Abstract
Rationale
Ketamine, a non-competitive NMDA receptor antagonist, induces acute effects resembling the positive, negative and cognitive symptoms of schizophrenia. Chronic use has been suggested to lead to persistent schizophrenia-like neurobiological changes.
Objectives
This study aims to test the hypothesis that chronic ketamine users have changes in brain neurochemistry and increased subthreshold psychotic symptoms compared to matched poly-drug users.
Methods
Fifteen ketamine users and 13 poly-drug users were included in the study. Psychopathology was assessed using the Comprehensive Assessment of At-Risk Mental State. Creatine-scaled glutamate (Glu/Cr), glutamate + glutamine (Glu + Gln/Cr) and N-acetyl aspartate (NAA/Cr) were measured in three brain regions—anterior cingulate, left thalamus and left medial temporal cortex using proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy.
Results
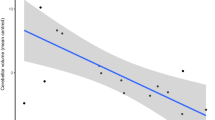
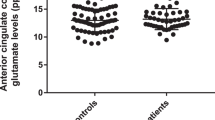
Chronic ketamine users had higher levels of subthreshold psychotic symptoms (p < 0.005, Cohen’s d = 1.48) and lower thalamic NAA/Cr (p < 0.01, d = 1.17) compared to non-users. There were no differences in medial temporal cortex or anterior cingulate NAA/Cr or in Glu/Cr or Glu + Gln/Cr in any brain region between the two groups. In chronic ketamine users, CAARMS severity of abnormal perceptions was directly correlated with anterior cingulate Glu/Cr (p < 0.05, r = 0.61—uncorrected), but NAA/Cr was not related to any measures of psychopathology.
Conclusions
The finding of lower thalamic NAA/Cr in chronic ketamine users may be secondary to the effects of ketamine use compared to other drugs of abuse and resembles previous reports in individuals at genetic or clinical risk of schizophrenia.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arikan MK, Kutukcu A, Karay A, Ozmen M (2009) A case of psychosis associated with left thalamic lacunar infarcts. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 33:729–730. doi:10.1016/j.pnpbp.2009.02.022
Bartha R, Williamson PC, Drost DJ, Malla A, Carr TJ, Cortese L, Canaran G, Rylett RJ, Neufeld RWJ (1997) Measurement of glutamate and glutamine in the medial prefrontal cortex of never-treated schizophrenic patients and healthy controls by proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Arch Gen Psychiatry 54:959–965. doi:10.1001/archpsyc.54.10.959
Behrendt RP (2006) Dysregulation of thalamic sensory “transmission” in schizophrenia: neurochemical vulnerability to hallucinations. J Psychopharmacol 20:356–372
Brugger S, Davis JM, Leucht S, Stone JM (2011) Proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy and illness stage in schizophrenia—a systematic review and meta-analysis. Biol Psychiatry 69:495–503. doi:10.1016/j.biopsych.2010.10.004
Carhart-Harris RL, Erritzoe D, Williams T, Stone JM, Reed LJ, Colasanti A, Tyacke RJ, Leech R, Malizia AL, Murphy K, Hobden P, Evans J, Feilding A, Wise RG, Nutt DJ (2012) Neural correlates of the psychedelic state as determined by fMRI studies with psilocybin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 109:2138–2143. doi:10.1073/pnas.1119598109
Carlsson M, Carlsson A (1990) Schizophrenia: a subcortical neurotransmitter imbalance syndrome? Schizophr Bull 16:425–432
Chang L, Ernst T, Strickland T, Mehringer CM (1999) Gender effects on persistent cerebral metabolite changes in the frontal lobes of abstinent cocaine users. Am J Psychiatry 156:716–722
Clinton SM, Meador-Woodruff JH (2004) Thalamic dysfunction in schizophrenia: neurochemical, neuropathological, and in vivo imaging abnormalities. Schizophr Res 69:237–253
