Abstract
Rationale
The primary antipsychotic-induced creatine kinase elevation (i.e., not due to neuroleptic malignant syndrome, extrapyramidal symptoms, etc.) is a poorly studied condition.
Objectives
The aims of the present study were to provide an overview of published cases with antipsychotic-induced creatine kinase elevation and give recommendations for the clinical practice.
Methods
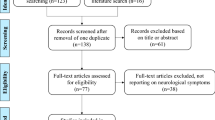
PubMed and EMBASE were searched for eligible trials, case series, and case reports. We set a threshold at ten times the upper normal limit of the creatine kinase value in order to define an elevation as significant.
Results
The prevalence of significant creatine kinase elevation ranged between 2 and 7 %. We found a total of 42 eligible cases. Men were overrepresented in our sample (81 %). Patients with myoglobinuria were more likely to be symptomatic (Fisher’s exact test, p = 0.006), whereas neither myoglobinuria (Mann-Whitney test, p > 0.10) nor symptoms (Mann-Whitney test, p = 0.64) were related to the magnitude of the creatine kinase (CK) elevation. In the majority of the cases, the antipsychotic medication was discontinued (86 %). Forced diuresis was given in 36 % of the patients. Eighty-three percent of the patients had no further complications. Only one case was found with a de novo acute renal failure.
Conclusions
The discontinuation of the antipsychotic medication was a sufficient measure for the CK elevation to subside in the majority of the cases. Cases with myoglobinuria should eventually be treated more aggressively. Further recommendations for the clinical practice are presented.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adityanjee (1991) The myth of elevated serum creatine phosphokinase level and neuroleptic malignant syndrome. Br J Psychiatry 158:706–707
Agarkar S (2011) Elevated creatine kinase levels with second-generation antipsychotics. J Neuropsychiatry Clin Neurosci 23(3):E49–E50. doi:10.1176/appi.neuropsych.23.3.E49
American Psychiatric Association (1994) Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders: DSM-IV, 4th edn. American Psychiatric Association, Washington DC
Apikoglu Rabus S, Izzettin F, Rabus M, Bilici M (2006) Severe creatine kinase increase during quetiapine and mirtazapine treatment. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 185(2):263–264
Asenjo Lobos C, Komossa K, Rummel-Kluge C, Hunger H, Schmid F, Schwarz S, Leucht S (2010) Clozapine versus other atypical antipsychotics for schizophrenia. Cochrane Database Syst Rev (11):CD006633. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD006633.pub2
Asmal L, Flegar SJ, Wang J, Rummel-Kluge C, Komossa K, Leucht S (2013) Quetiapine versus other atypical antipsychotics for schizophrenia. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 11:CD006625. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD006625.pub3
Baumgart U, Schmid R, Spiessl H (2005) Olanzapine-induced acute rhabdomyolysis—a case report. Pharmacopsychiatry 38(1):36–37
Boot E, de Haan L (2000) Massive increase in serum creatine kinase during olanzapine and quetiapine treatment, not during treatment with clozapine. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 150(3):347–348
Cavanaugh JJ, Finlayson RE (1984) Rhabdomyolysis due to acute dystonic reaction to antipsychotic drugs. J Clin Psychiatry 45(8):356–357
Chatzizisis YS, Misirli G, Hatzitolios AI, Giannoglou GD (2008) The syndrome of rhabdomyolysis: complications and treatment. Eur J Intern Med 19:568–574
Conley RR, Meltzer HY (2000) Adverse events related to olanzapine. J Clin Psychiatry 61(Suppl 8):26–29
Correll CU (2007) Acute and long-term adverse effects of antipsychotics. CNS Spectr 12(12 Suppl 21):10–14
De Hert M, Kalnicka D, van Winkel R, Wampers M, Hanssens L, van Eyck D, Scheen A, Peuschkens J (2006) Treatment with rosuvastatin for severe dyslipidemia in patients with schizophrenia and schizoaffective disorder. J Clin Psychiatry 67:1889–1896
Deravajan S, Dursun SM (2000) Antipsychotic drugs, serum creatine kinase (CPK) and possible mechanisms. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 152:122
