Abstract
Rationale
Initial lab studies suggest that adolescent drinkers crave alcohol when presented with alcohol cues. Whether this effect generalizes to the natural environment, however, remains unknown, and studies have not examined whether craving predicts drinking among youths.
Objectives
This study builds on existing research by pairing controlled lab-based cue reactivity assessments (CRAs) with data collected in the natural environment using ecological momentary assessment (EMA) methods. We examined whether alcohol cues evoke craving among adolescent drinkers in the lab and natural environment, and tested the clinical relevance of craving during adolescence by examining the prospective association between craving and alcohol use.
Methods
Non-treatment-seeking adolescent drinkers (N = 42; ages 15 to 20 years) completed a lab-based CRA followed by a 1-week EMA monitoring period. During the EMA period, youth were prompted randomly throughout the day to record momentary data on craving and contextual factors (e.g., alcohol cues, peers present).
Results
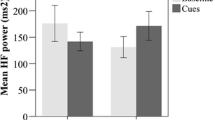
Alcohol cues elicited craving in the lab, and this effect generalized to the natural environment, especially among adolescents with more alcohol problems. In addition, craving predicted subsequent drinking levels in the natural environment.
Conclusions
This study demonstrates the utility of pairing lab paradigms with EMA methods to better characterize adolescents' reactivity to alcohol cues. Results implicate craving as a clinically meaningful motivator for drinking among adolescents and highlight a potentially important target of pharmacological or behavioral intervention.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ali MM, Dwyer DS (2010) Social network effects in alcohol consumption among adolescents. Addict Behav 35:337–342
American Psychiatric Association (2013) Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders, 5th edn, text revision. American Psychiatric Association, Washington, DC
Bottlender M, Soyka M (2004) Impact of craving on alcohol relapse during, and 12 months following, outpatient treatment. Alcohol Alcohol 39:357–361
Carter BL, Tiffany ST (1999) Meta-analysis of cue reactivity in addiction research. Addiction 94:327–340
Conklin CA, Salkeld RP, Perkins KA, Robin N (2013) Do people serve as cues to smoke? Nicotine Tob Res 15(12):2081–2087.
Curtin JJ, Barnett NP, Colby SM, Rohsenow DJ, Monti PM (2005) Cue reactivity in adolescents: measurement of separate approach and avoidance reactions. J Stud Alcohol 66:332–343
Dar R, Serlin RC, Omer H (1994) Misuse of statistical test in three decades of psychotherapy research. J Consult Clin Psychol 62:75–82
Deas D, Roberts J, Randall CL, Anton RF (2001) Adolescent obsessive–compulsive drinking scale: an assessment tool for problem drinking. J Natl Med Assoc 93:92–103
Deas D, Roberts J, Grindlinger D (2005) The utility of DSM-IV criteria in diagnosing substance abuse/dependence in adolescents. J Subst Abuse 10:10–21
Drummond DC (2001) Theories of drug craving, ancient and modern. Addiction 96:33–46
Flannery BA, Roberts AJ, Cooney N, Swift RM, Anton RF, Rohsenow DJ (2001) The role of craving in alcohol use, dependence and treatment. Alcohol Clin Exp 25:299–308
Flannery BA, Poole SA, Gallop RJ, Volpicelli JR (2003) Alcohol craving predicts drinking during treatment: an analysis of three assessment instruments. J Stud Alcohol 64:120–126
Ihssen N, Cox WM, Wiggett A, Fadardi JS, Linden DE (2011) Differentiating heavy from light drinkers by neural responses to visual alcohol cues and other motivational stimuli. Cereb Cortex 21:1408–1415
Kaufman J, Birmaher B, Brent D, Rao U, Flynn C, Moreci P, Williamson D, Ryan N (1997) Schedule for affective disorders and schizophrenia for school-age children-present version and lifetime version (K-SADS-PL): initial reliability and validity data. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry 36:980–988
Larsen H, Engels RC, Souren PM, Granic I, Overbeek G (2010) Peer influence in micro-perspective: imitation of alcoholic and non-alcoholic beverages. Addict Behav 35:49–52
Leeman RF, Corbin WR, Fromme K (2009) Craving predicts within session drinking behavior following placebo. Personality Individ Differ 46:693–698
Litt MD, Cooney ND, Morse P (2000) Reactivity to alcohol-related stimuli in the laboratory and in the field: predictors of craving in treated alcoholics. Addiction 95:889–900
