Abstract
Rationale
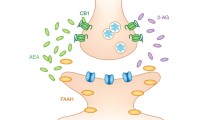
The central endocannabinoid system (eCB system) sustains the activity of the hypothalamus–pituitary–adrenal (HPA) axis in mediating individual emotional responses. Deviation in maturational trajectories of these two physiological systems, may persistently adjust individual behavioral phenotype.
Objective
We investigated, in outbred CD1 male mice, whether exposure to prenatal stress may influence short- and long-term emotional and neurochemical responses to a pharmacological stimulation of the eCB system during adolescence.
Methods
To mimic prenatal stress, pregnant mice were supplemented with corticosterone in the drinking water (33.3 mg/l); their adolescent male offspring received daily injections of the fatty acid amide hydrolase inhibitor, URB597 (0.4 mg/kg), in order to enhance eCB signaling. Mice were then tested for: locomotor activity during adolescence and locomotor activity, anxiogenic, and anhedonic profiles in adulthood. We analyzed the expression of CB1 receptors (CB1Rs) in prefrontal cortex, hippocampus, striatum, and cerebellum in adulthood.
Results
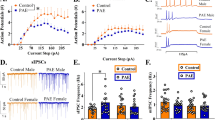
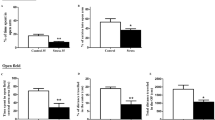
Corticosterone administration (PC group) resulted, in adolescence, in a reduction in body weight and locomotion, while in adulthood, in increased anxiety-related behavior and reduced CB1Rs expression in cerebellum. URB597 exposure reduced locomotor activity and increased anhedonia in adulthood. CB1Rs were up-regulated in striatum and hippocampus and down-regulated in the cerebellum. PC-URB597 mice failed to show reductions in locomotion; exhibited increased risk assessment behavior; and showed reduced CB1Rs expression within the prefrontal cortex.
Conclusions
Present results provide support to the hypothesis that precocious manipulations mapping onto the HPA axis and eCB system may persistently adjust individual emotional responses and eCB system plasticity.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abe R, Shioiri T, Someya T (2007) Suicide in Japan. Psychiatr Serv 58:1013–1013
Adriani W, Zoratto F, Romano E, Laviola G (2010) Cognitive impulsivity in animal models: role of response time and reinforcing rate in delay intolerance with two-choice operant tasks. Neuropharmacology 58:694–701
Anavi-Goffer S, Mulder J (2009) The polarised life of the endocannabinoid system in CNS development. Chembiochem 10:1591–1598
Antonelli T, Tomasini MC, Tattoli M, Cassano T, Tanganelli S, Finetti S, Mazzoni E, Trabace L, Steardo L, Cuomo V, Ferraro L (2005) Prenatal exposure to the CB1 receptor agonist WIN 55,212-2 causes learning disruption associated with impaired cortical NMDA receptor function and emotional reactivity changes in rat offspring. Cereb Cortex 15(12):2013–2020
Arseneault L, Cannon M, Poulton R, Murray R, Caspi A, Moffitt TE (2002) Cannabis use in adolescence and risk for adult psychosis: longitudinal prospective study. BMJ 325(7374):1212–1213
Berghuis P, Dobszay MB, Wang X, Spano S, Ledda F, Sousa KM, Schulte G, Ernfors P, Mackie K, Paratcha G, Hurd YL, Harkany T (2005) Endocannabinoids regulate interneuron migration and morphogenesis by transactivating the TrkB receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 102:19115–19120
Bevins RA, Besheer J (2005) Novelty reward as a measure of anhedonia. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 29:707–714
Bortolato MR, Fu J, Kim JH, Arguello O, Duranti A, Tontini A, Mor M, Tarzia G, Piomelli D. (2007) Antidepressant-like activity of the fatty acid amide hydrolase inhibitor URB597 in a rat model of chronic mild stress. Biol Psychiatry 2007 Nov 15;62(10):1103–10
Crosby KM, Bains JS (2012) The intricate link between glucocorticoids and endocannabinoids at stress-relevant synapses in the hypothalamus. Neuroscience 204:31–37