Flanagan RJ (2008) Side effects of clozapine and some other psychoactive drugs. Curr Drug Saf 3(2):115–122
Giannoglou GD, Chatzizisis YS, Misirli G (2007) The syndrome of rhabdomyolysis: pathophysiology and diagnosis. Eur J Int Med 18:90–100
Giner V, Muñoz R, Redón J (2002) Risperidone severe cerivastatin-induced rhabdomyolysis. J Intern Med 251(2):177–178
Harper CR, Jacobson TA (2007) The broad spectrum of statin myopathy: from myalgia to rhabdomyolysis. Curr Opin Lipidol 18:401–408
Himmerich H, Ehrlinger M, Hackenberg M, Löhr B, Nickel T (2006) Possible case of quetiapine-induced rhabdomyolysis in a patient with depression treated with fluoxetine. J Clin Psychopharmacol 26(6):676–677
Hoshi S, Itoh A, Kato S, Suzuki K, Kawamura S, Orikasa S (1999) Severe rhabdomyolysis as a complication of high-dose chemotherapy in a patient with advanced testicular cancer. Int J Urol 6(1):56–58
Karre PR, Gujral J, Rodriguez E (2009) Rhabdomyolysis with erratic serum creatinin phosphokinase levels: intramuscular injection of haloperidol decanoate. BMJ Case Rep. doi:10.1136/bcr.06.2009.1931
Keshavan MS, Stecker J, Kambhampati RK (1994) Creatine kinase elevations with clozapine. Br J Psychiatry 164(1):118–120
Kirson JI, McQuistion HL, Pierce DW (1995) Severe elevations in serum creatine kinase associated with clozapine. J Clin Psychopharmacol 15(4):287–288
Klein JP, Fiedler U, Appel H, Quante A, Jockers-Scherübl MC (2006) Massive creatine kinase elevations with quetiapine: report of two cases. Pharmacopsychiatry 39(1):39–40
Komossa K, Rummel-Kluge C, Hunger H, Schmid F, Schwarz S, Duggan L, Kissling W, Leucht S (2010) Olanzapine versus other atypical antipsychotics for schizophrenia. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD006654.pub2
Komossa K, Rummel-Kluge C, Schwarz S, Schmid F, Hunger H, Kissling W, Leucht S (2011) Risperidone versus other atypical antipsychotics for schizophrenia. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD006626.pub2
Koren W, Koren E, Nacasch N, Ehrenfeld M, Gur H (1998) Rhabdomyolysis associated with clozapine treatment in a patient with decreased calcium dependent potassium permeability of cell membranes. Clin Neuropharmacol 21(4):262–264
Lazarus AL, Toglia JU (1985) Fatal myoglobinuric renal failure in a patient with tardive dyskinesia. Neurology 35(7):1055–1057
Marcus EL, Vass A, Zislin J (1999) Marked elevation of serum creatine kinase associated with olanzapine therapy. Ann Pharmacother 33(6):697–700
Marinella MA (1997) Rhabdomyolysis associated with haloperidol without evidence of NMS. Ann Pharmacother 31(7–8):927–928
Marsh SJ, Dolson GM (1995) Rhabdomyolysis and acute renal failure during high-dose haloperidol therapy. Ren Fail 17(4):475–478
Martí-Bonmatí E, San Valero-Carcelén E, Ortega-García MP, Rubini-Puig R (2003) Olanzapine elevation of serum creatine kinase. J Clin Psychiatry 64(4):483–484
Martin PD, Warwick MJ, Dane AL, Hill SJ, Giles PB, Phillips PJ, Lenz E (2003) Metabolism, excretion, and pharmacokinetics of rosuvastatin in healthy adult male volunteers. Clin Ther 25(11):2822–2835
Marzetti E, Bocchino L, Teramo S, Scudieri G, Aulisa AG (2012) Rhabdomyolysis in a patient on aripiprazole with traumatic hip prosthesis luxation. J Neuropsychiatry Clin Neurosci 24(4):E40–E41. doi:10.1176/appi.neuropsych.11110328
McMahon GM, Zeng X, Walkar SS (2013) A risk prediction score for kidney failure or mortality in rhabdomyolysis. JAMA Intern Med. doi:10.1001/jamainternmed.2013.9774
Meltzer HY (1968) Creatine kinase and aldolase in serum: abnormality common to acute psychoses. Science 159:1368–1370
Meltzer HY (1969) Muscle enzyme release in the acute psychoses. Arch Gen Psychiatry 21:102–112
Meltzer HY (2000) Massive serum creatine kinase increases with atypical antipsychotic drugs: what is the mechanism and the message? Psychopharmacology (Berl) 150(3):349–350
Meltzer HY, Cola PA, Parsa M (1996) Marked elevations of serum creatine kinase activity associated with antipsychotic drug treatment. Neuropsychopharmacology 15(4):395–405
