Abstract
Rationale
Several compounds that potentiate GABA-induced inhibitory currents also decrease stress, anxiety and addiction-related behaviors. Because of the well-established connection between stress and addiction, compounds that reduce stress-induced responses might be efficacious in treating addiction. Since endogenous neurosteroids such as allopregnanolone may function in a manner similar to benzodiazepines to reduce HPA axis activation and anxiety following stressful stimuli, we hypothesized that exogenously applied neurosteroids would reduce cocaine reinforcement in two animal models.
Methods
Male Wistar rats were trained to self-administer cocaine and food under a concurrent alternating operant schedule of reinforcement. Two separate groups of rats were trained to self-administer cocaine or food pellets and were then exposed to similar cue-induced reinstatement paradigms. Both groups of rats were pretreated with various doses of neurosteroids.
Results
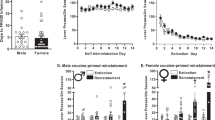
Allopregnanolone and 3α-hydroxy-3β-methyl-17β-nitro-5α-androstane (R6305-7, a synthetic neurosteroid) were ineffective in selectively decreasing cocaine relative to food self-administration. On the other hand, both allopregnanolone and R6305-7 significantly decreased the cue-induced reinstatement of extinguished cocaine seeking, confirmed by one-way ANOVA.
Conclusions
These results suggest that neurosteroids may be effective in reducing the relapse to cocaine use without affecting ongoing cocaine self-administration.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agís-Balboa RC, Pinna G, Zhubi A et al (2006) Characterization of brain neurons that express enzymes mediating neurosteroid biosynthesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 103:14602–14607
Akwa Y, Purdy RH, Koob GF, Britton KT (1999) The amygdala mediates the anxiolytic-like effect of the neurosteroid allopregnanolone in rat. Behav Brain Res 106:119–125
Andréen L, Nyberg S, Turkmen S et al (2009) Sex steroid induced negative mood may be explained by the paradoxical effect mediated by GABAA modulators. Psychoneuroendocrinology 34:1121–1132
Anker JJ, Carroll ME (2010) Sex differences in the effects of allopregnanolone on yohimbine-induced reinstatement of cocaine seeking in rats. Drug Alcohol Depend 107:264–267
Anker JJ, Larson EB, Gliddon LA, Carroll ME (2007) Effects of progesterone on the reinstatement of cocaine-seeking behavior in female rats. Exp Clin Psychopharmacol 15:472–480
Anker JJ, Holtz NA, Zlebnik N, Carroll ME (2009) Effects of allopregnanolone on the reinstatement of cocaine-seeking behavior in male and female rats. Psychopharmacology 203:63–72
Bäckström T, Haage D, Löfgren M et al (2011) Paradoxical effects of GABA-A modulators may explain sex steroid induced negative mood symptoms in some persons. Neuroscience 191:46–54
Barker JL, Harrison NL, Lange GD, Owen DG (1987) Potentiation of gamma-aminobutyric-acid-activated chloride conductance by a steroid anaesthetic in cultured rat spinal neurones. J Physiol 386:485–501
Barrett AC, Negus SS, Mello NK, Caine SB (2005) Effect of GABA agonists and GABA-A receptor modulators on cocaine- and food-maintained responding and cocaine discrimination in rats. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 315(2):858–871
Bianchi MT, Haas KF, Macdonald RL (2002) Alpha1 and alpha6 subunits specify distinct desensitization, deactivation and neurosteroid modulation of GABA(A) receptors containing the delta subunit. Neuropharmacology 43(4):492–502
Bitran D, Hilvers RJ, Kellogg CK (1991) Anxiolytic effects of 3 alpha-hydroxy-5 alpha[beta]-pregnan-20-one: endogenous metabolites of progesterone that are active at the GABAA receptor. Brain Res 561(1):157–161
