Abstract
Rationale
The zebrafish dopaminergic system is thought to be evolutionarily conserved and may be amenable to pharmacological manipulation using drugs developed for mammalian receptors. However, only few studies have examined the role of specific receptor subtypes in behaviour of adult zebrafish.
Objectives
The objectives of this study are to determine the translational relevance of the zebrafish and examine the psychopharmacology of specific dopamine receptors in this species.
Methods
Using a behavioural pharmacological approach, we examine the effect of D1 and D2/3 receptor antagonisms on motor patterns of adult zebrafish during acute drug exposure and withdrawal.
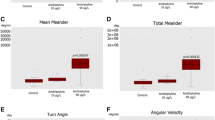
Results
Acute exposure to SCH-23390 (D1 receptor antagonist) decreased total distance travelled in a dose-dependent manner. Exposure to amisulpride (D2/3 receptor antagonist) induced a biphasic dose-response in total distance travelled and in angular velocity. The results provide support for the existence of structurally and functionally conserved postsynaptic D1 and D2 receptors, as well as presynaptic D2 autoreceptors in the zebrafish brain. The behavioural effects of the employed antagonists did not persist following 30 min of withdrawal.
Conclusion
The results suggest that zebrafish, a cheaper and simpler model organism compared to the rat and the mouse, may be an efficient translationally relevant tool for the analysis of the psychopharmacology of receptors of the vertebrate dopaminergic system.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barbazuk WB, Korf I, Kadavi C, Heyen H, Tate S, Wun E et al (2000) The syntenic relationship of the zebrafish and human genomes. Genome Res 10:1351–1358
Barghon R, Costentin JH (1980) Rotational behaviour induced by unilateral electrical stimulations of nigro-striatal dopamine neurons: modification by low doses of apomorphine. Eur J Pharmacol 64:39–46
Beaulieu J, Gainetdinov RR (2011) The physiology, signaling, and pharmacology of dopamine receptors. Pharmacol Rev 63:182–217
Berridge KC, Robison TE (1998) What is the role of dopamine in reward: hedonic impact, reward learning, or incentive salience? Brain Res Rev 28:309–369
Boehmler W, Obrecht-Pflumio S, Canfield V, Thisse C, Thisse B, Levenson R (2004) Evolution and expression of D2 and D3 receptor genes in zebrafish. Dev Dyn 230:481–493
Boehmler W, Carr T, Thisse C, Thisse B, Canfield V, Levenson R (2007) D4 dopamine receptor genes of zebrafish and effects of the antipsychotic clozapine on larval swimming behaviour. Genes Brain Behav 6:155–166
Bourne JA (2001) SCH 23390: the first selective dopamine D1-like receptor antagonist. CNS Drug Reviews 7:399–414
Briggs CA, Pollack NJ, Frail DE, Paxson CL, Rakowski RF, Kang CH, Kebabian JW (1991) Activation of the 5-HT1C receptor expressed in Xenopus oocytes by the benzazepines SCH 23390 and SKF 38393. Br J Pharmacol 104:1038–44
Connors KA, Valenti TW, Lawless K, Sackerman J, Onaivi ES, Brooks BW, Gould GG (2014) Similar anxiolytic effects of agonists targeting serotonin 5-HT1A or cannabinoid CB receptors on zebrafish behavior in novel environments. Aquat Toxicol 151:105–113
Cunha C, Wietzikoski EC, Ferro MM, Martinez GR, Vital MA, Hipolide D et al (2008) Hemiparkinsonian rats rotate toward the side with the weaker dopaminergic neurotransmission. Behav Brain Res 189:364–372
De Mei C, Ramos M, Iitaka C, Borrelli E (2009) Getting specialized: presynaptic and postsynaptic dopamine D2 receptors. Curr Opin Pharmacol 9:53–58
Decarvalho TN, Subedi A, Rock J, Harfe BD, Thisse C, Thisse B, Halpern ME, Hong E (2014) Neurotransmitter map of the asymmetric dorsal habenular nuclei of zebrafish. Genesis. doi:10.1002/dvg.22785
Di Chiara G, Bassareo V (2007) Reward system and addiction: what dopamine does and doesn’t do. Curr Opin Pharmacol 7:69–76
Eilam D, Szechtman H (1989) Biphasic effect of D-2 agonist quinpirole on locomotion and movements. Eur J Pharmacol 161:151–157
