Abstract
Rationale
Neurosteroids and likely other lipid modulators access transmembrane sites on the GABAA receptor (GABAAR) by partitioning into and diffusing through the plasma membrane. Therefore, specific components of the plasma membrane may affect the potency or efficacy of neurosteroid-like modulators. Here, we tested a possible role for phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate (PIP2), a phospholipid that governs activity of many channels and transporters, in modulation or function of GABAARs.
Objectives
In these studies, we sought to deplete plasma-membrane PIP2 and probe for a change in the strength of potentiation by submaximal concentrations of the neurosteroid allopregnanolone (3α5αP) and other anesthetics, including propofol, pentobarbital, and ethanol. We also tested for a change in the behavior of negative allosteric modulators pregnenolone sulfate and dipicrylamine.
Methods
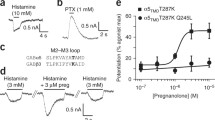
We used Xenopus oocytes expressing the ascidian voltage-sensitive phosphatase (Ci-VSP) to deplete PIP2. Voltage pulses to positive membrane potentials were used to deplete PIP2 in Ci-VSP-expressing cells. GABAARs composed of α1β2γ2L and α4β2δ subunits were challenged with GABA and 3α5αP or other modulators before and after PIP2 depletion. KV7.1 channels and NMDA receptors (NMDARs) were used as positive controls to verify PIP2 depletion.
Results
We found no evidence that PIP2 depletion affected modulation of GABAARs by positive or negative allosteric modulators. By contrast, Ci-VSP-induced PIP2 depletion depressed KV7.1 activation and NMDAR activity.
Conclusions
We conclude that despite a role for PIP2 in modulation of a wide variety of ion channels, PIP2 does not affect modulation of GABAARs by neurosteroids or related compounds.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akk G, Bracamontes J, Steinbach JH (2001) Pregnenolone sulfate block of GABAA receptors: mechanism and involvement of a residue in the M2 region of the α subunit. J Physiol Lond 532:673–684
Akk G, Shu HJ, Wang C, Steinbach JH, Zorumski CF, Covey DF, Mennerick S (2005) Neurosteroid access to the GABAA receptor. J Neurosci 25:11605–11613
Brown N, Kerby J, Bonnert TP, Whiting PJ, Wafford KA (2002) Pharmacological characterization of a novel cell line expressing human α4β3δ GABAA receptors. Br J Pharmacol 136:965–974
Carver CM, Reddy DS (2013) Neurosteroid interactions with synaptic and extrasynaptic GABA(A) receptors: regulation of subunit plasticity, phasic and tonic inhibition, and neuronal network excitability. Psychopharmacology (Berlin) 230:151–188
Chisari M, Eisenman LN, Krishnan K, Bandyopadhyaya AK, Wang C, Taylor A, Benz A, Covey DF, Zorumski CF, Mennerick S (2009) The influence of neuroactive steroid lipophilicity on GABAA receptor modulation: evidence for a low-affinity interaction. J Neurophysiol 102:1254–1264
Chisari M, Eisenman LN, Covey DF, Mennerick S, Zorumski CF (2010) The sticky issue of neurosteroids and GABAA receptors. Trends Neurosci 33:299–306
Chisari M, Wu K, Zorumski CF, Mennerick S (2011) Hydrophobic anions potently and uncompetitively antagonize GABAA receptor function in the absence of a conventional binding site. Br J Pharmacol 164:667–680
Eisenman LN, He Y, Fields C, Zorumski CF, Mennerick S (2003) Activation-dependent properties of pregnenolone sulfate inhibition of GABAA receptor-mediated current. J Physiol Lond 550:679–691
Farrant M, Nusser Z (2005) Variations on an inhibitory theme: phasic and tonic activation of GABAA receptors. Nat Rev Neurosci 6:215–229
Glykys J, Mann EO, Mody I (2008) Which GABAA receptor subunits are necessary for tonic inhibition in the hippocampus? J Neurosci 28:1421–1426
Hertel F, Switalski A, Mintert-Jancke E, Karavassilidou K, Bender K, Pott L, Kienitz MC (2011) A genetically encoded tool kit for manipulating and monitoring membrane phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate in intact cells. PLoS One 6:e20855
Hosie AM, Wilkins ME, da Silva HMA, Smart TG (2006) Endogenous neurosteroids regulate GABAA receptors via two discrete transmembrane sites. Nature 444:486–489
Hosie AM, Wilkins ME, Smart TG (2007) Neurosteroid binding sites on GABA(A) receptors. Pharmacol Ther 116:7–19
Hosie AM, Clarke L, da Silva H, Smart TG (2009) Conserved site for neurosteroid modulation of GABAA receptors. Neuropharmacology 56:149–154
Howard RJ, Murail S, Ondricek KE, Corringer PJ, Lindahl E, Trudell JR, Harris RA (2011) Structural basis for alcohol modulation of a pentameric ligand-gated ion channel. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 108:12149–12154
Iwasaki H, Murata Y, Kim Y, Hossain MI, Worby CA, Dixon JE, McCormack T, Sasaki T, Okamura Y (2008) A voltage-sensing phosphatase, Ci-VSP, which shares sequence identity with PTEN, dephosphorylates phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 105:7970–7975