Campbell UC, Carroll ME (2001) Effects of ketoconazole on the acquisition of intravenous cocaine self-administration under different feeding conditions in rats. Psychopharmacology 154(3):311–318
Carroll ME, Meisch RA (1981) Determinants of increased drug self-administration due to food deprivation. Psychopharmacology 74(3):197–200
Carter RB, Wood PL, Wieland S et al (1997) Characterization of the anticonvulsant properties of ganaxolone (CCD 1042; 3alpha-hydroxy-3beta-methyl-5alpha-pregnan-20-one), a selective, high-affinity, steroid modulator of the gamma-aminobutyric acid(A) receptor. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 280:1284–1295
Crawley JN, Glowa JR, Majewska MD, Paul SM (1986) Anxiolytic activity of an endogenous adrenal steroid. Brain Res 398:382–385
Deo GS, Dandekar MP, Upadhya MA et al (2010) Neuropeptide Y Y1 receptors in the central nucleus of amygdala mediate the anxiolytic-like effect of allopregnanolone in mice: behavioral and immunocytochemical evidences. Brain Res 1318:77–86
Engin E, Treit D (2007) The anxiolytic-like effects of allopregnanolone vary as a function of intracerebral microinfusion site: the amygdala, medial prefrontal cortex, or hippocampus. Behav Pharmacol 18:461–470
Feltenstein MW, See RE (2007) Plasma progesterone levels and cocaine-seeking in freely cycling female rats across the estrous cycle. Drug Alcohol Depend 89(2–3):183–189
Festa ED, Jenab S, Chin J, Gazi FM, Wu HB, Russo SJ, Quinones-Jenab V (2003) Frequency of cocaine administration affects behavioral and endocrine responses in male and female Fischer rats. Cell Mol Biol (Noisy-le-grand) 49(8):1275–1280
Finn DA, Roberts AJ, Long S et al (2003) Neurosteroid consumption has anxiolytic effects in mice. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 76:451–462
Fox HC, Hong K-IA, Siedlarz K, Sinha R (2008) Enhanced sensitivity to stress and drug/alcohol craving in abstinent cocaine-dependent individuals compared to social drinkers. Neuropsychopharmacology 33:796–805
Frye CA (2007) Progestins influence motivation, reward, conditioning, stress, and/or response to drugs of abuse. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 86(2):209–219, Review
Fuchs RA, Evans KA, Mehta RH et al (2005) Influence of sex and estrous cyclicity on conditioned cue-induced reinstatement of cocaine-seeking behavior in rats. Psychopharmacology 179:662–672
Fuchs RA, Feltenstein MW, See RE (2006) The role of the basolateral amygdala in stimulus-reward memory and extinction memory consolidation and in subsequent conditioned cued reinstatement of cocaine seeking. Eur J Neurosci 23:2809–2813
Gabriele A, See RE (2010) Reversible inactivation of the basolateral amygdala, but not the dorsolateral caudate putamen, attenuates consolidation of cocaine-cue associative learning in a reinstatement model of drug-seeking. Eur J Neurosci 32:1024–1029
Goeders NE, Guerin GF (2008) Effects of the combination of metyrapone and oxazepam on cocaine and food self-administration in rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 91:181–189
Goeders NE, Ikemoto S, Dorairaj NR, Simpson ST, Guerin GF (1997) Effects of initial exposure to saline in rats trained under a multiple schedule of food reinforcement and cocaine self-administration. Neurosci Abstr 23:1095
Goeders NE, Clampitt DM, Keller C et al (2009) Alprazolam and oxazepam block the cue-induced reinstatement of extinguished cocaine seeking in rats. Psychopharmacology 201:581–588
Grobin AC, VanDoren MJ, Porrino LJ, Morrow AL (2005) Cortical 3 alpha-hydroxy-5 alpha-pregnan-20-one levels after acute administration of Delta 9-tetrahydrocannabinol, cocaine and morphine. Psychopharmacology 179:544–550
