Abstract
Rationale
It has been proposed that drugs of abuse reinforce behavior partly, or wholly, because they facilitate learning by enhancing memory consolidation. Cocaine can clearly serve as a reinforcer, but its effect on learning has not been fully characterized.
Objectives
To explore the effects of different regimens of pre- and post-training cocaine administration on win-stay and object learning.
Methods
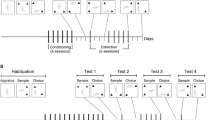
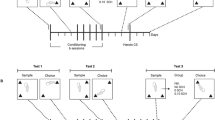
Cocaine naïve and cocaine pre-exposed (30 mg/kg/day, ×5 days followed by 7 days drug-free) male Sprague-Dawley rats received cocaine (0, 1, 2.5, 7.5, or 20 mg/kg, i.p.) immediately following training on a win-stay task in a radial maze or following the sample phase of an object learning task. Win-stay performance was also assessed in tests of extinction and after a set shift.
Results
Post-training cocaine did not improve accuracy on the win-stay task and produced performance deficits at 20 mg/kg. These deficits were attenuated by prior cocaine exposure. There was indirect evidence of facilitated learning in extinction and set shift tests, but the effective dosage was different (2.5 and 7.5 mg/kg, respectively). Post-training cocaine produced dose-dependent improvements in object learning.
Conclusion
Post-training cocaine administration can facilitate learning, but this effect is highly dependent on the dose and the type of task employed.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allen CP, Leri F (2010) Effect of acute and repeated cocaine exposure on response matching capabilities of Sprague-Dawley rats responding for sucrose on concurrent schedules of reinforcement. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 96:96–103
Arroyo M, Markou A, Robbins TW, Everitt B (1998) Acquisition, maintenance and reinstatement of intravenous cocaine self-administration under a second-order schedule of reinforcement in rats: effects of conditioned cues and continuous access to cocaine. Psychopharmacology 140:331–344
Balderas I, Moreno-Castilla P, Bermudez-Rattoni F (2013) Dopamine D1 receptor activity modulates object recognition memory consolidation in the perirhinal cortex but not in the hippocampus. Hippocampus. doi:10.1002/hipo.22143
Balderas I, Rodriguez-Ortiz CJ, Salgado-Tonda P, Chavez-Hurtado J, McGaugh JL, Bermudez-Rattoni F (2008) The consolidation of object and context recognition memory involve different regions of the temporal lobe. Learn Mem 15:618–624
Bardo MT, Rowlett JK, Harris M (1995) Conditioned place preference using opiate and stimulant drugs: a meta-analysis. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 19:39–51
Brown MW, Barker GR, Aggleton JP, Warburton EC (2012) What pharmacological interventions indicate concerning the role of the perirhinal cortex in recognition memory. Neuropsychologia 50:3122–3140
Cahill L, McGaugh JL (1990) Amygdaloid complex lesions differentially affect retention of tasks using appetitive and aversive reinforcement. Behav Neurosci 104:532–543
Cappell H, LeBlanc AE (1975) Modification of the punishing effects of psychoactive drugs in rats by previous drug experience. J Comp Physiol Psychol 89:347–356
Castellano C, Zocchi A, Cabib S, Puglisi-Allegra S (1996) Strain-dependent effects of cocaine on memory storage improvement induced by post-training physostigmine. Psychopharmacology 123:340–345
Cloke JM, Rkieh N, Leri F (2013) Effect of post-training administration of cocaine, diazepam and their combination on a win-stay task. Pharmacol Biochem Behav, Nov 15;116C:69-74. doi:10.1016/j.pbb.2013.11.010
da Silveira CK, Furini CR, Benetti F, Monteiro C, Izquierdo I (2013) The role of histamine receptors in the consolidation of object recognition memory. Neurobiol Learn Mem 103:64–71
de Lima MN, Presti-Torres J, Dornelles A, Scalco FS, Roesler R, Garcia VA, Schroder N (2011) Modulatory influence of dopamine receptors on consolidation of object recognition memory. Neurobiol Learn Mem 95:305–310
Dornelles A, de Lima MN, Grazziotin M, Presti-Torres J, Garcia VA, Scalco FS, Roesler R, Schroder N (2007) Adrenergic enhancement of consolidation of object recognition memory. Neurobiol Learn Mem 88:137–142
Ersche KD, Roiser JP, Robbins TW, Sahakian BJ (2008) Chronic cocaine but not chronic amphetamine use is associated with perseverative responding in humans. Psychopharmacology 197:421–431
Ettenberg A, Geist TD (1991) Animal model for investigating the anxiogenic effects of self-administered cocaine. Psychopharmacology 103:455–461
Fillmore MT, Rush CR (2006) Polydrug abusers display impaired discrimination-reversal learning in a model of behavioural control. J Psychopharmacol 20:24–32
