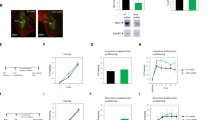
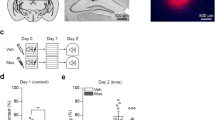
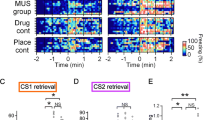
Abstract
Rationale and objectives
A conditioned stimulus (CS) is associated with a fearful unconditioned stimulus (US) in the traditional fear conditioning model. After fear conditioning, the CS–US association memory undergoes the consolidation process to become stable. Consolidated memory enters an unstable state after retrieval and requires the reconsolidation process to stabilize again. Evidence indicates the important role of Rac (Ras-related C3 botulinum toxin substrate) in the acquisition and extinction of fear memory. In the present study, we hypothesized that Rac in the amygdala is crucial for the reconsolidation of auditory and contextual Pavlovian fear memory.
Methods
Auditory and contextual fear conditioning and microinjections of the Rac inhibitor NSC23766 were used to explore the role of Rac in the reconsolidation of auditory and contextual Pavlovian fear memory in rats.
Results
A microinjection of NSC23766 into the basolateral amygdala (BLA) but not central amygdala (CeA) or cornu ammonis 1 (CA1) immediately after memory retrieval disrupted the reconsolidation of auditory Pavlovian fear memory. A microinjection of NSC23766 into the CA1 but not BLA or CeA after memory retrieval disrupted the reconsolidation of contextual Pavlovian fear memory.
Conclusions
Our experiments demonstrate that Rac in the BLA is crucial for the reconsolidation of auditory Pavlovian fear memory, whereas Rac in the CA1 is critical for the reconsolidation of contextual Pavlovian fear memory.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amaral DG (2003) The amygdala, social behavior, and danger detection. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1000:337–47
Bahar A, Dorfman N, Dudai Y (2004) Amygdalar circuits required for either consolidation or extinction of taste aversion memory are not required for reconsolidation. Eur J Neurosci 19:1115–8
Baldi E, Mariottini C, Bucherelli C (2008) Differential roles of the basolateral amygdala and nucleus basalis magnocellularis during post-reactivation contextual fear conditioning reconsolidation in rats. Neurobiol Learn Mem 90:604–9
Barak S, Liu F, Ben Hamida S, Yowell QV, Neasta J, Kharazia V, Janak PH, Ron D (2013) Disruption of alcohol-related memories by mTORC1 inhibition prevents relapse. Nat Neurosci 16:1111–7
Barnes P, Kirtley A, Thomas KL (2012) Quantitatively and qualitatively different cellular processes are engaged in CA1 during the consolidation and reconsolidation of contextual fear memory. Hippocampus 22:149–71
Borrelli S, Musilli M, Martino A, Diana G (2013) Long-lasting efficacy of the cognitive enhancer cytotoxic necrotizing factor 1. Neuropharmacology 64:74–80
Bucherelli C, Baldi E, Mariottini C, Passani MB, Blandina P (2006) Aversive memory reactivation engages in the amygdala only some neurotransmitters involved in consolidation. Learning & memory (Cold Spring Harbor, NY) 13:426–30
Cammarota M, Bevilaqua LR, Rossato JI, Lima RH, Medina JH, Izquierdo I (2008) Parallel memory processing by the CA1 region of the dorsal hippocampus and the basolateral amygdala. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 105:10279–84
Campolongo P, Roozendaal B, Trezza V, Hauer D, Schelling G, McGaugh JL, Cuomo V (2009) Endocannabinoids in the rat basolateral amygdala enhance memory consolidation and enable glucocorticoid modulation of memory. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 106:4888–93
