Abstract
Rationale
Inhalant abuse is prevalent in adolescent populations, with chronic use resulting in neurobiological and cognitive abnormalities in adulthood. However, the nature and persistence of cognitive dysfunction, particularly following adolescent inhalant abuse, remain equivocal.
Objective
The present study assessed specific cognitive processes beginning in late adolescence and adulthood following adolescent inhalation of toluene, a main component of many compounds readily abused.
Methods
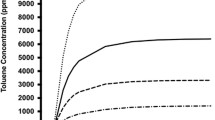
Adolescent male Wistar rats (postnatal day (PN) 27) were exposed to chronic intermittent inhaled toluene (10,000 ppm) for 1 h/day, 3 days/week for 4 weeks (PN 27–52) to mimic the patterns observed in human adolescent inhalant abusers. Following toluene exposure, motor and cognitive function was assessed.
Results
Adolescent toluene exposure did not alter motor learning in the Rotarod task (PN 58) or acquisition, reversal, or retention of spatial learning in the Morris water maze (PN 55–64). In contrast, it delayed acquisition of instrumental responding for sucrose (5 % w/v) and impaired operant reversal learning and cue-induced reinstatement of sucrose seeking in adulthood (PN 57–100).
Conclusion
This study demonstrates that exposure to toluene at an abuse concentration during adolescence results in specific impairments in aspects of instrumental learning, without altering motor function and spatial learning in late adolescence/early adulthood. Our data imply that persistent alterations in reward processing may occur following adolescent inhalant misuse.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aydin K, Sencer S, Demir T, Ogel K, Tunaci A, Minareci O (2002) Cranial MR findings in chronic toluene abuse by inhalation. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 23:1173–1179
Aydin K, Kircan S, Sarwar S, Okur O, Balaban E (2009) Smaller gray matter volumes in frontal and parietal cortices of solvent abusers correlate with cognitive deficits. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 30:1922–1928
Badanich KA, Becker HC, Woodward JJ (2011) Effects of chronic intermittent ethanol exposure on orbitofrontal and medial prefrontal cortex-dependent behaviors in mice. Behav Neurosci 125:879–891
Balleine BW, Killcross AS, Dickinson A (2003) The effect of lesions of the basolateral amygdala on instrumental conditioning. J Neurosci 23:666–675
Batis JC, Hannigan JH, Bowen SE (2010) Differential effects of inhaled toluene on locomotor activity in adolescent and adult rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 96:438–448
Beasley TE, Evansky PA, Bushnell PJ (2012) Behavioral effects of sub-acute inhalation of toluene in adult rats. Neurotoxicol Teratol 34:83–89
Beckley JT, Evins CE, Fedarovich H, Gilstrap MJ, Woodward JJ (2013) Medial prefrontal cortex inversely regulates toluene-induced changes in markers of synaptic plasticity of mesolimbic dopamine neurons. J Neurosci 33:804–813
Benignus VA, Boyes WK, Kenyon EM, Bushnell PJ (2007) Quantitative comparisons of the acute neurotoxicity of toluene in rats and humans. Toxicol Sci 100:146–155
Blokhina EA, Dravolina OA, Bespalov AY, Balster RL, Zvartau EE (2004) Intravenous self-administration of abused solvents and anesthetics in mice. Eur J Pharmacol 485:211–218
Blundell P, Hall G, Killcross S (2003) Preserved sensitivity to outcome value after lesions of the basolateral amygdala. J Neurosci 23:7702–7709
Bowen SE, McDonald P (2009) Abuse pattern of toluene exposure alters mouse behavior in a waiting-for-reward operant task. Neurotoxicol Teratol 31:18–25
Bowen SE, Batis JC, Peaz-Martinez N, Cruz SL (2006) The last decade of solvent research in animal models of abuse: mechanistic and behavioural studies. Neurotoxicol Teratol 28:636–647
Cairney S, Maruff P, Burns CB, Currie J, Currie BJ (2005) Neurological and cognitive recovery following abstinence from petrol sniffing. Neuropsychopharmacology 30:1019–1027
Cairney S, O'Connor N, Dingwall KM, Maruff P, Shafiq-Antonacci R, Currie J, Currie BJ (2013) A prospective study of neurocognitive changes 15 years after chronic inhalant abuse. Addiction 108:1107–1114
Calu DJ, Stalnaker TA, Franz TM, Singh T, Shaham Y, Schoenbaum G (2007) Withdrawal from cocaine self-administration produces long-lasting deficits in orbitofrontal-dependent reversal learning in rats. Learn Mem 14:325–328