Gulacsi A, Lee CR, Sík A, Viitanen T, Kaila K, Tepper JM, Freund TF (2003) Cell type-specific differences in chloride-regulatory mechanisms and GABA(A) receptor-mediated inhibition in rat substantia nigra. J Neurosci 23(23):8237–8246
Hirani K, Sharma AN, Jain NS et al (2005) Evaluation of GABAergic neuroactive steroid 3alpha-hydroxy-5alpha-pregnane-20-one as a neurobiological substrate for the anti-anxiety effect of ethanol in rats. Psychopharmacology 180:267–278
Jackson LR, Robinson TE, Becker JB (2006) Sex differences and hormonal influences on acquisition of cocaine self-administration in rats. Neuropsychopharmacology 31(1):129–138
Jaworska-Feil L (1998) Opposite effects of inhibitory and excitatory neurosteroids on dopamine release from rat nucleus accumbens. Pol J Pharmacol 50:449–452
Kalivas PW (2007) Neurobiology of cocaine addiction: implications for new pharmacotherapy. Am J Addict 16(2):71–78, Review
Kaminski RM, Gasior M, Carter RB, Witkin JM (2003) Protective efficacy of neuroactive steroids against cocaine kindled-seizures in mice. Eur J Pharmacol 474(2–3):217–222
Keller CM, Cornett EM, Guerin GF, Goeders NE (2013) Combinations of oxazepam and metyrapone attenuate cocaine and methamphetamine cue reactivity. Drug Alcohol Depend 133(2):405–412
Kerstetter KA, Aguilar VR, Parrish AB, Kippin TE (2008) Protracted time-dependent increases in cocaine-seeking behavior during cocaine withdrawal in female relative to male rats. Psychopharmacol (Berl) 198:63–75
Kippin TE, Fuchs RA, Mehta RH, Case JM, Parker MP, Bimonte-Nelson HA, See RE (2005) Potentiation of cocaine-primed reinstatement of drug seeking in female rats during estrus. Psychopharmacol (Berl) 182(2):245–252
Lan NC, Bolger MB, Gee KW (1991) Identification and characterization of a pregnane steroid recognition site that is functionally coupled to an expressed GABAA receptor. Neurochem Res 16:347–356
Larson EB, Anker JJ, Gliddon LA, Fons KS, Carroll ME (2007) Effects of estrogen and progesterone on the escalation of cocaine self-administration in female rats during extended access. Exp Clin Psychopharmacol 15(5):461–471
Lee JLC, Milton AL, Everitt BJ (2006) Cue-induced cocaine seeking and relapse are reduced by disruption of drug memory reconsolidation. J Neurosci 26:5881–5887
Leśkiewicz M, Budziszewska B, Jaworska-Feil L, Kubera M, Basta-Kaim A, Lasoń W (2003) Inhibitory effect of some neuroactive steroids on cocaine-induced kindling in mice. Pol J Pharmacol 55(6):1131–1136
Lynch WJ (2008) Acquisition and maintenance of cocaine self-administration in adolescent rats: effects of sex and gonadal hormones. Psychopharmacol (Berl) 197(2):237–246
Lynch WJ, Carroll ME (1999) Sex differences in the acquisition of intravenously self-administered cocaine and heroin in rats. Psychopharmacol (Berl) 144(1):77–82
Mellon SH, Griffin LD, Compagnone NA (2001) Biosynthesis and action of neurosteroids. Brain Res Rev 37:3–12
Motzo C, Porceddu ML, Maira G et al (1996) Inhibition of basal and stress-induced dopamine release in the cerebral cortex and nucleus accumbens of freely moving rats by the neurosteroid allopregnanolone. J Psychopharmacol 10:266–272
Negus SS, Mello NK, Fivel PA (2000) Effects of GABA agonists and GABA-A receptor modulators on cocaine discrimination in rhesus monkeys. Psychopharmacol (Berl) 152(4):398–407
Niyomchai T, Jenab S, Festa ED, Akhavan A, Quiñones-Jenab V (2006) Effects of short- and long-term estrogen and progesterone replacement on behavioral responses and c-fos mRNA levels in female rats after acute cocaine administration. Brain Res 1126(1):193–199