Foltin RW, Christiansen I, Levin FR, Fischman MW (1995) Effect of single and multiple intravenous cocaine injections in humans maintained on methadone. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 275:38–47
Freeman KB, Riley AL (2005) Cocaine-induced conditioned taste avoidance over extended conditioned stimulus-unconditioned stimulus intervals. Behav Pharmacol 16:591–595
Furinini CR, Rossato JI, Bitencourt LL, Medina JH, Izquierdo I, Cammarota M (2010) Beta-adrenergic receptors link NO/sGC/PKG signaling to BDNF expression during the consolidation of object recognition long-term memory. Hippocampus 20:672–683
Galuska CM, Woods JH (2005) Acquisition of cocaine self-administration with unsignaled delayed reinforcement in rhesus monkeys. J Exp Anal Behav 84:269–280
Goudie AJ, Dickins DW, Thornton EW (1978) Cocaine-induced conditioned taste aversions in rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 8:757–761
Goulart BK, de Lima MN, de Farias CB, Reolon GK, Almeida VR, Quevedo J, Kapczinski F, Schroder N, Roesler R (2010) Ketamine impairs recognition memory consolidation and prevents learning-induced increase in hippocampal brain-derived neurotrophic factor levels. Neuroscience 167:969–973
Grigson PS (1997) Conditioned taste aversions and drugs of abuse: a reinterpretation. Behav Neurosci 111:129–136
Hull C (1943) Principles of behavior: An introduction to behavior theory. Appleton-Century-Crofts, New York
Hunt T, Amit Z (1986) Conditioned taste aversion induced by self-administered drugs: paradox revisited. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 11:107–130
Huston JP, Mueller C, Mondadori C (1977) Memory facilitation by posttrial hypothalamic stimulation and other reinforcers: a central theory of reinforcement. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 1:143–150
Huston JP, Oitzl MS (1989) The relationship between reinforcement and memory: parallels in the rewarding and mnemonic effects of the neuropeptide substance P. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 13:171–180
Ill-Raga G, Kohler C, Radiske A, Lima RH, Rosen MD, Munoz FJ, Cammarota M (2013) Consolidation of object recognition memory requires HRI kinase-dependent phosphorylation of eIF2a in the hippocampus. Hippocampus 6:431–436
Inagaki T, Gautreaux C, Luine V (2010) Acute estrogen treatment facilitates recognition memory consolidation and alters monoamine levels in memory-related brain areas. Horm Behav 58:415–426
Iniguez SD, Charntikov S, Baella SA, Herbert MS, Bolanos-Guzman CA, Crawford CA (2012) Post-training cocaine exposure facilitates spatial memory consolidation in C7BL/6 mice. Hippocampus 22:802–813
Introini-Collison IB, McGaugh JL (1989) Cocaine enhances memory storage in mice. Psychopharmacology 99:537–541
Janak PH, Keppel G, Martinez JL Jr (1992) Cocaine enhances retention of avoidance conditioning in rats. Psychopharmacology 106:383–387
Koob GF, Le Moal M (2006) Neurobiology of addiction. Academic, London
Leri F, Nahas E, Henderson K, Limebeer CL, Parker LA, White NM (2013) Effects of post-training heroin and d-amphetamine on consolidation of win-stay learning and fear conditioning. J Neuropsychopharmacol 27:292–301
Leri F, Zhou Y, Goddard B, Cummins E, Kreek MJ (2006) Effects of high-dose methadone maintenance on cocaine place conditioning, cocaine self-administration, and mu-opioid receptors mRNA expression in the rat brain. Neuropsychopharmacology 31:1462–1474
Lima RH, Rossato JI, Furini CR, Bevilaqua LR, Izquierdo I, Cammarota M (2009) Infusion of protein synthesis inhibitors in the entorhinal cortex blocks consolidation but not reconsolidation of object recognition memory. Neurobiol Learn Mem 91:466–472
MacPhail RC (1982) Studies on the flavor aversions induced by trialkyltin compounds. Neurobehav Toxicol Teratol 4:225–230
Mayer LA, Parker LA (1993) Rewarding and aversive properties of IP and SC cocaine: assessment by place and taste conditioning. Psychopharmacology 112:189–194
McGaugh JL (1966) Time-dependent processes in memory storage. Science 153:1352–1358
McGaugh JL (2000) Memory—a century of consolidation. Science 287:348–351
Mello-Carpes PB, Izquierdo I (2013) The nucleus of the solitary tract ->nucleus paragigantocellularis ->locus coeruleus ->CA1 region of dorsal hippocampus pathway is important for consolidation of object recognition memory. Neurobiol Learn Mem 100:56–63
Olmstead MC, Parkinson JA, Miles FJ, Everitt BJ, Dickinson A (2000) Cocaine-seeking by rats: regulation, reinforcement and activation. Psychopharmacology 152:123–131
Packard MG, White NM (1989) Memory facilitation produced by dopamine agonists: role of receptor subtype and mnemonic requirements. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 33:511–518
