Abstract
Rationale
Ethanol is commonly used and abused during adolescence. Although adolescents display differential behavioral responses to ethanol, the mechanisms by which this occurs are not known. The protein kinase C (PKC) pathway has been implicated in mediating many ethanol-related effects in adults, as well as gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABAA) receptor regulation.
Objectives
The present study was designed to characterize cortical PKC isoform and GABAA receptor subunit expression during adolescence relative to adults as well as assess PKC involvement in ethanol action.
Results
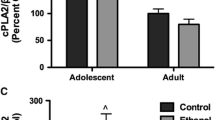
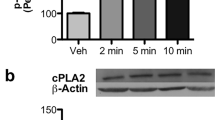
Novel PKC isoforms were elevated, while PKCγ was lower during mid-adolescence relative to adults. Whole-cell lysate and synaptosomal preparations correlated for all isoforms except PKCδ. In parallel, synaptosomal GABAA receptor subunit expression was also developmentally regulated, with GABAAR δ and α4 being lower while α1 and γ2 were higher or similar, respectively, in adolescents compared to adults. Following acute ethanol exposure, synaptosomal novel and atypical PKC isoform expression was decreased only in adolescents. Behaviorally, inhibiting PKC with calphostin C, significantly increased ethanol-induced loss of righting reflex (LORR) in adolescents but not adults, whereas activating PKC with phorbol dibutyrate was ineffective in adolescents but decreased LORR duration in adults. Further investigation revealed that inhibiting the cytosolic phospholipase A2/arachidonic acid (cPLA2/AA) pathway increased LORR duration in adolescents, but was ineffective in adults.
Conclusions
These data indicate that PKC isoforms are variably regulated during adolescence and may contribute to adolescent ethanol-related behavior. Furthermore, age-related differences in the cPLA2/AA pathway may contribute to ethanol’s age-related effects on novel and atypical PKC isoform expression and behavior.






Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AA:
-
arachidonic acid
- cPLA2 :
-
cytoplasmic phospholipase A2
- GABA:
-
gamma-aminobutyric acid
- GABAAR:
-
GABA type A receptor
- PKC:
-
protein kinase C
References
Almeida T, Cunha RA, Ribeiro JA (1999) Facilitation by arachidonic acid of acetylcholine release from the rat hippocampus. Brain Res 826:104–11
Basavarajappa BS, Cooper TB, Hungund BL (1998) Effect of chronic ethanol exposure on mouse brain arachidonic acid specific phospholipase A2. Biochem Pharmacol 55:515–21
Blednov YA, Borghese CM, McCracken ML, Benavidez JM, Geil CR, Osterndorff-Kahanek E, Werner DF, Iyer S, Swihart A, Harrison NL, Homanics GE, Harris RA (2011) Loss of ethanol conditioned taste aversion and motor stimulation in knockin mice with ethanol-insensitive alpha2-containing GABAA receptors. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 336:145–54
Bowers BJ, Owen EH, Collins AC, Abeliovich A, Tonegawa S, Wehner JM (1999) Decreased ethanol sensitivity and tolerance development in gamma-protein kinase C null mutant mice is dependent on genetic background. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 23:387–97
Brandon NJ, Delmas P, McDonald BJ, Sieghart W, Brown DA, Smart TG, Moss SJ (2000) GABAA receptor phosphorylation and functional modulation in cortical neurons by a protein kinase C-dependent pathway. J Biol Chem 275:38856–38862
Carlson SL, Kumar S, Werner DF, Comerford CE, Morrow AL (2013) Ethanol activation of PKA regulates GABAA alpha1 receptor function and trafficking in cultured cerebral cortical neurons. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 345:317–25
