Abstract
Rationale
Ethanol and nicotine are frequently co-abused. The biological basis for the high co-morbidity rate is not known. Alcohol-preferring (P) rats will self-administer EtOH or nicotine directly into the posterior ventral tegmental area (pVTA).
Objective
The current experiments examined whether sub-threshold concentrations of EtOH and nicotine would support the development of self-administration behaviors if the drugs were combined.
Methods
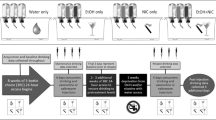
Rats were implanted with a guide cannula aimed at the pVTA. Rats were randomly assigned to groups that self-administered sub-threshold concentrations of EtOH (50 mg%) or nicotine (1 μM) or combinations of ethanol (25 or 50 mg%) and nicotine (0.5 or 1.0 μM). Alterations in gene expression downstream projections areas (nucleus accumbens shell, AcbSh) were assessed following a single, acute exposure to EtOH (50 mg%), nicotine (1 μM), or ethanol and nicotine (50 mg% + 1 μM) directly into the pVTA.
Results
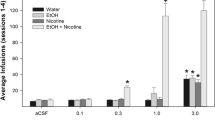
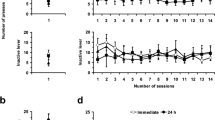
The results indicated that P rats would co-administer EtOH and nicotine directly into the pVTA at concentrations that did not support individual self-administration. EtOH and nicotine directly administered into the pVTA resulted in alterations in gene expression in the AcbSh (50.8-fold increase in brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF), 2.4-fold decrease in glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor (GDNF), 10.3-fold increase in vesicular glutamate transporter 1 (Vglut1)) that were not observed following microinjections of equivalent concentrations/doses of ethanol or nicotine.
Conclusion
The data indicate that ethanol and nicotine act synergistically to produce reinforcement and alter gene expression within the mesolimbic dopamine system. The high rate of co-morbidity of alcoholism and nicotine dependence could be the result of the interactions of EtOH and nicotine within the mesolimbic dopamine system.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ait-Daoud N, Wiesback GA, Bienkowski P, Li MD, Pfutzer RH, Singer MV, Lesch OM, Johnson BA (2005) Comorbid alcohol and nicotine dependence: from the biomolecular basis to clinical consequences. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 29:1541–1549
Beck KD, Valverde J, Alexi T, Poulsen K, Moffat B, Vandlen RA, Rosenthal A, Hefti F (1995) Mesencephalic dopamine neurons protected by GDNF from axotomy-induced degeneration in the adult brain. Nature 373:339–341
Benowitz NL (1997) Systemic absorption and effects of nicotine from smokeless tobacco. Adv Dent Res 11:336–341
Bolanos CA, Nestler EJ (2004) Neurotrophic mechanisms in drug addiction. Neuromol Med 5:69–83
Carnicella S, Ron D (2009) GDNF—a potential target to treat addiction. Pharmacol Ther 122:9–18
Carnicella S, Kharazia V, Jeanblanc J, Janak PH, Ron D (2008) GDNF is a fast-acting potent inhibitor of alcohol consumption and relapse. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 105:8114–8119
Carnicella S, Amamoto R, Ron D (2009) Excessive alcohol consumption is blocked by glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor. Alcohol 43:35–43
Choi DC, Gourley SL, Ressler KJ (2012) Prelimbic BDNF and TrkB signaling regulates consolidation of both appetitive and aversive emotional learning. Transl Psychiatry 2:e205
Clark A, Little HJ (2004) Interaction between low concentrations of ethanol and nicotine on firing rate of ventral tegmental dopamine neurones. Drug Alcohol Depend 16:199–206
Commons KG, Serock MR (2009) Coincidence of neurokinin 1 receptors with the vesicular glutamate transporter (VGLUT3) in the rat forebrain. Neurosci Lett 464:188–192
Diamond JS, Jahr CE (1997) Transporters buffer synaptically release glutamate on a submillisecond time scale. J Neurosci 17:4672–4687
DiFranza JR, Guerrera MP (1990) Alcoholism and smoking. J Stud Alcohol 51:130–135
Ding ZM, Rodd ZA, Engleman EA, McBride WJ (2009) Sensitization of ventral tegmental area dopamine neurons to the stimulating effects of ethanol. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 33:1571–1581
Doyon WM, Thomas AM, Ostroumov A, Dong Y, Dani JA (2013) Potential substrates for nicotine and alcohol interactions: a focus on the mesocorticolimbic dopamine system. Biochem Pharmacol 86:1181–1193
Enoch MA, Zhou Z, Kimura M, Mash DC, Yuan Q, Goldman D (2011) GABAergic gene expression in postmortem hippocampus from alcoholics and cocaine addicts; corresponding findings in alcohol-naïve P and NP rats. PLoS ONE 7:e29369