Chen C, Kim JJ, Thompson RF, Tonegawa S (1996) Hippocampal lesions impair contextual fear conditioning in two strains of mice. Behav Neurosci 110:1177–80
Cingolani LA, Goda Y (2008) Actin in action: the interplay between the actin cytoskeleton and synaptic efficacy. Nat Rev Neurosci 9:344–56
Davis M (1992) The role of the amygdala in fear and anxiety. Annu Rev Neurosci 15:353–75
de la Fuente V, Freudenthal R, Romano A (2011) Reconsolidation or extinction: transcription factor switch in the determination of memory course after retrieval. J Neurosci 31:5562–73
Debiec J, LeDoux JE, Nader K (2002) Cellular and systems reconsolidation in the hippocampus. Neuron 36:527–38
Diana G, Valentini G, Travaglione S, Falzano L, Pieri M, Zona C, Meschini S, Fabbri A, Fiorentini C (2007) Enhancement of learning and memory after activation of cerebral Rho GTPases. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 104:636–41
Ding ZB, Wu P, Luo YX, Shi HS, Shen HW, Wang SJ, Lu L (2013) Region-specific role of Rac in nucleus accumbens core and basolateral amygdala in consolidation and reconsolidation of cocaine-associated cue memory in rats. Psychopharmacology 228:427–37
Dudai Y (2006) Reconsolidation: the advantage of being refocused. Curr Opin Neurobiol 16:174–8
Duvarci S, Nader K, LeDoux JE (2005) Activation of extracellular signal-regulated kinase- mitogen-activated protein kinase cascade in the amygdala is required for memory reconsolidation of auditory fear conditioning. Eur J Neurosci 21:283–9
Elzinga BM, Bremner JD (2002) Are the neural substrates of memory the final common pathway in posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD)? J Affect Disord 70:1–17
Etienne-Manneville S, Hall A (2002) Rho GTPases in cell biology. Nature 420:629–35
Fanselow MS (2000) Contextual fear, gestalt memories, and the hippocampus. Behav Brain Res 110:73–81
Ghashghaei HT, Barbas H (2002) Pathways for emotion: interactions of prefrontal and anterior temporal pathways in the amygdala of the rhesus monkey. Neuroscience 115:1261–79
Hall J, Thomas KL, Everitt BJ (2001) Cellular imaging of zif268 expression in the hippocampus and amygdala during contextual and cued fear memory retrieval: selective activation of hippocampal CA1 neurons during the recall of contextual memories. J Neurosci: Off J Soc Neurosci 21:2186–93
Hellemans KG, Everitt BJ, Lee JL (2006) Disrupting reconsolidation of conditioned withdrawal memories in the basolateral amygdala reduces suppression of heroin seeking in rats. J Neurosci: Off J Soc Neurosci 26:12694–9
Hoeffer CA, Cowansage KK, Arnold EC, Banko JL, Moerke NJ, Rodriguez R, Schmidt EK, Klosi E, Chorev M, Lloyd RE, Pierre P, Wagner G, LeDoux JE, Klann E (2011) Inhibition of the interactions between eukaryotic initiation factors 4E and 4G impairs long-term associative memory consolidation but not reconsolidation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 108:3383–8
Huang W, Zhu PJ, Zhang S, Zhou H, Stoica L, Galiano M, Krnjevic K, Roman G, Costa-Mattioli M (2013) mTORC2 controls actin polymerization required for consolidation of long-term memory. Nat Neurosci 16:441–8
Huff ML, Miller RL, Deisseroth K, Moorman DE, LaLumiere RT (2013) Posttraining optogenetic manipulations of basolateral amygdala activity modulate consolidation of inhibitory avoidance memory in rats. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 110:3597–602
Hughes V (2012) Stress: the roots of resilience. Nature 490:165–7
Jaffe AB, Hall A (2005) Rho GTPases: biochemistry and biology. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 21:247–69