Peltier RL, Guerin GF, Dorairaj N, Goeders NE (2001) Effects of saline substitution on responding and plasma corticosterone in rats trained to self-administer different doses of cocaine. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 299(1):114–120
Peris J (1996) Repeated cocaine injections decrease the function of striatal gamma-aminobutyric acid(A) receptors. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 276(3):1002–1008
Perrotti LI, Russo SJ, Fletcher H, Chin J, Webb T, Jenab S, Quiñones-Jenab V (2001) Ovarian hormones modulate cocaine-induced locomotor and stereotypic activity. Ann N Y Acad Sci 937:202–216
Pillai GV, Smith AJ, Hunt PA, Simpson PB (2004) Multiple structural features of steroids mediate subtype-selective effects on human alpha4beta3delta GABAA receptors. Biochem Pharmacol 68(5):819–831
Quinones-Jenab V, Jenab S (2010) Progesterone attenuates cocaine-induced responses. Horm Behav 58(1):22–32
Quinones-Jenab V, Perrotti LI, Mc Monagle J, Ho A, Kreek MJ (2000) Ovarian hormone replacement affects cocaine-induced behaviors in ovariectomized female rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 67(3):417–422
Quinones-Jenab V, Minerly ACE, Niyomchia T et al (2008) Progesterone and allopregnanolone are induced by cocaine in serum and brain tissues of male and female rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 89:292–297
Quinton MS, Gerak LR, Moerschbaecher JM, Winsauer PJ (2006) Effects of pregnanolone in rats discriminating cocaine. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 85:385–392
Reddy DS, Rogawski MA (2002) Stress-induced deoxycorticosterone-derived neurosteroids modulate GABA(A) receptor function and seizure susceptibility. J Neurosci 22(9):3795–3805
Roberts DC, Koob GF (1982) Disruption of cocaine self-administration following 6-hydroxydopamine lesions of the ventral tegmental area in rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 17(5):901–904
Roberts DC, Koob GF, Klonoff P, Fibiger HC (1980) Extinction and recovery of cocaine self-administration following 6-hydroxydopamine lesions of the nucleus accumbens. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 12(5):781–787
Roberts DC, Bennett SA, Vickers GJ (1989) The estrous cycle affects cocaine self-administration on a progressive ratio schedule in rats. Psychopharmacol (Berl) 98(3):408–411
Rodgers RJ, Johnson NJ (1998) Behaviorally selective effects of neuroactive steroids on plus-maze anxiety in mice. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 59(1):221–232
Romieu P, Martin-Fardon R, Bowen WD, Maurice T (2003) Sigma 1 receptor-related neuroactive steroids modulate cocaine-induced reward. J Neurosci 23:3572–3576
Romieu P, Lucas M, Maurice T (2006) Sigma1 receptor ligands and related neuroactive steroids interfere with the cocaine-induced state of memory. Neuropsychopharmacology 31:1431–1443
Roth ME, Carroll ME (2004) Sex differences in the escalation of intravenous cocaine intake following long- or short-access to cocaine self-administration. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 78(2):199–207
Runyon SP, Orr M, Navarro HA et al (2009) 17beta-Nitro-5alpha-androstan-3alpha-ol and its 3beta-methyl derivative: neurosteroid analogs with potent anticonvulsant and anxiolytic activities. Eur J Pharmacol 617:68–73
Rupprecht R (2003) Neuroactive steroids: mechanisms of action and neuropsychopharmacological properties. Psychoneuroendocrinology 28:139–168
Rupprecht R, Holsboer F (1999) Neuroactive steroids: mechanisms of action and neuropsychopharmacological perspectives. Trends Neurosci 22:410–416
Russo SJ, Festa ED, Fabian SJ, Gazi FM, Kraish M, Jenab S, Quiñones-Jenab V (2003) Gonadal hormones differentially modulate cocaine-induced conditioned place preference in male and female rats. Neuroscience 120(2):523–533