Chudasama Y, Robbins TW (2003) Dissociable contributions of the orbitofrontal and infralimbic cortex to pavlovian autoshaping and discrimination reversal learning: further evidence for the functional heterogeneity of the rodent frontal cortex. J Neurosci 23:8771–8780
Corbit LH, Balleine BW (2003) The role of prelimbic cortex in instrumental conditioning. Behav Brain Res 146:145–157
Corbit LH, Balleine BW (2005) Double dissociation of basolateral and central amygdala lesions on the general and outcome-specific forms of pavlovian-instrumental transfer. J Neurosci 25:962–970
Dingwall KM, Maruff P, Fredrickson A, Cairney S (2011) Cognitive recovery during and after treatment for volatile solvent abuse. Drug Alcohol Depend 118:180–185
Duncan JR, Dick AL, Egan G, Kolbe S, Gavrilescu M, Wright D, Lubman DI, Lawrence AJ (2012) Adolescent toluene inhalation in rats affects white matter maturation with the potential for recovery following abstinence. PloS one 7:e44790
Duncan JR, Gibbs SJ, Lawrence AJ (2013) Chronic intermittent toluene inhalation in adolescent rats alters behavioural responses to amphetamine and MK801. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol. doi: 10.1016/j.euroneuro.2013.06.001
Featherby T, van den Buuse M, Lubman DI, Lawrence AJ (2008) Persistent downregulation of hippocampal CREB mRNA parallels a Y-maze deficit in adolescent rats following semi-chronic amphetamine administration. Br J Pharmacol 154:417–428
Funada M, Sato M, Makino Y, Wada K (2002) Evaluation of rewarding effect of toluene by the conditioned places preference procedure in mice. Brain Res Protoc 10:47–54
Giedd JN (2004) Structural magnetic resonance imaging of the adolescent brain. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1021:77–85
Gmaz JM, Matthews BA, McKay BE (2012a) Toluene inhalation modulates dentate gyrus granule cell output in vivo. Neurotoxicol Teratol 34:403–412
Gmaz JM, Yang L, Ahrari A, McKay BE (2012b) Binge inhalation of toluene vapor produces dissociable motor and cognitive dysfunction in water maze tasks. Behav Pharmacol 23:669–677
Huerta-Rivas A, Lopez-Rubalcava C, Sanchez-Serrano SL, Valdez-Tapia M, Lamas M, Cruz SL (2012) Toluene impairs learning and memory, has antinociceptive effects, and modifies histone acetylation in the dentate gyrus of adolescent and adult rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 102:48–57
Ishikawa A, Ambroggi F, Nicola SM, Fields HL (2008) Contributions of the amygdala and medial prefrontal cortex to incentive cue responding. Neuroscience 155:573–584
Izquierdo A, Belcher AM, Scott L, Cazares VA, Chen J, O'Dell SJ, Malvaez M, Wu T, Marshall JF (2010) Reversal-specific learning impairments after a binge regimen of methamphetamine in rats: possible involvement of striatal dopamine. Neuropsychopharmacology 35:505–514
Jacquot L, Pourie G, Buron G, Monnin J, Brand G (2006) Effects of toluene inhalation exposure on olfactory functioning: behavioral and histological assessment. Toxicol Lett 165:57–65
Jarosz PA, Fata E, Bowen SE, Jen KL, Coscina DV (2008) Effects of abuse pattern of gestational toluene exposure on metabolism, feeding and body composition. Physiol Behav 93:984–993
Jupp B, Krivdic B, Krstew E, Lawrence AJ (2011) The orexin(1) receptor antagonist SB-334867 dissociates the motivational properties of alcohol and sucrose in rats. Brain Res 1391:54–59
Ladefoged O, Strange P, Moller A, Lam HR, Ostergaard G, Larsen JJ, Arlien-Soborg P (1991) Irreversible effects in rats of toluene (inhalation) exposure for 6 months. Pharmacol Toxicol 68:384–390
Lasseter HC, Wells AM, Xie X, Fuchs RA (2011) Interaction of the basolateral amygdala and orbitofrontal cortex is critical for drug context-induced reinstatement of cocaine-seeking behavior in rats. Neuropsychopharmacology 36:711–720
Lin BF, Ou MC, Chung SS, Pang CY, Chen HH (2010) Adolescent toluene exposure produces enduring social and cognitive deficits in mice: an animal model of solvent-induced psychosis. World J Biol Psychiatry 11:792–802
Lubman DI, Yucel M, Hall WD (2007) Substance use and the adolescent brain: a toxic combination. J Psychopharmacol 21:792–794
Lubman DI, Yucel M, Lawrence AJ (2008) Inhalant abuse among adolescents: neurobiological considerations. Br J Pharmacol 154:316–326