Cowan RL, Joers JM, Dietrich MS (2009) N-Acetylaspartate (NAA) correlates inversely with cannabis use in a frontal language processing region of neocortex in MDMA (Ecstasy) polydrug users: a 3 T magnetic resonance spectroscopy study. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 92:105–110. doi:10.1016/j.pbb.2008.10.022
Crail-Melendez D, Atriano-Mendieta C, Carrillo-Meza R, Ramirez-Bermudez J (2012) Schizophrenia-like psychosis associated with right lacunar thalamic infarct. Neurocase. doi:10.1080/13554794.2011.654211
Danos P, Baumann B, Bernstein HG, Franz M, Stauch R, Northoff G, Krell D, Falkai P, Bogerts B (1998) Schizophrenia and anteroventral thalamic nucleus: selective decrease of parvalbumin-immunoreactive thalamocortical projection neurons. Psychiatry Res 82:1–10
de la Fuente-Sandoval C, Leon-Ortiz P, Azcarraga M, Stephano S, Favila R, Diaz-Galvis L, Alvarado-Alanis P, Ramirez-Bermudez J, Graff-Guerrero A (2013) Glutamate levels in the associative striatum before and after 4 weeks of antipsychotic treatment in first-episode psychosis: a longitudinal proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy study. JAMA Psychiatry 70:1057–1066. doi:10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2013.289
Demjaha A, Egerton A, Murray RM, Kapur S, Howes OD, Stone JM, McGuire PK (2013) Antipsychotic treatment resistance in schizophrenia associated with elevated glutamate levels but normal dopamine function. Biol Psychiatry. doi:10.1016/j.biopsych.2013.06.011
Egerton A, Brugger S, Raffin M, Barker GJ, Lythgoe DJ, McGuire PK, Stone JM (2012) Anterior cingulate glutamate levels related to clinical status following treatment in first-episode schizophrenia. Neuropsychopharmacology. doi:10.1038/npp.2012.113
Gazdzinski S, Durazzo TC, Weiner MW, Meyerhoff DJ (2008) Are treated alcoholics representative of the entire population with alcohol use disorders? A magnetic resonance study of brain injury. Alcohol 42:67–76. doi:10.1016/j. alcohol .2008.01.002
Haijma SV, Van Haren N, Cahn W, Koolschijn PC, Hulshoff Pol HE, Kahn RS (2012) Brain volumes in schizophrenia: a meta-analysis in over 18 000 subjects. Schizophr Bull. doi:10.1093/schbul/sbs118
Hermann D, Sartorius A, Welzel H, Walter S, Skopp G, Ende G, Mann K (2007) Dorsolateral prefrontal cortex N-acetylaspartate/total creatine (NAA/tCr) loss in male recreational cannabis users. Biol Psychiatry 61:1281–1289. doi:10.1016/j.biopsych.2006.08.027
Ihaka R, Gentleman R (1996) R: a language for data analysis and graphics. J Comput Graph Stat 5:299–314
Jakary A, Vinogradov S, Feiwell R, Deicken RF (2005) N-Acetylaspartate reductions in the mediodorsal and anterior thalamus in men with schizophrenia verified by tissue volume corrected proton MRSI. Schizophrenia Res 76:173–185
Jansen JF, Backes WH, Nicolay K, Kooi ME (2006) 1H MR spectroscopy of the brain: absolute quantification of metabolites. Radiology 240:318–332. doi:10.1148/radiol.2402050314
Kegeles LS, Mao X, Stanford AD, Girgis R, Ojeil N, Xu X, Gil R, Slifstein M, Abi-Dargham A, Lisanby SH, Shungu DC (2012) Elevated prefrontal cortex gamma-aminobutyric acid and glutamate–glutamine levels in schizophrenia measured in vivo with proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Arch Gen Psychiatry 69:449–459. doi:10.1001/archgenpsychiatry.2011.1519
Keilhoff G, Becker A, Grecksch G, Wolf G, Bernstein HG (2004) Repeated application of ketamine to rats induces changes in the hippocampal expression of parvalbumin, neuronal nitric oxide synthase and cFOS similar to those found in human schizophrenia. Neuroscience 126:591–598
Kim SY, Lee H, Kim HJ, Bang E, Lee SH, Lee DW, Woo DC, Choi CB, Hong KS, Lee C, Choe BY (2011) In vivo and ex vivo evidence for ketamine-induced hyperglutamatergic activity in the cerebral cortex of the rat: potential relevance to schizophrenia. NMR Biomed 24:1235–1242. doi:10.1002/nbm.1681