Exley R, Maubourguet N, David V, Eddine R, Evrard A, Pons S, Marti F, Threlfell S, Cazala P, McIntosh JM, Changeux J-P, Maskos W, Cragg SJ, Faure P (2011) Distinct contributions of nicotinic acetylcholine receptor subunit α4 and subunit α6 to the reinforcing effects of nicotine. PNAS 108:7577–7582
Farquhar MJ, Latimer MP, Winn P (2012) Nicotine self-administered directly into the VTA by rats is weakly reinforcing but has strong reinforcement enhancing properties. Psychopharmacology 220:43–54
Ferrea S, Winterer G (2009) Neuroprotective and neurotoxic effects of nicotine. Pharmacopsychiatry 42:255–265
Flatscher-Bader T, Zuvela N, Landis N, Wilce PA (2008) Smoking and alcoholism target genes associated with plasticity and glutamate transmission in the human ventral tegmental area. Hum Mol Genet 17:38–51
Gilbertson R, Frye RF, Nixon SJ (2011) Nicotine as a factor in stress responsiveness among detoxified alcoholics. Alcohol Alcohol 46:39–51
Hauser SR, Katner SN, Deehan GA Jr, Toalston JE, Scott BJ, Bell RL, McBride WJ, Rodd ZA (2012) Development of an oral operant nicotine/ethanol co-use model in alcohol-preferring (P) rats. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 36:1963–1972
Hauser SR, Bracken AL, Deehan GA Jr, Toalston JE, Ding ZM, Truitt WA, Bell RL, McBride WJ, Rodd ZA (2013) Selective breeding for high alcohol preference increases the sensitivity of the posterior VTA to the reinforcing effects of nicotine. Addict Biol (Epub ahead of print)
He DY, McGough NN, Ravindranathan A, Jeanblacn J, Logrip ML, Phamluong K, Janak PH, Ron D (2005) Glial cell ine-derived neurotrophic factor mediates the desirable actions of the anti-addiction drug ibogaine against alcohol consumption. J Neurosci 25:619–628
Hingson RW, Heeren T, Edwards EM (2008) Age at drinking onset, alcohol dependence, and their relation to drug use and dependence, driving under the influence of drugs, and motor-vehicle crash involvement because of drugs. J Stud Alcohol Drugs 69:192–201
Ikemoto S, Qin M, Liu ZH (2006) Primary reinforcing effects of nicotine are triggered from multiple regions both inside and outside the ventral tegmental area. J Neurosci 26:723–730
Jackson MB, Yakel JL (1995) The 5-HT3 receptor channel. Ann Rev Physiol 57:447–468
John U, Hill A, Rumpf HJ, Hapke U, Meyer C (2003a) Alcohol high risk drinking, abuse, and dependence among tobacco smoking medical care patients and the general population. Drug Alcohol Depend 64:233–241
John U, Meyer C, Rumpf HJ, Schumann A, Thyrian JR, Hapke U (2003b) Strength of the relationship between tobacco smoking, nicotine dependence and the severity of alcohol dependence syndrome criteria in a population-based sample. Alcohol Alcohol 38:606–612
Kalivas PW (2009) The glutamate homeostasis hypothesis of addiction. Nat Rev Neurosci 10: 561–572
Knackstedt LA, LaRowe S, Merdikian P, Malcolm R, Upadhyaya H, Hedden S, Markou A, Kalivas PW (2009) The role of cysteine-glutamate exchange in nicotine dependence in rat and humans. Biol Psychiatry 65:841–845
Knackstedt LA, Moussawi K, Lalumiere R, Schwendt M, Klugmann M, Kalivas PW (2010) Extinction training after cocaine self-administration induces glutamatergic plasticity to inhibit cocaine seeking. J Neurosci 30:7984–7992
Lê AD, Li Z, Funk D, Shram M, Li T-K, Shaham Y (2006) Increased vulnerability to nicotine self-administration and relapse in alcohol-naïve offspring of rats selectively bred for high alcohol intake. J Neurosci 26:1872–1879
Lê AD, Lo S, Harding S, Juzytsch W, Marinelli PW, Funk D (2010) Coadministration of intravenous nicotine and oral alcohol in rats. Psychopharmacology 208(3):475–486
Li X, DeJoesph MR, Urban JH, Bahi A, Dreyer JL, Meredith GE, Ford KA, Ferrario CR, Loweth JA, Wolf ME (2013) Different roles of BDNF in the nucleus accumbens core versus shell during the incubation of cue-induced cocaine craving and its long-term maintenance. J Neurosci 33:1130–1142
Liu W, Thielen RJ, Rodd ZA, McBride WJ (2006) Activation of serotonin-3 receptors increases dopamine release within the ventral tegmental of Wistar and alcohol-preferring (P) rats. Alcohol 40:167–176
Messer CJ, EischAJ, Carlezon WA Jr., Whisler K, Shen L, Wolf DH, Westphal H, Collins F, Russell DS, Nestler EJ (2000) Role for GDNF in biochemical and behavioral adaptations to drugs of abuse. Neuron 26:247–257
Moonat S, Sakharkar AJ, Zhang H, Pandey SC (2011) The role of amygdaloid brain-derived neurotrophic factor, activity-regulated cytoskeleton-associated protein and dendritic spines in anxiety and alcoholism. Addict Biol 16:238–250