Cryan JF, Kelly PH, Chaperon F, Gentsch C, Mombereau C, Lingenhoehl K, Froestl W, Bettler B, Kaupmann K, Spooren WP (2004) Behavioral characterization of the novel GABAB receptor-positive modulator GS39783 (N,N′-dicyclopentyl-2-methylsulfanyl-5-nitro-pyrimidine-4,6-diamine): anxiolytic-like activity without side effects associated with baclofen or benzodiazepines. 310(3):952–63
Dell’Omo G, Vannoni E, Vyssotski AL, Di Bari MA, Nonno R, Agrimi U, Lipp HP (2002) Early behavioural changes in mice infected with BSE and scrapie: automated home cage monitoring reveals prion strain differences. Eur J Neurosci 16:735–742
De Kloet ER, Joels M, Holsboer F (2005) Stress and the brain: from adaptation to disease. Nat Rev Neurosci 6:463–475
Deminiere JM, Piazza PV, Guegan G, Abrous N, Maccari S, Lemoal M, Simon H (1992) Increased locomotor response to novelty and propensity to intravenous amphetamine self-administration in adult offspring of stressed mothers. Brain Res 586:135–139
Depke M, Fusch G, Domanska G, Geffers R, Volker U, Schuett C, Kiank C (2008) Hypermetabolic syndrome as a consequence of repeated psychological stress in mice. Endocrinology 149:2714–2723
Dudley KJ, Li X, Kobor MS, Kippin TE, Bredy TW (2011) Epigenetic mechanisms mediating vulnerability and resilience to psychiatric disorders. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 35(7):1544–1551
Eisenstein SA, Holmes PV, Hohmann AG (2009) Endocannabinoid modulation of amphetamine sensitization is disrupted in a rodent model of lesion-induced dopamine dysregulation. Synapse 63:941–950
Fride E, Gobshtis N, Dahan H, Weller A, Giuffrida A, Ben-Shabat S (2009) The endocannabinoid system during development: emphasis on perinatal events and delayed effects. Vitam Horm 81:139–158
Gobbi G, Bambico FR, Mangieri R, Bortolato M, Campolongo P, Solinas M, Cassano T, Morgese MG, Debonnel G, Duranti A, Tontini A, Tarzia G, Mor M, Trezza V, Goldberg SR, Cuomo V, Piomelli D (2005) Antidepressant-like activity and modulation of brain monoaminergic transmission by blockade of anandamide hydrolysis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 102:18620–18625
Gorzalka BB, Hill MN, Hillard CJ (2008) Regulation of endocannabinoid signaling by stress: implications for stress-related affective disorders. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 32:1152–1160
Hauser J, Feldon J, Pryce CR (2006) Prenatal dexamethasone exposure, postnatal development, and adulthood prepulse inhibition and latent inhibition in Wistar rats. Behav Brain Res 175:51–61
Hauser J, Feldon J, Pryce CR (2009) Direct and dam-mediated effects of prenatal dexamethasone on emotionality, cognition and HPA axis in adult Wistar rats. Horm Behav 56:364–375
Haussmann MF, Longenecker AS, Marchetto NM, Juliano SA, Bowden RM (2011) Embryonic exposure to corticosterone modifies the juvenile stress response, oxidative stress and telomere length. Proc Biol Sci 279:1447–1456
Heim C, Nemeroff CB (2002) Neurobiology of early life stress: clinical studies. Semin Clin Neuropsychiatry 7:147–159
Helm KA, Ziegler DR, Gallagher M (2004) Habituation to stress and dexamethasone suppression in rats with selective basal forebrain cholinergic lesions. Hippocampus 14:628–635
Herkenham M, Lynn AB, Little MD, Johnson MR, Melvin LS, de Costa BR, Rice KC (1990) Cannabinoid receptor localization in brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 87:1932–1936
Hill MN, Carrier EJ, Ho WS, Shi L, Patel S, Gorzalka BB, Hillard CJ (2008) Prolonged glucocorticoid treatment decreases cannabinoid CB1 receptor density in the hippocampus. Hippocampus 18:221–226
Hill MN, Mcewen BS (2010) Involvement of the endocannabinoid system in the neurobehavioural effects of stress and glucocorticoids. Prog Neuro-Psychopharmacol Biol Psychiatr 34:791–797
Hill MN, McEwen BS (2009) Endocannabinoids: the silent partner of glucocorticoids in the synapse. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 106:4579–4580