Krystal JH, Karper LP, Seibyl JP, Freeman GK, Delaney R, Bremner JD, Heninger GR, Bowers MB Jr, Charney DS (1994) Subanesthetic effects of the noncompetitive NMDA antagonist, ketamine, in humans. Psychotomimetic, perceptual, cognitive, and neuroendocrine responses. Arch Gen Psychiatry 51:199–214
Lahti AC, Holcomb HH, Medoff DR, Tamminga CA (1995) Ketamine activates psychosis and alters limbic blood flow in schizophrenia. Neuroreport 6:869–872
Lawrie SM, Whalley H, Kestelman JN, Abukmeil SS, Byrne M, Hodges A, Rimmington JE, Best JJ, Owens DG, Johnstone EC (1999) Magnetic resonance imaging of brain in people at high risk of developing schizophrenia. Lancet 353:30–33
Liao Y, Tang J, Corlett PR, Wang X, Yang M, Chen H, Liu T, Chen X, Hao W, Fletcher PC (2011) Reduced dorsal prefrontal gray matter after chronic ketamine use. Biol Psychiatry 69:42–48. doi:10.1016/j.biopsych.2010.08.030
Marsman A, van den Heuvel MP, Klomp DW, Kahn RS, Luijten PR, Hulshoff Pol HE (2013) Glutamate in schizophrenia: a focused review and meta-analysis of (1)H-MRS studies. Schizophr Bull 39:120–129. doi:10.1093/schbul/sbr069
Mittal M, Khan S (2010) Starvation causes acute psychosis due to anterior thalamic infarction. South Med J 103:701–703. doi:10.1097/SMJ.0b013e3181e1e2f3
Narendran R, Frankle WG, Keefe R, Gil R, Martinez D, Slifstein M, Kegeles LS, Talbot PS, Huang Y, Hwang DR, Khenissi L, Cooper TB, Laruelle M, Abi-Dargham A (2005) Altered prefrontal dopaminergic function in chronic recreational ketamine users. Am J Psychiatry 162:2352–2359
Nordahl TE, Salo R, Natsuaki Y, Galloway GP, Waters C, Moore CD, Kile S, Buonocore MH (2005) Methamphetamine users in sustained abstinence: a proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy study. Arch Gen Psychiatry 62:444–452. doi:10.1001/archpsyc.62.4.444
Reneman L, Majoie CB, Flick H, den Heeten GJ (2002) Reduced N-acetylaspartate levels in the frontal cortex of 3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine (Ecstasy) users: preliminary results. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 23:231–237
Reynolds GP, Harte MK (2007) The neuronal pathology of schizophrenia: molecules and mechanisms. Biochem Soc Trans 35:433–436
Reynolds LM, Cochran SM, Morris BJ, Pratt JA, Reynolds GP (2005) Chronic phencyclidine administration induces schizophrenia-like changes in N-acetylaspartate and N-acetylaspartylglutamate in rat brain. Schizophr Res 73:147–152
Rowland LM, Bustillo JR, Mullins PG, Jung RE, Lenroot R, Landgraf E, Barrow R, Yeo R, Lauriello J, Brooks WM (2005) Effects of ketamine on anterior cingulate glutamate metabolism in healthy humans: a 4-T proton MRS study. Am J Psychiatry 162:394–396
Salo R, Nordahl TE, Natsuaki Y, Leamon MH, Galloway GP, Waters C, Moore CD, Buonocore MH (2007) Attentional control and brain metabolite levels in methamphetamine abusers. Biol Psychiatry 61:1272–1280. doi:10.1016/j.biopsych.2006.07.031
Sharp FR, Tomitaka M, Bernaudin M, Tomitaka S (2001) Psychosis: pathological activation of limbic thalamocortical circuits by psychomimetics and schizophrenia? Trends Neurosci 24:330–334
Steen RG, Hamer RM, Lieberman JA (2005) Measurement of brain metabolites by 1H magnetic resonance spectroscopy in patients with schizophrenia: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Neuropsychopharmacology 30:1949–1962
Stone JM, Day F, Tsagaraki H, Valli I, McLean MA, Lythgoe DJ, O'Gorman RL, Barker GJ, McGuire PK (2009) Glutamate dysfunction in people with prodromal symptoms of psychosis: relationship to gray matter volume. Biol Psychiatry 66:533–539. doi:10.1016/j.biopsych.2009.05.006