Mohr WK, Petti TA, Mohr BD (2003) Adverse effects associated with physical restraint. Can J Psychiatry 48(5):330–337
Naranjo CA, Busto U, Sellers EM, Sandor P, Ruiz I, Roberts EA, Janecek E, Domecq C, Greenblatt DJ (1981) A method for estimating the probability of adverse drug reaction. Clin Pharm Ther 30(2):239–245
Oulis P, Koulouris GC, Konstantakopoulos G, Masdrakis VG (2007) Marked elevation of creatine kinase with sertindole: a case report. Pharmacopsychiatry 40(6):295–296
Pearlman C, Wheadon D, Epstein S (1988) Creatine kinase elevation after neuroleptic treatment. Am J Psychiatry 145(8):1018–1019
Perlov E, Tebartz van Elst L, Czygan M, Bubl E, Ebert D (2005) Serum creatine kinase elevation as a possible complication of therapy with olanzapine. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol 372(2):168–169
Punukollu B, Rutherford H (2008) Serum creatine kinase elevation associated with olanzapine treatment. BMJ Case Rep. doi:10.1136/bcr.06.2008.0040
Reznik I, Volchek L, Mester R, Kotler M, Sarova-Pinhas I, Spivak B, Weizman A (2000) Myotoxicity and neurotoxicity during clozapine treatment. Clin Neuropharmacol 23(5):276–280
Robert F, Koenig M, Robert A, Boyer S, Cathébras P, Camdessanché JP (2010) Acute camptocormia induced by olanzapine: a case report. J Med Case Rep 25(4):192. doi:10.1186/1752-1947-4-192
Scelsa SN, Simpson DM, McQuistion HL, Fineman A, Ault K, Reichler B (1996) Clozapine induced myotoxicity in patients with chronic psychotic disorders. Neurology 47:1518–1523
Scharman EJ, Troutman WG (2013) Prevention of kidney injury following rhabdomyolysis: a systematic review. Ann Pharmacother 47(1):90–105. doi:10.1345/aph.1R215
Schennach-Wolff R, Stübner S, Riedel M, Müller N (2010) Extensive elevation of creatine kinase with generic clozapine, but not with Leponex. Psychiatry Res. 30;176(1):93. doi:10.1016/j.psychres.2009.03.014
Shuster J (2000) Olanzapine and rhabdomyolysis. Nursing 30(9):87
Terao T, Matsuda S, Kojima H, Okuno K, Hori H, Kaku A, Ueda N, Etoh A (1999) Incidence and risk factors of benign creatine phosphokinase elevations in chronic psychiatric patients. Neuropsychobiology 39(4):173–180
Thase ME, Shostak M (1984) Rhabdomyolysis complicating rapid intramuscular neuroleptization. J Clin Psychopharmacol 4(1):46–48
Thompson PD, Zmuda JM, Domalik LJ, Zimet RJ, Staggers J, Guyton JR (1997) Lovastatin increases exercise-induced skeletal muscle injury. Metabolism 46(10):1206–1210
Tseng KC, Hwang TJ (2009) Rhabdomyolysis following dose increase of clozapine and combination therapy with lithium. J Clin Psychopharmacol 29(4):398–399. doi:10.1097/JCP.0b013e3181accfc3
Ursini F, Succurro E, Grembiale A, Arturi F (2010) Acute rhabdomyolysis during treatment with amisulpride and metformin. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 66(3):321–322. doi:10.1007/s00228-009-0773-x
Velasco-Montes J, Oriñuela-González I, Sanjuán-López AZ (2012) Rhabdomyolysis secondary to quetiapine. Actas Esp Psiquiatr 40(2):97–99
Webber MA, Mahmud W, Lightfoot JD, Shekhar A (2004) Rhabdomyolysis and compartment syndrome with coadministration of risperidone and simvastatin. J Psychopharmacol 18(3):432–434
Wirshing DA (2001) Adverse effects of atypical antipsychotics. J Clin Psychiatry 62(Suppl 21):7–10
Wu YF, Chang KY (2011) Aripiprazole-associated rhabdomyolysis in a patient with schizophrenia. J Neuropsychiatry Clin Neurosci 23(3):E51. doi:10.1176/appi.neuropsych.23.3.E51
Zink M, Knopf U, Argiriou S, Kuwilsky A (2006) A case of pulmonary thromboembolism and rhabdomyolysis during therapy with mirtazapine and risperidone. J Clin Psychiatry 67(5):835
Acknowledgments
None.
Conflicts of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Appendix
Appendix
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Laoutidis, Z.G., Kioulos, K.T. Antipsychotic-induced elevation of creatine kinase: a systematic review of the literature and recommendations for the clinical practice. Psychopharmacology 231, 4255–4270 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-014-3764-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-014-3764-2