Hill MN, Patel S, Campolongo P, Tasker JG, Wotjak CT, Bains JS (2010) Functional interactions between stress and the endocannabinoid system: from synaptic signaling to behavioral output. J Neurosci 30:14980–14986
Kathuria S, Gaetani S, Fegley D, Valino F, Duranti A, Tontini A, Mor M, Tarzia G, La Rana G, Calignano A, Giustino A, Tattoli M, Palmery M, Cuomo V, Piomelli D (2003) Modulation of anxiety through blockade of anandamide hydrolysis. Nat Med 9:76–81
Kippin TE, Szumlinski KK, Kapasova Z, Rezner B, See RE (2008) Prenatal stress enhances responsiveness to cocaine. Neuropsychopharmacology 33:769–782
Koehl M, Bjijou Y, Le Moal M, Cador M (2000) Nicotine-induced locomotor activity is increased by preexposure of rats to prenatal stress. Brain Res 882:196–200
Koot S, Zoratto F, Cassano T, Colangeli R, Laviola G, van den Bos R, Adriani W (2012) Compromised decision-making and increased gambling proneness following dietary serotonin depletion in rats. Neuropharmacology 62:1640–1650
Laricchiuta D, Rojo ML, Rodriguez-Gaztelumendi A, Ferlazzo F, Petrosini L, Fowler CJ (2012) CB1 receptor autoradiographic characterization of the individual differences in approach and avoidance motivation. PLoS One.7: e42111
Lee J, Di Marzo V, Brotchie JM (2006) A role for vanilloid receptor 1 (TRPV1) and endocannabinnoid signalling in the regulation of spontaneous and L-DOPA induced locomotion in normal and reserpine-treated rats. Neuropharmacology 51:557–565
Lee TT, Gorzalka BB (2012) Timing is everything: evidence for a role of corticolimbic endocannabinoids in modulating hypothalamic–pituitary–adrenal axis activity across developmental periods. Neuroscience 204:17–30
Lemke MR, Wendorff T, Mieth B, Buhl K, Linnemann M (2000) Spatiotemporal gait patterns during over ground locomotion in major depression compared with healthy controls. J Psychiatr Res 34:277–283
Leussis MP, Andersen SL (2008) Is adolescence a sensitive period for depression? Behavioral and neuroanatomical findings from a social stress model. Synapse 62(1):22–30
Leventopoulos M, Russig H, Feldon J, Pryce CR, Opacka-Juffry J (2009) Early deprivation leads to long-term reductions in motivation for reward and 5-HT1A binding and both effects are reversed by fluoxetine. Neuropharmacology 56(3):692–701
Levine S (1957) Infantile experience and resistance to physiological stress. Science 126:(3270):405
Levine S (1994) The ontogeny of the hypothalamic–pituitary–adrenal axis. The influence of maternal factors. Ann NY Acad Sci 746:275–288
Lopez-Gallardo M, Lopez-Rodriguez AB, Llorente-Berzal A, Rotllant D, Mackie K, Armario A, Nadal R, Viveros MP (2012) Maternal deprivation and adolescent cannabinoid exposure impact hippocampal astrocytes, CB1 receptors and brain-derived neurotrophic factor in a sexually dimorphic fashion. Neuroscience 204:90–103
Maccari S, Morley-Fletcher S (2007) Effects of prenatal restraint stress on the hypothalamus–pituitary–adrenal axis and related behavioural and neurobiological alterations. Psychoneuroendocrinology 1:S10–S15
Mackie K (2005) Cannabinoid receptor homo- and heterodimerization. Life Sci 77:1667–1673
Macrì S, Ceci C, Canese R, Laviola G (2012) Prenatal stress and peripubertal stimulation of the endocannabinoid system differentially regulate emotional responses and brain metabolism in mice. PLoS One 7:e41821
Macrì S, Pasquali P, Bonsignore LT, Pieretti S, Cirulli F, Chiarotti F, Laviola G (2007) Moderate neonatal stress decreases within-group variation in behavioral, immune and HPA responses in adult mice. PLoS One 2:e1015
Macrì S, Ceci C, Altabella L, Canese R, Laviola G (2013) The Directive 2010/63/EU on animal experimentation may skew the conclusions of pharmacological and behavioural studies. Scientific Reports. 3:2380