Farrell TC, Cario CL, Milanese C, Vogt A, Jeong JH, Burton EA (2011) Evaluation of spontaneous propulsive movement as a screening tool to detect rescue of Parkinsonism phenotypes in zebrafish models. Neurobiol Dis 44:9–18
Garcia-Munoz M, Patino P, Wright AJ, Arbuthnott GW (1983) The anatomical substrate of the turning behaviour seen after lesions in the nigrostriatal dopamine system. Neuroscience 8:87–95
Gerlai R, Lahav M, Guo S, Rosenthanol A (2000) Drinks like a fish: zebrafish (Danio rerio) as a behavior genetic model to study alcohol effects. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 67:773–82
Giacomini N, Rose B, Kobayashi K, Guo S (2006) Antipsychotics produce locomotor impairment in larval zebrafish. Neurotoxicol Teratol 28:245–250
Giros B, Sokoloff P, Martres M, Riou J, Emorine L, Schwartz J (1989) Alternative splicing directs the expression of two D2 dopamine receptor isoforms. Nature 342:923–926
Guryev V (2006) Genetic variation in the zebrafish. Genome Res 4:491–497
Hoffman DC, Beninger RJ (1985) The D1 dopamine receptor antagonist, SCH-23390 reduces locomotor activity and rearing in rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 22:341–342
Hudson J, van Horne C, Stromberg I, Brock S, Clayton J, Masserano J, Hoffer B, Gerhardt G (1993) Correlation of apomorphine- and amphetamine-induced turning with nigrostriatal dopamine content in unilateral 6-hydroxydopamine lesioned rats. Brain Res 626:167–174
Irons TD, Kelly PE, Hunter DL, MacPhail RC, Padilla S (2013) Acute administration of dopaminergic drugs has differential effects on locomotion in larval zebrafish. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 103:792–813
Jerussi TP, Glick SD (1975) Apomorphine-induced rotation in normal rats and interaction with unilateral caudate lesions. Psychopharmacologia 40:329–334
Jia J, Zeng X, Li Y, Ma S, Bai J (2013) Ephedrine induced thioredoxin-1 expression through beta-adrenergic receptor/cyclic AMP/protein kinase A/dopamine- and cyclic AMP-regulated phosphoprotein signaling pathway. Cell Signal 25:1194–1201
Kily LJM, Cowe YC, Hussain O, Patel S, McElwaine S, Cotter FE, Brennan CH (2008) Gene expression changes in a zebrafish model of drug dependency suggest conservation of neuro-adaptation pathways. J Exp Biol 211:1623–1634
Klee EW, Schneider H, Clark KJ, Cousin MA, Ebbert JO et al (2012) Zebrafish: a model for the study of addiction genetics. Hum Genet 131:977–1008
Klinker F, Hasan K, Paulus W, Nitsche MA, Liebetanz D (2013) Pharmacological blockade and genetic absence of the dopamine D2 receptor specifically modulate voluntary locomotor activity in mice. Behav Brain Res 242:117–124
Koshikawa N, Mori E, Maruyama Y, Yatsushige N, Kobayashi M (1990) Role of dopamine D-1 and D2 receptors in the ventral striatum in the turning behaviour of rats. Eur J Pharmacol 178:233–237
Levin E, Bencan Z, Cerutti D (2007) Anxiolytic effects of nicotine in zebrafish. Physiol Behav 90:54–58
Li P, Shah S, Huang L, Carr AL, Gao Y, Thisse C, Thisse B, Li L (2007) Cloning and spatial and temporal expression of the zebrafish dopamine D1 receptor. Dev Dyn 236:1339–1346
Liu C, Hu D, Liu F, Chen Z, Luo J (2008) Apomorphine-induced turning behavior in 6-hydroxydopamine lesioned rats is increased by histidine and decreased by histidine decarboxylase, histamine H1 and H2 receptor antagonists, and H3 receptor agonist. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 90:325–330
Maximino C, Puty B, Mato Oliveira KR, Herculano AM (2013) Behavioural and neurochemical changes in the zebrafish leopard strain. Genes Brain Behav 12:576–582
Meyer ME, Shults JM (1993) Dopamine D1 receptor family agonists, SK&F38393, SK&F77434, and SK&F82958, Differentially affect locomotor activities in rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 46:269–274
Millan MJ, Newman-Tancredi A, Quentric Y, Cussac D (2001) The “selective” dopamine D1 receptor antagonist, SCH23390, is a potent and high efficacy agonist at cloned human serotonin2C receptors. Psychopharmacology 156:58–62