Choi DS, Wei W, Deitchman JK, Kharazia VN, Lesscher HM, McMahon T, Wang D, Qi ZH, Sieghart W, Zhang C, Shokat KM, Mody I, Messing RO (2008) Protein kinase Cdelta regulates ethanol intoxication and enhancement of GABA-stimulated tonic current. J Neurosci 28:11890–9
Cohen AS, Lin DD, Coulter DA (2000) Protracted postnatal development of inhibitory synaptic transmission in rat hippocampal area CA1 neurons. J Neurophysiol 84:2465–76
Connolly CN, Kittler JT, Thomas P, Uren JM, Brandon NJ, Smart TG, Moss SJ (1999) Cell surface stability of gamma-aminobutyric acid type A receptors. Dependence on protein kinase C activity and subunit composition. J Biol Chem 274:36565–72
Darstein M, Albrecht C, Lopez-Francos L, Knorle R, Holter SM, Spanagel R, Feuerstein TJ (1998) Release and accumulation of neurotransmitters in the rat brain: acute effects of ethanol in vitro and effects of long-term voluntary ethanol intake. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 22:704–9
el Touny S, Khan W, Hannun Y (1990) Regulation of platelet protein kinase C by oleic acid. Kinetic analysis of allosteric regulation and effects on autophosphorylation, phorbol ester binding, and susceptibility to inhibition. J Biol Chem 265:16437–43
Fleming RL, Wilson WA, Swartzwelder HS (2007) Magnitude and ethanol sensitivity of tonic GABAA receptor-mediated inhibition in dentate gyrus changes from adolescence to adulthood. J Neurophysiol 97:3806–11
Franks NP, Lieb WR (1990) Mechanisms of general anesthesia. Environ Heal Perspect 87:199–205
Galeotti N, Ghelardini C (2011) Antidepressant phenotype by inhibiting the phospholipase Cbeta(1)–protein kinase Cgamma pathway in the forced swim test. Neuropharmacology 60:937–43
Grosshans DR, Clayton DA, Coultrap SJ, Browning MD (2002) Analysis of glutamate receptor surface expression in acute hippocampal slices. Sci STKE 2002:pl8
Hahm ET, Lee JJ, Min BI, Cho YW (2005) Developmental change of GABAergic postsynaptic current in rat periaqueductal gray. Neurosci Lett 380:187–92
Harris RA, McQuilkin SJ, Paylor R, Abeliovich A, Tonegawa S, Wehner JM (1995) Mutant mice lacking the gamma isoform of protein kinase C show decreased behavioral actions of ethanol and altered function of gamma-aminobutyrate type A receptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 92:3658–62
Hellstrand M, Eriksson E, Nilsson CL (2002) Dopamine D(2) receptor-induced COX-2-mediated production of prostaglandin E(2) in D(2)-transfected Chinese hamster ovary cells without simultaneous administration of a Ca(2+)-mobilizing agent. Biochem Pharmacol 63:2151–8
Herring D, Huang R, Singh M, Robinson LC, Dillon GH, Leidenheimer NJ (2003) Constitutive GABAA receptor endocytosis is dynamin-mediated and dependent on a dileucine AP2 adaptin-binding motif within the beta 2 subunit of the receptor. J Biol Chem 278:24046–52
Hodge CW, Mehmert KK, Kelley SP, McMahon T, Haywood A, Olive MF, Wang D, Sanchez-Perez AM, Messing RO (1999) Supersensitivity to allosteric GABAA receptor modulators and alcohol in mice lacking PKCepsilon. Nat Neurosci 2:997–1002
Itoh Y, Sendo T, Yano T, Saito M, Kubota T, Oishi R (2004) Comparison of cellular mechanisms underlying histamine release from rat mast cells induced by ionic and nonionic radiographic contrast media. Invest Radiol 39:455–61
Johnston LD, O’Malley PM, Bachman JG, Schulenberg JE (2012) Monitoring the future national results on adolescent drug use: overview of key findings 2011. Institute for Social Research, The University of Michigan, Ann Arbor