Marco EM, García-Gutiérrez MS, Bermúdez-Silva FJ, Moreira FA, Guimarães F, Manzanares J, Viveros MP. (2011) Endocannabinoid system and psychiatry: in search of a neurobiological basis for detrimental and potential therapeutic effects. Front Behav Neurosci 5;5: 63
Marco EM, Macri S, Laviola G (2011b) Critical age windows for neurodevelopmental psychiatric disorders: evidence from animal models. Neurotox Res 19:286–307
Marco EM, Rubino T, Adriani W, Viveros MP, Parolaro D, Laviola G (2009) Long-term consequences of URB597 administration during adolescence on cannabinoid CB1 receptor binding in brain areas. Brain Res 1257:25–31
Marco EM, Scattoni ML, Rapino C, Ceci C, Chaves N, Macrì S, Maccarrone M Laviola G (2013) Emotional, endocrine and brain anandamide response to social challenge in infant male rats. Psychoneuroendocrinology (in press)
Mato S, Pazos A (2004) Influence of age, postmortem delay and freezing storage period on cannabinoid receptor density and functionality in human brain. Neuropharmacology 46:716–726
Morley-Fletcher S, Maccari S (2004) Long-term effects of prenatal stress as animal model of depression. A pharmacological study. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol 7:S61–S61
Morley-Fletcher S, Puopolo M, Gentili S, Gerra G, Macchia T, Laviola G (2004) Prenatal stress affects 3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine pharmacokinetics and drug-induced motor alterations in adolescent female rats. Eur J Pharmacol 489:89–92
Mulder J, Aguado T, Keimpema E, Barabas K, Ballester Rosado CJ, Nguyen L, Monory K, Marsicano G, Di Marzo V, Hurd YL, Guillemot F, Mackie K, Lutz B, Guzman M, Lu HC, Galve-Roperh I, Harkany T (2008) Endocannabinoid signaling controls pyramidal cell specification and long-range axon patterning. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 105:8760–8765
Nazzaro C, Greco B, Cerovic M, Baxter P, Rubino T, Trusel M, Parolaro D, Tkatch T, Benfenati F, Pedarzani P, Tonini R (2012) SK channel modulation rescues striatal plasticity and control over habit in cannabinoid tolerance. Nat Neurosci 15:284–293
Nemeroff CB (1996) The corticotropin-releasing factor (CRF) hypothesis of depression: new findings and new directions. Mol Psychiatry 1:336–342
O’Regan D, Kenyon CJ, Seckl JR, Holmes MC (2008) Prenatal dexamethasone ‘programmes’ hypotension, but stress-induced hypertension in adult offspring. J Endocrinol 196:343–352
Ognibene E, Bovicelli P, Adriani W, Saso L, Laviola G (2008) Behavioral effects of 6-bromoflavanone and 5-methoxy-6,8-dibromoflavanone as anxiolytic compounds. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatr 32:128–134
Patel S, Hillard CJ (2008) Adaptations in endocannabinoid signaling in response to repeated homotypic stress: a novel mechanism for stress habituation. Eur J Neurosci 27:2821–2829
Riebe CJ, Wotjak CT (2011) Endocannabinoids and stress. Stress 14:384–397
Rivalan M, Ahmed SH, Dellu-Hagedorn F (2009) Risk-prone individuals prefer the wrong options on a rat version of the Iowa Gambling Task. Biol Psychiatry 66:743–749
Rodgers RJ, Cao BJ, Dalvi A, Holmes A (1997) Animal models of anxiety: an ethological perspective. Braz J Med Biol Res 30:289–304
Romeo RD, McEwen BS (2006) Stress and the adolescent brain. Ann NY Acad Sci 1094:202–214
Romeo RD (2010) Adolescence: a central event in shaping stress reactivity. Dev Psychobiol 52:244–253
Romero J, Berrendero F, Garcia-Gil L, de la Cruz P, Ramos JA, Fernandez-Ruiz JJ (1998) Loss of cannabinoid receptor binding and messenger RNA levels and cannabinoid agonist-stimulated [35S]guanylyl-5′O-(thio)-triphosphate binding in the basal ganglia of aged rats. Neuroscience 84:1075–1083
Rubino T, Parolaro D (2008) Long lasting consequences of cannabis exposure in adolescence. Mol Cell Endocrinol 286:S108–S113
Rubino T, Zamberletti E, Parolaro D (2012) Adolescent exposure to cannabis as a risk factor for psychiatric disorders. J Psychopharmacol 26:177–188