Stone JM, Bramon E, Pauls A, Sumich A, McGuire PK (2010) Thalamic neurochemical abnormalities in individuals with prodromal symptoms of schizophrenia—relationship to auditory event-related potentials. Psychiatry Res 183:174–176. doi:10.1016/j.pscychresns.2010.05.004
Stone JM, Dietrich C, Edden R, Mehta MA, De Simoni S, Reed LJ, Krystal JH, Nutt D, Barker GJ (2012) Ketamine effects on brain GABA and glutamate levels with 1H-MRS: relationship to ketamine-induced psychopathology. Mol Psychiatry PMID: 22212598; doi:10.1038/mp.2011.171
Szulc A, Waszkiewicz N, Bibulowicz D, Konarzewska B, Tarasow E (2013) Proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy changes after antipsychotic treatment. Curr Med Chem 20:414–427
Taylor MJ, Tiangga ER, Ni Mhuircheartaigh R, Cowen P (2011) Lack of effect of ketamine on cortical glutamate and glutamine in healthy volunteers: a proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy study. J Psychopharmacol. doi:10.1177/0269881111405359
Théberge J, Bartha R, Drost DJ, Menon RS, Malla A, Takhar J, Neufeld RW, Rogers J, Pavlosky W, Schaefer B, Densmore M, Al-Semaan Y, Williamson PC (2002) Glutamate and glutamine measured with 4.0 T proton MRS in never-treated patients with schizophrenia and healthy volunteers. Am J Psychiatry 159:1944–1946. doi:10.1176/appi.ajp.159.11.1944
Theberge J, Al-Semaan Y, Drost DJ, Malla AK, Neufeld RW, Bartha R, Manchanda R, Menon R, Densmore M, Schaefer B, Williamson PC (2004) Duration of untreated psychosis vs. N-acetylaspartate and choline in first episode schizophrenia: a 1H magnetic resonance spectroscopy study at 4.0 Tesla. Psychiatry Res 131:107–114
Tibbo P, Hanstock C, Valiakalayil A, Allen P (2004) 3-T proton MRS investigation of glutamate and glutamine in adolescents at high genetic risk for schizophrenia. Am J Psychiatry 161:1116–1118
Tsai G, Coyle JT (2002) Glutamatergic mechanisms in schizophrenia. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 42:165–179. doi:10.1146/annurev.pharmtox.42.082701.160735
Vollenweider FX, Geyer MA (2001) A systems model of altered consciousness: integrating natural and drug-induced psychoses. Brain Res Bull 56:495–507
Wood SJ, Yücel M, Wellard RM, Harrison BJ, Clarke K, Fornito A, Velakoulis D, Pantelis C (2007) Evidence for neuronal dysfunction in the anterior cingulate of patients with schizophrenia: a proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy study at 3 T. Schizophr Res 94:328–331
Yang S, Salmeron BJ, Ross TJ, Xi ZX, Stein EA, Yang Y (2009) Lower glutamate levels in rostral anterior cingulate of chronic cocaine users—A (1)H-MRS study using TE-averaged PRESS at 3 T with an optimized quantification strategy. Psychiatry Res 174:171–176. doi:10.1016/j.pscychresns.2009.05.004
Yoo SY, Yeon S, Choi CH, Kang DH, Lee JM, Shin NY, Jung WH, Choi JS, Jang DP, Kwon JS (2009) Proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy in subjects with high genetic risk of schizophrenia: investigation of anterior cingulate, dorsolateral prefrontal cortex and thalamus. Schizophr Res 111:86–93
Yung AR, Yuen HP, McGorry PD, Phillips LJ, Kelly D, Dell'Olio M, Francey SM, Cosgrave EM, Killackey E, Stanford C, Godfrey K, Buckby J (2005) Mapping the onset of psychosis: the comprehensive assessment of at-risk mental states. Aust N Z J Psychiatry 39:964–971. doi:10.1111/j.1440-1614.2005.01714.x
Funding source
This work was supported by an MRC grant to Oliver Howes (grant code: MC_A656_5QD30).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Celia Morgan and Oliver D. Howes contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Stone, J.M., Pepper, F., Fam, J. et al. Glutamate, N-acetyl aspartate and psychotic symptoms in chronic ketamine users. Psychopharmacology 231, 2107–2116 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-013-3354-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-013-3354-8