Millan MJ, Seguin L, Gobert A, Cussac D, Brocco M (2004) The role of dopamine D3 compared with D2 receptors in the control of locomotor activity: a combined behavioural and neurochemical analysis with novel, selective antagonists in rats. Psychopharmacol (Berl) 174:341–357
Monsma F, McVittie L, Gerfen C, Mahan L, Sibley D (1989) Multiple D2 dopamine receptors produced by alternative RNA splicing. Nature 342:926–929
Pannia E, Tran S, Rampersad M, Gerlai R (2014) Acute ethanol exposure induces behavioural differences in two zebrafish (Danio rerio) strains: a time course analysis. Behav Brain Res 259:174–185
Perrault G, Depoortere R, Morel E, Sanger DJ, Scatton B (1997) Psychopharmacological profile of amisulpride: an antipsychotic drug with presynaptic D2/D3 dopamine receptor antagonistic activity and limbic selectivity. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 280:73–82
Pritchard LM, Logue AD, Hayes S, Welge JA, Xu M, Zhang J, Berger SP, Richtand NM (2003) 7-OH-DPAT and PD 128907 selectively activate the D3 dopamine receptor in a novel environment. Neuropsychopharmacology 28:100–107
Rico EP, Rosemberg DB, Seibt KJ, Capiotti KM, Da Silva RS, Bonan CD (2011) Zebrafish neurotransmitter systems as potential pharmacological and toxicological targets. Neurotoxicol Teratol 33:608–617
Rink E, Wullimann M (2001) The teleostean (zebrafish) dopaminergic system ascending to the subpallium (striatum) is located in the basal diencephalon (posterior tuberculum). Brain Res 889:316–330
Rink E, Wullimann M (2002) Connections of the ventral telencephalon and tyrosine hydroxylase distribution in the zebrafish brain (Danio rerio) lead to identification of an ascending dopaminergic system in the teleost. Brain Res Bull 52:385–387
Rink E, Wullimann M (2007) Connections of the ventral telencephalon in the zebrafish. Brain Res 1011:206–220
Roussigne M, Blader P, Wilson SW (2012) Breaking symmetry: the zebrafish as a model for understanding left-right asymmetry in the developing brain. Dev Neurobiol 72:269–281
Scerbina T, Chatterjee D, Gerlai R (2012) Dopamine receptor antagonism disrupts social preference in zebrafish: a strain comparison study. Amino Acids 43:2059–2072
Schoemaker H, Chlaustre Y, Fage D, Rouquier L, Cherqui K, Curet O, Oblin A et al (1997) Neurochemical characteristics of amisulpride, an atypical dopamine D2/D3 receptor antagonist with both presynaptic and limbic selectivity. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 280:83–97
Sivamani S, Benin J, Nishwetha K, Bibhas K (2013) Zebrafish as a model for bioavailability testing of over the counter drug. Intl J Drug Dev Res 5:159–163
Sobrian SK, Jones BL, Varhese S, Holson RR (2003) Behavioural response profiles following drug challenge with dopamine receptor subtype agonists and antagonists in developing rat. Neurotoxicol Teratol 25:311–328
Stolzenberg DS, Zhang KY, Luskin K, Ranker L, Bress J, Numan M (2010) Dopamine D1 receptor activation of adenylyl cyclise, not phospholipase C, in the nucleus accumbens promotes maternal behavior onset in rats. Horm Behav 57:96–104
Tran S, Gerlai R (2013a) Time-course of behavioural changes induced by ethanol in zebrafish (Danio rerio). Behav Brain Res 252:204–213
Tran S, Gerlai R (2013b) Individual differences in activity levels in zebrafish (Danio rerio). Behav Brain Res 257:224–229
Tran S, Chatterjee D, Gerlai R (2014) An integrative analysis of ethanol tolerance and withdrawal in zebrafish (Danio rerio). Behav Brain Res. doi:10.1016/j.pnpbp.2014.02.008
Wahlsten D (1990) Insensitivity of the analysis of variance to heredity x environment interaction. Behav Brain Sci 13:109–61
Acknowledgments
This study is supported by an NSERC Discovery grant (#311637) issued to R.G.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tran, S., Nowicki, M., Muraleetharan, A. et al. Differential effects of dopamine D1 and D2/3 receptor antagonism on motor responses. Psychopharmacology 232, 795–806 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-014-3713-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-014-3713-0