Parker LA (1984) Behavioral conditioned responses across multiple conditioning/testing trials elicited by lithium- and amphetamine-paired flavors. Behav Neural Biol 41:190–199
Parker LA (1993) Taste reactivity responses elicited by cocaine-, phencyclidine- and methamphetamine-paired sucrose solutions. Behav Neurosci 107:118–129
Parker LA (1995) Rewarding drugs produce taste avoidance, but not taste aversion. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 19:143–157
Parker LA (2003) Taste avoidance and taste aversion: evidence for two different processes. Learn Behav 31:165–172
Puglisi-Allegra S, Cestari V, Cabib C, Castellano C (1994) Strain-dependent effects of post-training cocaine or nomifensine on memory storage involve both D1 and D2 dopamine receptors. Psychopharmacology 115:157–162
Reichel CM, Wilkinson JL, Bevins RA (2010) Reference place conditioning procedure with cocaine: increased sensitivity for measuring associatively motivated choice behavior in rats. Behav Pharmacol 21:323–331
Reicher M, Holman E (1977) Location preference and flavor aversion reinforced by amphetamine in rats. Anim Learn Behav 5:343–346
Riley AL, Diamond HF (1998) The effects of cocaine preexposure on the acquisition of cocaine-induced taste aversions. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 60:739–745
Rogerio R, Takahashi RN (1992) Anxiogenic properties of cocaine in the rat evaluated with the elevated plus-maze. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 43:631–633
Roozendaal B, Castello NA, Vedana G, Barsegyan A, McGaugh JL (2008a) Noradrenergic activation of the basolateral amygdala modulates consolidation of object recognition memory. Neurobiol Learn Mem 90:576–579
Roozendaal B, Castello NA, Vedana G, Barsegyan A, McGaugh JL (2008b) Noradrenergic activation of the basolateral amygdala modulates consolidation of object recognition memory. Neurobiol Learn Mem 90:576–579
Rossato JI, Radiske A, Kohler CA, Gonzalez C, Bevilaqua LR, Medina JH, Cammarota M (2013) Consolidation of object recognition memory requires simultaneous activation of dopamine D(1)/D(5) receptors in the amygdala and medial prefrontal cortex but not in the hippocampus. Neurobiol Learn Mem 24:66–70
Schoenbaum G, Saddoris MP, Ramus SJ, Shaham Y, Setlow B (2004) Cocaine-experienced rats exhibit learning deficits in a task sensitive to orbitofrontal cortex lesions. Eur J Neurosci 19:1997–2002
Serafine KM, Briscione MA, Rice KC, Riley AL (2012) Dopamine mediates cocaine-induced conditioned taste aversions as demonstrated with cross-drug preexposure to GBR 12909. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 102:269274
Simon NW, Setlow B (2006) Post-training amphetamine administration enhances memory consolidation in appetitive Pavlovian conditioning: implications for drug addiction. Neurobiol Learn Mem 86:305–310
Stalnaker TA, Roesch MR, Franz TM, Burke KA, Schoenbaum G (2006) Abnormal associative encoding in orbitofrontal neurons in cocaine-experienced rats during decision-making. Eur J Neurosci 24:2643–2653
Thomsen M, Caine SB (2006) Cocaine self-administration under fixed and progressive ration reinforcement: comparison of C57BL/6 J, 129X1/SvJ, and129S6/SvEvTac inbred mice. Psychopharmacology 184:145–154
Underwood BJ (1957) Interference and forgetting. Psychol Rev 64:49–60
White NM (1996) Addictive drugs as reinforcers: multiple partial actions on memory systems. Addiction 91:921–949
White NM, Milner PM (1992) The psychobiology of reinforcers. Ann Rev Psychol 43:443–471
Wiig KA, Whitlock JR, Epstein MH, Carpenter RL, Bear MF (2009) The levo enantiomer of amphetamine increases memory consolidation and gene expression in the hippocampus without producing locomotor stimulation. Neurobiol Learn Mem 92:106–113
Winters BD, Bussey TJ (2005) Transient inactivation of perirhinal cortex disrupts encoding, retrieval, and consolidation of object recognition memory. J Neurosci 25:52–61
Wixted JT (2004) The psychology and neuroscience of forgetting. Annu Rev Psychol 55:235–269
Yang XM, Gorman AL, Dunn AJ, Goeders NE (1992) Neurochemical and behavioral studies. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 41:643–650
Acknowledgments
These studies are funded by the Natural Sciences and Research Council of Canada (NSERC).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rkieh, N., Cloke, J.M., Gallagher, N. et al. Drugs of abuse as memory modulators: a study of cocaine in rats. Psychopharmacology 231, 2339–2348 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-013-3390-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-013-3390-4