Manitt C, Mimee A, Eng C, Pokinko M, Stroh T, Cooper HM, Kolb B, Flores C (2011) The netrin receptor DCC is required in the pubertal organization of mesocortical dopamine circuitry. J Neurosci 31:8381–8394
McFarland K, Lapish CC, Kalivas PW (2003) Prefrontal glutamate release into the core of the nucleus accumbens mediates cocaine-induced reinstatement of drug-seeking behavior. J Neurosci 23:3531–3537
Morris RG, Hagan JJ, Rawlins JN (1986) Allocentric spatial learning by hippocampectomised rats: a further test of the “spatial mapping” and “working memory” theories of hippocampal function. T Q J Exp Psychol B 38:365–395
O'Leary-Moore SK, Galloway MP, McMechan AP, Irtenkauf S, Hannigan JH, Bowen SE (2009) Neurochemical changes after acute binge toluene inhalation in adolescent and adult rats: a high-resolution magnetic resonance spectroscopy study. Neurotoxicol Teratol 31:382–389
Ostlund SB, Balleine BW (2005) Lesions of medial prefrontal cortex disrupt the acquisition but not the expression of goal-directed learning. J Neurosci 25:7763–7770
Riegel AC, Zapata A, Shippenberg TS, French ED (2007) The abused inhalant toluene increases dopamine release in the nucleus accumbens by directly stimulating ventral tegmental area neurons. Neuropsychopharmacology 32:1558–1569
Rosenberg NL, Grigsby J, Dreisbach J, Busenbark D, Grigsby P (2002) Neuropsychologic impairment and MRI abnormalities associated with chronic solvent abuse. J Toxicol Clin Toxicol 40:21–34
Schoenbaum G, Nugent SL, Saddoris MP, Setlow B (2002) Orbitofrontal lesions in rats impair reversal but not acquisition of go, no-go odor discriminations. Neuroreport 13:885–890
Schoenbaum G, Saddoris MP, Ramus SJ, Shaham Y, Setlow B (2004) Cocaine-experienced rats exhibit learning deficits in a task sensitive to orbitofrontal cortex lesions. Eur J Neurosci 19:1997–2002
Seo HS, Yang M, Song MS, Kim JS, Kim SH, Kim JC, Kim H, Shin T, Wang H, Moon C (2010) Toluene inhibits hippocampal neurogenesis in adult mice. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 94:588–594
Spear LP (2000) The adolescent brain and age-related behavioral manifestations. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 24:417–463
Torregrossa MM, Gordon J, Taylor JR (2013) Double dissociation between the anterior cingulate cortex and nucleus accumbens core in encoding the context versus the content of pavlovian cocaine cue extinction. J Neurosci 33:8370–8377
von Euler G, Ogren SO, Li XM, Fuxe K, Gustafsson JA (1993) Persistent effects of subchronic toluene exposure on spatial learning and memory, dopamine-mediated locomotor activity and dopamine D2 agonist binding in the rat. Toxicology 77:223–232
Weiss B, Wood RW, Macys DA (1979) Behavioral toxicology of carbon disulfide and toluene. Environ Health Perspect 30:39–45
Williams JM, Stafford D, Steketee JD (2005) Effects of repeated inhalation of toluene on ionotropic GABA A and glutamate receptor subunit levels in rat brain. Neurochem Int 46:1–10
Wu LT, Pilowsky DJ, Schlenger WE (2004) Inhalant abuse and dependence among adolescents in the United States. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry 43:1206–1214
Yamanouchi N, S-i O, Kodama K, Hirai S, Hiroshi S, Murakami A, Komatsu N, Sakamot T, Sato T (1995) White matter changes caused by chronic solvent abuse. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 16:1643–1649
Yucel M, Takagi M, Walterfang M, Lubman DI (2008) Toluene misuse and long-term harms: a systematic review of the neuropsychological and neuroimaging literature. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 32:910–926
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Ms. Zakia Haque for assistance with running animals through the inhalant exposure paradigm. This study was supported by The National Health and Medical Research Council of Australia of which AJL is a Principal Research Fellow (1020737), the Australian Research Council (DP 110100379) of which JRD is a Future Fellow (100100235) and the Victorian Government's Operational Infrastructure Support Scheme.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dick, A.L.W., Axelsson, M., Lawrence, A.J. et al. Specific impairments in instrumental learning following chronic intermittent toluene inhalation in adolescent rats. Psychopharmacology 231, 1531–1542 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-013-3363-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-013-3363-7