Lukasiewicz M, Benyamina A, Reynaud M, Falissard B (2005) An in vivo study of the relationship between craving and reaction time during alcohol detoxification using the ecological momentary assessment. Alcohol Clin Exp 29:2135–2143
Martin C, Kaczynski N, Maisto S, Bukstein O, Moss H (1995) Patterns of DSM-IV alcohol abuse and dependence symptoms in adolescent drinkers. J Stud Alcohol 56:672–680
Mercken L, Steglich C, Knibbe R, Vries H (2012) Dynamics of friendship networks and alcohol use in early and mid-adolescence. J Stud Alcohol Drugs 73:99–110
Merikangas KR, McClair VL (2012) Epidemiology of substance use disorders. Hum Genet 131:779–789
Miranda R Jr, MacKillop J, Monti PM, Rohsenow DJ, Tidey J, Gwaltney C, Swift R, Ray L, McGeary J (2008) Effects of topiramate on urge to drink and the subjective effects of alcohol: a preliminary lab study. Alcohol Clin Exp 32:489–497
Monti PM, Binkoff JA, Abrams DB, Zwick WR, Nirenberg TD, Liepman MR (1987) Reactivity of alcoholics and nonalcoholics to drinking cues. J Abnorm Psychol 96:122–126
O'Brien CP (2005) Anticraving medications for relapse prevention: a possible new class of psychoactive medications. Am J Psychiatry 162:1423–1431
Oslin DW, Cary M, Slaymaker V, Colleran C, Blow FC (2009) Daily ratings measures of alcohol craving during an inpatient stay define subtypes of alcohol addiction that predict subsequent risk for resumption of drinking. Drug Alcohol Depend 103:131–136
Palta M (2003) Quantitative methods in population health: Extensions of ordinary regression. Wiley, Hoboken
Pan W (2001) Akaike's information criterion in generalized estimating equations. Biometrics 57:120–125
Ray LA, Miranda R Jr, Tidey JW, McGeary JE, MacKillop J, Gwaltney CJ, Rohsenow DJ, Swift RM, Monti PM (2010) Polymorphisms of the mu-opioid receptor and dopamine D4 receptor genes and subjective responses to alcohol in the natural environment. J Abnorm Psychol 119:115–125
Rohsenow DJ, Monti PM, Rubonis AV, Sirota AD, Niaura RS, Colby SM, Wunschel SM, Abrams DB (1994) Cue reactivity as a predictor of drinking among male alcoholics. J Consult Clin Psychol 62:620–626
Rohsenow DJ, Monti PM, Hutchison KE, Swift RM, Colby SM, Kaplan GB (2000) Naltrexone's effects on reactivity to alcohol cues among alcoholic men. J Abnorm Psychol 109:738–742
Sobell LC, Sobell MB (1992) Timeline follow-back: A technique for assessing self reported ethanol consumption. In: Allen J, Litten RZ (eds) Measuring alcohol consumption: Psychological and biological methods. Humana Press, Totowa, pp 41–72
Swendsen J, Burstein M, Case B, Conway KP, Dierker L, He J, Merikangas KR (2012) Use and abuse of alcohol and illicit drugs in US adolescents: results of the National comorbidity survey—adolescent supplement. Arch Gen Psychiatry 69:390–398
Tapert SF, Cheung EH, Brown GG, Frank LR, Paulus MP, Schweinsburg B, Meloy MJ, Brown SA (2003) Neural response to alcohol stimuli in adolescents with alcohol use disorder. Arch Gen Psychiatry 60:727–735
Thomas SE, Drobes DJ, Deas D (2005) Alcohol cue reactivity in alcohol dependent adolescents. J Stud Alcohol 66:354–360
Tiffany ST, Wray JM (2012) The clinical significance of drug craving. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1248:1–17
Tu YK, Gunnell D, Gilthorpe MS (2008) Simpson's paradox, Lord's paradox, and suppressioneffects are the same phenomenon—the reversal paradox. Emerg Themes Epidemiol 5:2. doi:10.1186/1742-7622-5-2
White HR, Labouvie ER (1989) Towards the assessment of adolescent problem drinking in adolescence. J Stud Alcohol 50:30–37
Zeger SL, Liang KY, Albert PS (1988) Models of longitudinal data: a generalized estimating equation approach. Biometrics 44:1049–1060
Acknowledgment
The National Institute of Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism at the National Institutes of Health supported this work (AA017273, AA07850). We thank Alexander Blanchard, Jason Frezza, Jacqueline Lee, Bethany Rallis, and Justin Souliere for their assistance with this project.
Conflict of interest
None
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ramirez, J., Miranda, R. Alcohol craving in adolescents: bridging the laboratory and natural environment. Psychopharmacology 231, 1841–1851 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-013-3372-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-013-3372-6