Moran MM, McFarland K, Melendez RI, Kalivas PW, Seamans JK (2005) Cystine/glutamate exchange regulates metabotropic glutamate receptor presynaptic inhibition of excitatory transmission and vulnerability to cocaine seeking. J Neurosci 25:6389–6393
National Research Council (1996) National Science Education Standards. Washington, DC: The National Academies Press
Nayak SV, Ronde P, Spier AD, Lummis SCR, Nichols RA (2000) Nicotinic receptors co-localize with 5-HT3 serotonin receptors on striatal nerve terminals. Neuropharmacology 39:2681–2690
Paxinos GW, Watson C (2005) The rat brain in stereotaxic coordinates. Academic, Oxford
Perna MK, Brown RW (2013) Adolescent nicotine sensitization and effects of nicotine on accumbal dopamine release in a rodent model of increased dopamine D(2) receptor sensitivity. Behav Brain Res 242:102–109
Pidoplichko VI, Noguchi J, Areola OO, Liang Y, Peterson J, Zhang T, Dani JA (2004) Nicotinic cholinergic synaptic mechanisms in the ventral tegmental area contribute to nicotine addiction. Learn Mem 11:60–69
Rodd ZA, Bell RL, Melendez RI, Kuc KA, Lumeng L, Li T-K, Murphy JM, McBride WJ (2004a) Comparison of intracranial self-administration of ethanol within the posterior ventral tegmental area between alcohol-preferring (P) and Wistar rats. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 28:1212–1219
Rodd ZA, Melendez RI, Bell RL, Kuc KA, Zhang Y, Murphy JM, McBride WJ (2004b) Intracranial self-administration of ethanol within the ventral tegmental area of male Wistar rats: evidence for involvement of dopamine neurons. J Neurosci 24(5):1050–1057
Rodd-Henricks ZA, McKinzie DL, Melendez RI, Berry N, Murphy JM, McBride WJ (2003) The effects of serotonin-3 receptor antagonists on the intracranial self-administration of ethanol into the posterior VTA of Wistar rats. Psychopharmacology 165:252–259
Rahman S, Zhang J, Engleman EA, Corrigall WA (2004) Neuroadaptive changes in the mesoaccumbens dopamine system after chronic nicotine self-administration: a microdialysis study. Neuroscience 129:415–424
Tizabi Y, Copeland RL Jr, Louis VA, Taylor RE (2002) Effects of systemic alcohol and central nicotine administration into the ventral tegmental area on dopamine release in the nucleus accumbens. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 26:394–399
Tizabi Y, Bai L, Copeland RL Jr, Taylor RE (2007) Combined effects of systemic alcohol and nicotine on dopamine release in the nucleus accumbens shell. Alcohol Alcohol 42:413–416
Toledano AMI, Toledano-Diaz A (2010) Diversity and variability of the effects of nicotine on different cortical regions of the brain—therapeutic and toxicological implications. Cent Nerv Syst Agents Med Chem 1:180–206
True WE, Xian H, Scherrer JF, Madden PA, Bucholz KK, Heath AC, Eisen SA, Lyons MJ, Goldberg J, Tsuang M (1999) Common genetic vulnerability for nicotine and alcohol dependence in men. Arch Gen Psychiatry 56:655–661
Vandesompele J, De Preter K, Pattyn F, Poppe B, Van Roy N, De Paepe A, Speleman F (2002) Accurate normalization of real-time quantitative RT-PCR data by geometric averaging of multiple internal control genes. Geneom Biol 18;3(7)
Vargas-Perez H, Ting-A Kee R, Walton CH, Hansen DM, Razavi R, Clarke L, Bufalino MR, Allison DW, Stefffensen SC, van der Kooy C (2009) Ventral tegmental area BDNF induces an opiate-dependent-like reward state in naïve rats. Science 324:1732–1734
Wang CY, Yang F, He X, Chow A, Du J, Russell JR, Lu B (2001) Ca (2+) binding protein frequenin mediates GDNF-induced potentiation of CA (2+) channels and transmitter release. Neuron 32:99–112
Acknowledgments
The skillful technical assistance of Tylene Pommer is gratefully acknowledged. This research was supported in part by AA07462, AA07611, and AA019366.
Conflict of interest
None of the authors has a conflict of interest associated with this research. The content of this manuscript is solely the responsibility of the authors and does not necessarily represent the official views of the NIAAA or NIH.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Truitt, W.A., Hauser, S.R., Deehan, G.A. et al. Ethanol and nicotine interaction within the posterior ventral tegmental area in male and female alcohol-preferring rats: evidence of synergy and differential gene activation in the nucleus accumbens shell. Psychopharmacology 232, 639–649 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-014-3702-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-014-3702-3