See RE (2002) Neural substrates of conditioned-cued relapse to drug-seeking behavior. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 71(3):517–529
Shen H, Gong QH, Aoki C et al (2007) Reversal of neurosteroid effects at alpha4beta2delta GABAA receptors triggers anxiety at puberty. Nat Neurosci 10:469–477
Shirayama Y, Muneoka K, Fukumoto M et al (2011) Infusions of allopregnanolone into the hippocampus and amygdala, but not into the nucleus accumbens and medial prefrontal cortex, produce antidepressant effects on the learned helplessness rats. Hippocampus 21:1105–1113
Sinha R, Talih M, Malison R et al (2003) Hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis and sympatho-adreno-medullary responses during stress-induced and drug cue-induced cocaine craving states. Psychopharmacology 170:62–72
Sinha R, Garcia M, Paliwal P et al (2006) Stress-induced cocaine craving and hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal responses are predictive of cocaine relapse outcomes. Arch Gen Psychiatry 63:324–331
Smith SS (1994) Female sex steroid hormones: from receptors to networks to performance—actions on the sensorimotor system. Prog Neurobiol 44(1):55–86, Review
Sofuoglu M, Kosten TR (2006) Emerging pharmacological strategies in the fight against cocaine addiction. Expert Opin Emerg Drugs 11(1):91–98, Review
Sundström I, Bäckström T, Wang M et al (1999) Premenstrual syndrome, neuroactive steroids and the brain. Gynecol Endocrinol Off J Int Soc Gynecol Endocrinol 13:206–220
Ugale RR, Sharma AN, Kokare DM et al (2007) Neurosteroid allopregnanolone mediates anxiolytic effect of etifoxine in rats. Brain Res 1184:193–201
Uzunova V, Ceci M, Kohler C et al (2003) Region-specific dysregulation of allopregnanolone brain content in the olfactory bulbectomized rat model of depression. Brain Res 976:1–8
Vanover KE, Suruki M, Huber M, Wilent WB, Carter RB (2000) Neuroactive steroids attenuate cocaine-induced sucrose intake in rats, but not cocaine-induced hyperactivity in mice. Psychopharmacol (Berl) 149(3):269–276
Vocci F, Ling W (2005) Medications development: successes and challenges. Pharmacol Ther 108(1):94–108
Volkow ND, Wang G-J, Telang F et al (2006) Cocaine cues and dopamine in dorsal striatum: mechanism of craving in cocaine addiction. J Neurosci 26:6583–6588
Wang C, Marx CE, Morrow AL et al (2007) Neurosteroid modulation of GABAergic neurotransmission in the central amygdala: a role for NMDA receptors. Neurosci Lett 415:118–123
Weerts EM, Froestl W, Griffiths RR (2005) Effects of GABAergic modulators on food and cocaine self-administration in baboons. Drug Alcohol Depend 80(3):369–376
Wieland S, Lan NC, Mirasedeghi S, Gee KW (1991) Anxiolytic activity of the progesterone metabolite 5 alpha-pregnan-3 alpha-o1-20-one. Brain Res 565(2):263–268
Wieland S, Belluzzi JD, Stein L, Lan NC (1995) Comparative behavioral characterization of the neuroactive steroids 3 alpha-OH,5 alpha-pregnan-20-one and 3 alpha-OH,5 beta-pregnan-20-one in rodents. Psychopharmacology 118:65–71
Wilson MA, Biscardi R (1997) Influence of gender and brain region on neurosteroid modulation of GABA responses in rats. Life Sci 60:1679–1691
Funding source
Research was financially supported by institutional funding from the Department of Pharmacology, Toxicology & Neuroscience and Research Triangle Institute.
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schmoutz, C.D., Runyon, S.P. & Goeders, N.E. Effects of inhibitory GABA-active neurosteroids on cocaine seeking and cocaine taking in rats. Psychopharmacology 231, 3391–3400 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-013-3404-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-013-3404-2