Salomon S, Bejar C, Schorer-Apelbaum D, Weinstock M (2011) Corticosterone mediates some but not other behavioural changes induced by prenatal stress in rats. J Neuroendocrinol 23:118–128
Schneider M (2008) Puberty as a highly vulnerable developmental period for the consequences of cannabis exposure. Addict Biol 13:253–263
Schneider M, Koch M (2003) Chronic pubertal, but not adult chronic cannabinoid treatment impairs sensorimotor gating, recognition memory, and the performance in a progressive ratio task in adult rats. Neuropsychopharmacology 28:1760–1769
Shepherd JK, Grewal SS, Fletcher A, Bill DJ, Dourish CT (1994) Behavioural and pharmacological characterisation of the elevated “zero-maze” as an animal model of anxiety. Psychopharmacol (Berl) 116:56–64
Sim-Selley LJ, Schechter NS, Rorrer WK, Dalton GD, Hernandez J, Martin BR, Selley DE (2006) Prolonged recovery rate of CB1 receptor adaptation after cessation of long-term cannabinoid administration. Mol Pharmacol 70:986–996
Suárez J, Llorente R, Romero-Zerbo SY, Mateos B, Bermúdez-Silva FJ, de Fonseca FR, Viveros MP (2009) Early maternal deprivation induces gender-dependent changes on the expression of hippocampal CB(1) and CB(2) cannabinoid receptors of neonatal rats. Hippocampus 19:623–632
Suarez J, Rivera P, Llorente R, Romero-Zerbo SY, Bermudez-Silva FJ, de Fonseca FR, Viveros MP (2010) Early maternal deprivation induces changes on the expression of 2-AG biosynthesis and degradation enzymes in neonatal rat hippocampus. Brain Res 1349:162–173
Vaughan OR, Sferruzzi-Perri AN, Fowden AL (2012) Maternal corticosterone regulates nutrient allocation to fetal growth in mice. J Physiol 590:5529–5540
Viveros MP, Llorente R, Moreno E, Marco EM (2005) Behavioural and neuroendocrine effects of cannabinoids in critical developmental periods. Behav Pharmacol 16:353–362
Wall PM, Messier C (2001) Methodological and conceptual issues in the use of the elevated plus-maze as a psychological measurement instrument of animal anxiety-like behavior. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 25(3):275–286
Ward SJ, Dykstra LA (2005) The role of CB1 receptors in sweet versus fat reinforcement: effect of CB1 receptor deletion, CB1 receptor antagonism (SR141716A) and CB1 receptor agonism (CP-55940). Behav Pharmacol 16:381–388
Weinstock M (2005) The potential influence of maternal stress hormones on development and mental health of the offspring. Brain Behav Immun 19:296–308
Weinstock M (2008) The long-term behavioural consequences of prenatal stress. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 32:1073–1086
Zoratto F, Berry A, Anzidei F, Fiore M, Laviola G, Macrì S (2011) Effects of maternal L-tryptophan depletion and corticosterone administration on neurobehavioral adjustments in mouse dams and their adolescent and adult daughters. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatr Aug 1 35(6):1479–1492
Zoratto F, Fiore M, Ali SF, Laviola G, Macrì S (2013) Neonatal tryptophan depletion and corticosterone supplementation modify emotional responses in adult male mice. Psychoneuroendocrinology 38(1):24–39
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by “ECB-EMOTION: resilience” from the Dep. of Antidrug Policies c/o Presidency of the Council of Ministres (Italy) to GL and SM and from Instituto de Salud Carlos III (Spain), Redes temáticas de Investigación Cooperativa en salud RD06/0001/1013; GRUPOS UCM-BSCH (GRUPO UCM 951579) to EMM and MPV.
Conflict of interest
The authors certify that there is no actual or potential conflict of interest in relation to this article.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ceci, C., Mela, V., Macrì, S. et al. Prenatal corticosterone and adolescent URB597 administration modulate emotionality and CB1 receptor expression in mice. Psychopharmacology 231, 2131–2144 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-013-3367-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-013-3367-3