Jin XC, Lu YF, Yang XF, Ma L, Li BM (2007) Glucocorticoid receptors in the basolateral nucleus of amygdala are required for postreactivation reconsolidation of auditory fear memory. Eur J Neurosci 25:3702–12
Johansen JP, Cain CK, Ostroff LE, LeDoux JE (2011) Molecular mechanisms of fear learning and memory. Cell 147:509–24
Kennedy MB, Beale HC, Carlisle HJ, Washburn LR (2005) Integration of biochemical signalling in spines. Nat Rev Neurosci 6:423–34
Krettek JE, Price JL (1978) A description of the amygdaloid complex in the rat and cat with observations on intra-amygdaloid axonal connections. J Comp Neurol 178:255–80
LaLumiere RT, Buen TV, McGaugh JL (2003) Post-training intra-basolateral amygdala infusions of norepinephrine enhance consolidation of memory for contextual fear conditioning. J Neurosci: Off J Soc Neurosci 23:6754–8
LeDoux J (2003) The emotional brain, fear, and the amygdala. Cell Mol Neurobiol 23:727–38
LeDoux JE (2000) Emotion circuits in the brain. Annu Rev Neurosci 23:155–84
Lee JL (2009) Reconsolidation: maintaining memory relevance. Trends Neurosci 32:413–20
Lee JL, Everitt BJ, Thomas KL (2004) Independent cellular processes for hippocampal memory consolidation and reconsolidation. Science (New York, NY) 304:839–43
Li FQ, Xue YX, Wang JS, Fang Q, Li YQ, Zhu WL, He YY, Liu JF, Xue LF, Shaham Y, Lu L (2010) Basolateral amygdala cdk5 activity mediates consolidation and reconsolidation of memories for cocaine cues. J Neurosci: Off J Soc Neurosci 30:10351–9
Li YQ, Li FQ, Wang XY, Wu P, Zhao M, Xu CM, Shaham Y, Lu L (2008) Central amygdala extracellular signal-regulated kinase signaling pathway is critical to incubation of opiate craving. J Neurosci 28:13248–57
Lu L, Hope BT, Dempsey J, Liu SY, Bossert JM, Shaham Y (2005) Central amygdala ERK signaling pathway is critical to incubation of cocaine craving. Nat Neurosci 8:212–9
Lu L, Uejima JL, Gray SM, Bossert JM, Shaham Y (2007) Systemic and central amygdala injections of the mGluR(2/3) agonist LY379268 attenuate the expression of incubation of cocaine craving. Biol Psychiatry 61:591–8
Lubin FD, Sweatt JD (2007) The IkappaB kinase regulates chromatin structure during reconsolidation of conditioned fear memories. Neuron 55:942–57
Luo YX, Xue YX, Shen HW, Lu L (2013) Role of amygdala in drug memory. Neurobiol Learn Mem 105:159–73
Luskin MB, Price JL (1983) The topographic organization of associational fibers of the olfactory system in the rat, including centrifugal fibers to the olfactory bulb. J Comp Neurol 216:264–91
Maddox SA, Watts CS, Schafe GE (2013) p300/CBP histone acetyltransferase activity is required for newly acquired and reactivated fear memories in the lateral amygdala. Learning & memory (Cold Spring Harbor, NY) 20:109–19
Maren S (2001) Neurobiology of Pavlovian fear conditioning. Annu Rev Neurosci 24:897–931
Maren S (2005a) Building and burying fear memories in the brain. Neuroscientist: Rev J bringing Neurobiol, Neurol Psychiatry 11:89–99
Maren S (2005b) Synaptic mechanisms of associative memory in the amygdala. Neuron 47:783–6
Maren S, Phan KL, Liberzon I (2013) The contextual brain: implications for fear conditioning, extinction and psychopathology. Nat Rev Neurosci 14:417–28
Martinez LA, Klann E, Tejada-Simon MV (2007) Translocation and activation of Rac in the hippocampus during associative contextual fear learning. Neurobiol Learn Mem 88:104–13
McGaugh JL (1966) Time-dependent processes in memory storage. Science (New York, NY) 153:1351–8
