and insula by lorazepam during emotion processing. Arch Gen Psychiatry 62:282–288
Rack-Gomer AL, Liau J, Liu TT (2009) Caffeine reduces resting-state BOLD functional connectivity in the motor cortex. Neuroimage 46:56–63
Ramaekers JG, Evers EA, Theunissen EL, Kuypers KP, Goulas A, Stiers P (2013) Methylphenidate reduces functional connectivity of nucleus accumbens in brain reward circuit. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 229:219–226
Riss J, Cloyd J, Gates J, Collins S (2008) Benzodiazepines in epilepsy: pharmacology and pharmacokinetics. Acta Neurol Scand 118:69–86
Smith SM, Nichols TE (2009) Threshold-free cluster enhancement: addressing problems of smoothing, threshold dependence and localisation in cluster inference. Neuroimage 44:83–98
Smith SM, Fox PT, Miller KL, Glahn DC, Fox PM, Mackay CE, Filippini N, Watkins KE, Toro R, Laird AR, Beckmann CF (2009) Correspondence of the brain’s functional architecture during activation and rest. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 106:13040–13045
Spielberger CD, Gorssuch RL, Lushene PR, Vagg P, Jacobs G (1983) Manual for the state-trait anxiety inventory. Consulting Psychologists Press, Inc.
Tiihonen J, Kuikka J, Rasanen P, Lepola U, Koponen H, Liuska A, Lehmusvaara A, Vainio P, Kononen M, Bergstrom K, Yu M, Kinnunen I, Akerman K, Karhu J (1997) Cerebral benzodiazepine receptor binding and distribution in generalized anxiety disorder: a fractal analysis. Mol Psychiatry 2:463–471
van Lier H, Drinkenburg WH, van Eeten YJ, Coenen AM (2004) Effects of diazepam and zolpidem on EEG beta frequencies are behavior-specific in rats. Neuropharmacology 47:163–174
Vida I, Bartos M, Jonas P (2006) Shunting inhibition improves robustness of gamma oscillations in hippocampal interneuron networks by homogenizing firing rates. Neuron 49:107–117
Wang GJ, Volkow ND, Overall J, Hitzemann RJ, Pappas N, Pascani K, Fowler JS (1996) Reproducibility of regional brain metabolic responses to lorazepam. J Nucl Med: Off Publ Soc Nucl Med 37:1609–1613
Wong CW, Olafsson V, Tal O, Liu TT (2012) Anti-correlated networks, global signal regression, and the effects of caffeine in resting-state functional MRI. Neuroimage 63:356–364
Zilles K, Amunts K (2009) Receptor mapping: architecture of the human cerebral cortex. Curr Opin Neurol 22:331–339
Conflicts of interest
The study has been funded by the Medical Research Council.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
C Patrick Pflanz and Abbie Pringle contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pflanz, C.P., Pringle, A., Filippini, N. et al. Effects of seven-day diazepam administration on resting-state functional connectivity in healthy volunteers: a randomized, double-blind study. Psychopharmacology 232, 2139–2147 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-014-3844-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-014-3844-3