Li P, Bracamontes J, Katona BW, Covey DF, Steinbach JH, Akk G (2007) Natural and enantiomeric etiocholanolone interact with distinct sites on the rat α1β2γ2L GABAA receptor. Mol Pharmacol 71:1582–1590
Lindner M, Leitner MG, Halaszovich CR, Hammond GR, Oliver D (2011) Probing the regulation of TASK potassium channels by PI4,5P(2) with switchable phosphoinositide phosphatases. J Physiol Lond 589:3149–3162
Mandal M, Yan Z (2009) Phosphatidylinositol (4,5)-bisphosphate regulation of N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor channels in cortical neurons. Mol Pharmacol 76:1349–1359
McLaughlin S, Wang J, Gambhir A, Murray D (2002) PIP(2) and proteins: interactions, organization, and information flow. Annu Rev Biophys Biomol Struct 31:151–175
Mennerick S, Lamberta M, Shu HJ, Hogins J, Wang C, Covey DF, Eisenman LN, Zorumski CF (2008) Effects on membrane capacitance of steroids with antagonist properties at GABAA receptors. Biophys J 95:176–185
Michailidis IE, Helton TD, Petrou VI, Mirshahi T, Ehlers MD, Logothetis DE (2007) Phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate regulates NMDA receptor activity through alpha-actinin. J Neurosci 27:5523–5532
Murata Y, Okamura Y (2007) Depolarization activates the phosphoinositide phosphatase Ci-VSP, as detected in Xenopus oocytes coexpressing sensors of PIP2. J Physiol Lond 583:875–889
Murata Y, Iwasaki H, Sasaki M, Inaba K, Okamura Y (2005) Phosphoinositide phosphatase activity coupled to an intrinsic voltage sensor. Nature 435:1239–1243
Rusinova R, Hobart EA, Koeppe RE 2nd, Andersen OS (2013) Phosphoinositides alter lipid bilayer properties. J Gen Physiol 141:673–690
Sauguet L, Howard RJ, Malherbe L, Lee US, Corringer PJ, Harris RA, Delarue M (2013) Structural basis for potentiation by alcohols and anaesthetics in a ligand-gated ion channel. Nat Commun 4:1697
Shen W, Mennerick S, Covey DF, Zorumski CF (2000) Pregnenolone sulfate modulates inhibitory synaptic transmission by enhancing GABAA receptor desensitization. J Neurosci 20:3571–3579
Shu HJ, Bracamontes J, Taylor A, Wu K, Eaton MM, Akk G, Manion B, Evers AS, Krishnan K, Covey DF, Zorumski CF, Steinbach JH, Mennerick S (2012) Characteristics of concatemeric GABA(A) receptors containing alpha4/delta subunits expressed in Xenopus oocytes. Br J Pharmacol 165:2228–2243
Sooksawate T, Simmonds MA (1998) Increased membrane cholesterol reduces the potentiation of GABAA currents by neurosteroids in dissociated hippocampal neurones. Neuropharmacology 37:1103–1110
Suh BC, Hille B (2008) PIP2 is a necessary cofactor for ion channel function: how and why? Annu Rev Biophys 37:175–195
Wafford KA, Thompson SA, Thomas D, Sikela J, Wilcox AS, Whiting PJ (1996) Functional characterization of human gamma-aminobutyric acidA receptors containing the α4 subunit. Mol Pharmacol 50:670–678
Wafford KA, van Niel MB, Ma QP, Horridge E, Herd MB, Peden DR, Belelli D, Lambert JJ (2009) Novel compounds selectively enhance δ subunit containing GABAA receptors and increase tonic currents in thalamus. Neuropharmacology 56:182–189
Wang M, He Y, Eisenman LN, Fields C, Zeng CM, Mathews J, Benz A, Fu T, Zorumski E, Steinbach JH, Covey DF, Zorumski CF, Mennerick S (2002) 3β -hydroxypregnane steroids are pregnenolone sulfate-like GABAA receptor antagonists. J Neurosci 22:3366–3375
Wrobel E, Tapken D, Seebohm G (2012) The KCNE tango—how KCNE1 interacts with Kv7.1. Front Pharmacol 3:142
Wu D, Pan H, Delaloye K, Cui J (2010) KCNE1 remodels the voltage sensor of Kv7.1 to modulate channel function. Biophys J 99:3599–3608
Yip GM, Chen ZW, Edge CJ, Smith EH, Dickinson R, Hohenester E, Townsend RR, Fuchs K, Sieghart W, Evers AS, Franks NP (2013) A propofol binding site on mammalian GABA receptors identified by photolabeling. Nat Chem Biol 9:715–720
Zaydman MA, Silva JR, Delaloye K, Li Y, Liang H, Larsson HP, Shi J, Cui J (2013) Kv7.1 ion channels require a lipid to couple voltage sensing to pore opening. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 110:13180–13185
Acknowledgments
We thank Jianmin Cui for the gift of Ci-VSP, Kv7.1, and KCNE1 constructs and Joe Henry Steinbach for the discussion related to the conception of these experiments. Thanks to Hong-Jin Shu for the help in the RNA preparation. This work was funded by a gift from the Bantly Foundation and NIH grants GM47969, MH078823, MH099658, MH077791, and AA017413.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mennerick, S., Taylor, A.A. & Zorumski, C.F. Phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate depletion fails to affect neurosteroid modulation of GABAA receptor function. Psychopharmacology 231, 3493–3501 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-014-3486-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-014-3486-5