McGaugh JL (2000) Memory–a century of consolidation. Science (New York, NY) 287:248–51
McKenzie S, Eichenbaum H (2011) Consolidation and reconsolidation: two lives of memories? Neuron 71:224–33
Miki H, Suetsugu S, Takenawa T (1998) WAVE, a novel WASP-family protein involved in actin reorganization induced by Rac. EMBO J 17:6932–41
Monfils MH, Cowansage KK, Klann E, LeDoux JE (2009) Extinction-reconsolidation boundaries: key to persistent attenuation of fear memories. Science (New York, NY) 324:951–5
Nader K, Hardt O (2009) A single standard for memory: the case for reconsolidation. Nat Rev Neurosci 10:224–34
Nader K, Schafe GE, Le Doux JE (2000) Fear memories require protein synthesis in the amygdala for reconsolidation after retrieval. Nature 406:722–6
Nobes CD, Hall A (1995) Rho, rac, and cdc42 GTPases regulate the assembly of multimolecular focal complexes associated with actin stress fibers, lamellipodia, and filopodia. Cell 81:53–62
Nomura H, Nonaka A, Imamura N, Hashikawa K, Matsuki N (2012) Memory coding in plastic neuronal subpopulations within the amygdala. NeuroImage 60:153–61
Olshavsky ME, Song BJ, Powell DJ, Jones CE, Monfils MH, Lee HJ (2013) Updating appetitive memory during reconsolidation window: critical role of cue-directed behavior and amygdala central nucleus. Frontiers Behav Neurosci 7:186
Pare D, Quirk GJ, Ledoux JE (2004) New vistas on amygdala networks in conditioned fear. J Neurophysiol 92:1–9
Pitts MW, Todorovic C, Blank T, Takahashi LK (2009) The central nucleus of the amygdala and corticotropin-releasing factor: insights into contextual fear memory. J Neurosci: Official J Soc Neurosci 29:7379–88
Rajnicek AM, Foubister LE, McCaig CD (2006) Temporally and spatially coordinated roles for Rho, Rac, Cdc42 and their effectors in growth cone guidance by a physiological electric field. J Cell Sci 119:1723–35
Rau V, DeCola JP, Fanselow MS (2005) Stress-induced enhancement of fear learning: an animal model of posttraumatic stress disorder. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 29:1207–23
Ridley AJ, Paterson HF, Johnston CL, Diekmann D, Hall A (1992) The small GTP-binding protein rac regulates growth factor-induced membrane ruffling. Cell 70:401–10
Roozendaal B, Schelling G, McGaugh JL (2008) Corticotropin-releasing factor in the basolateral amygdala enhances memory consolidation via an interaction with the beta-adrenoceptor-cAMP pathway: dependence on glucocorticoid receptor activation. J Neurosci: Off J Soc Neurosci 28:6642–51
Rudy JW, Huff NC, Matus-Amat P (2004) Understanding contextual fear conditioning: insights from a two-process model. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 28:675–85
Sacchetti B, Lorenzini CA, Baldi E, Tassoni G, Bucherelli C (1999) Auditory thalamus, dorsal hippocampus, basolateral amygdala, and perirhinal cortex role in the consolidation of conditioned freezing to context and to acoustic conditioned stimulus in the rat. J Neurosci: Off J Soc Neurosci 19:9570–8
Sah P, Faber ES, Lopez De Armentia M, Power J (2003) The amygdaloid complex: anatomy and physiology. Physiol Rev 83:803–34
Sah P, Westbrook RF (2008) Behavioural neuroscience: the circuit of fear. Nature 454:589–90
Sahai E, Marshall CJ (2002) RHO-GTPases and cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 2:133–42
Sananbenesi F, Fischer A, Wang X, Schrick C, Neve R, Radulovic J, Tsai LH (2007) A hippocampal Cdk5 pathway regulates extinction of contextual fear. Nat Neurosci 10:1012–9
Schafe GE, LeDoux JE (2000) Memory consolidation of auditory pavlovian fear conditioning requires protein synthesis and protein kinase A in the amygdala. J Neurosci: Off J Soc Neurosci 20:RC96
Si J, Yang J, Xue L, Yang C, Luo Y, Shi H, Lu L (2012) Activation of NF-kappaB in basolateral amygdala is required for memory reconsolidation in auditory fear conditioning. PloS One 7:e43973
Stehberg J, Moraga-Amaro R, Salazar C, Becerra A, Echeverria C, Orellana JA, Bultynck G, Ponsaerts R, Leybaert L, Simon F, Saez JC, Retamal MA (2012) Release of gliotransmitters through astroglial connexin 43 hemichannels is necessary for fear memory consolidation in the basolateral amygdala. FASEB J: Off Publ Fed Am Soc Exp Biol 26:3649–57
Strekalova T, Zorner B, Zacher C, Sadovska G, Herdegen T, Gass P (2003) Memory retrieval after contextual fear conditioning induces c-Fos and JunB expression in CA1 hippocampus. Genes Brain Behav 2:3–10
Tayler KK, Tanaka KZ, Reijmers LG, Wiltgen BJ (2013) Reactivation of neural ensembles during the retrieval of recent and remote memory. Curr Biol: CB 23:99–106
Tejada-Simon MV, Villasana LE, Serrano F, Klann E (2006) NMDA receptor activation induces translocation and activation of Rac in mouse hippocampal area CA1. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 343:504–12
Thomas KL, Arroyo M, Everitt BJ (2003) Induction of the learning and plasticity-associated gene Zif268 following exposure to a discrete cocaine-associated stimulus. Eur J Neurosci 17:1964–72
Vazdarjanova A, McGaugh JL (1999) Basolateral amygdala is involved in modulating consolidation of memory for classical fear conditioning. J Neurosci: Off J Soc Neurosci 19:6615–22
von Hertzen LS, Giese KP (2005) Memory reconsolidation engages only a subset of immediate-early genes induced during consolidation. J Neurosci: Off J Soc Neurosci 25:1935–42
Wang XY, Zhao M, Ghitza UE, Li YQ, Lu L (2008) Stress impairs reconsolidation of drug memory via glucocorticoid receptors in the basolateral amygdala. J Neurosci: Off J Soc Neurosci 28:5602–10
Xue YX, Luo YX, Wu P, Shi HS, Xue LF, Chen C, Zhu WL, Ding ZB, Bao YP, Shi J, Epstein DH, Shaham Y, Lu L (2012) A memory retrieval-extinction procedure to prevent drug craving and relapse. Science (New York, NY) 336:241–5
Yang C, Liu JF, Chai BS, Fang Q, Chai N, Zhao LY, Xue YX, Luo YX, Jian M, Han Y, Shi HS, Lu L, Wu P, Wang JS (2013) Stress within a restricted time window selectively affects the persistence of long-term memory. PloS one 8:e59075
Yim AJ, Moraes CR, Ferreira TL, Oliveira MG (2006) Protein synthesis inhibition in the basolateral amygdala following retrieval does not impair expression of morphine-associated conditioned place preference. Behav Brain Res 171:162–9
Zhu WL, Shi HS, Wang SJ, Wu P, Ding ZB, Lu L (2011) Hippocampal CA3 calcineurin activity participates in depressive-like behavior in rats. J Neurochem 117:1075–86
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Natural Science Foundation of China (no. 81201032, 31230033, and 8H1225009). The authors declare that they do not have any conflicts of interest (financial or otherwise) related to the data presented in this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Ping Wu and Zeng-Bo Ding Equally contributed to this work
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, P., Ding, ZB., Meng, SQ. et al. Differential role of Rac in the basolateral amygdala and cornu ammonis 1 in the reconsolidation of auditory and contextual Pavlovian fear memory in rats. Psychopharmacology 231, 2909–2919 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-014-3462-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-014-3462-0