Khan WA, Blobe GC, Richards AL, Hannun YA (1994) Identification, partial purification, and characterization of a novel phospholipid-dependent and fatty acid-activated protein kinase from human platelets. J Biol Chem 269:9729–35
Khan WA, Blobe GC, Hannun YA (1995) Arachidonic acid and free fatty acids as second messengers and the role of protein kinase C. Cellular signalling 7:171–84
Kretschmannova K, Hines RM, Revilla-Sanchez R, Terunuma M, Tretter V, Jurd R, Kelz MB, Moss SJ, Davies PA (2013) Enhanced tonic inhibition influences the hypnotic and amnestic actions of the intravenous anesthetics etomidate and propofol. J Neurosci 33:7264–73
Kumar S, Sieghart W, Morrow AL (2002) Association of protein kinase C with GABAA receptors containing alpha1 and alpha4 subunits in the cerebral cortex: selective effects of chronic ethanol consumption. J Neurochem 82:110–7
Kumar S, Khisti RT, Morrow AL (2005) Regulation of native GABAA receptors by PKC and protein phosphatase activity. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 183:241–7
Kumar S, Lane BM, Morrow AL (2006) Differential effects of systemic ethanol administration on protein kinase cepsilon, gamma, and beta isoform expression, membrane translocation, and target phosphorylation: reversal by chronic ethanol exposure. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 319:1366–75
Kumar S, Porcu P, Werner DF, Matthews DB, Diaz-Granados JL, Helfand RS, Morrow AL (2009) The role of GABAA receptors in the acute and chronic effects of ethanol: a decade of progress. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 205:529–64
Kumar S, Suryanarayanan A, Boyd KN, Comerford CE, Lai MA, Ren Q, Morrow AL (2010) Ethanol reduces GABAA alpha1 subunit receptor surface expression by a protein kinase Cgamma-dependent mechanism in cultured cerebral cortical neurons. Mol Pharmacol 77:793–803
Kumar S, Ren Q, Beckley JH, O’Buckley TK, Gigante ED, Santerre JL, Werner DF, Morrow AL (2012) Ethanol activation of protein kinase A regulates GABAA receptor subunit expression in the cerebral cortex and contributes to ethanol-induced hypnosis. Front Neurosci 6(44)
Kurz T, Tolg R, Richardt G (1997) Bradykinin B2-receptor-mediated stimulation of exocytotic noradrenaline release from cardiac sympathetic neurons. J Mol Cell Cardiol 9:2561–9
LaBelle EF, Polyak E (1998) Norepinephrine stimulates arachidonic acid release from vascular smooth muscle via activation of cPLA2. Am J Physiol 4:1129–37
Liang J, Spigelman I, Olsen RW (2009) Tolerance to sedative/hypnotic actions of GABAergic drugs correlates with tolerance to potentiation of extrasynaptic tonic currents of alcohol-dependent rats. J Neurophysiol 102:224–33
Lovinger DM, Homanics GE (2007) Tonic for what ails us? high-affinity GABAA receptors and alcohol. Alcohol 41:139–43
Markwiese BJ, Acheson SK, Levin ED, Wilson WA, Swartzwelder HS (1998) Differential effects of ethanol on memory in adolescent and adult rats. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 22:416–21
Martin LJ, Zurek AA, Bonin RP, Oh GH, Kim JH, Mount HT, Orser BA (2011) The sedative but not the memory-blocking properties of ethanol are modulated by alpha5-subunit-containing gamma-aminobutyric acid type A receptors. Behav Brain Res 217:379–85
Masliah E, Yoshida K, Shimohama S, Gage FH, Saitoh T (1991) Differential expression of protein kinase C isozymes in rat glial cell cultures. Brain Res 549:106–11
McDonald BJ, Moss SJ (1997) Conserved phosphorylation of the intracellular domains of GABAA receptor beta2 and beta3 subunits by cAMP-dependent protein kinase, cGMP-dependent protein kinase protein kinase C and Ca2+/calmodulin type II-dependent protein kinase. Neuropharmacology 36:1377–85
Moss SJ, Doherty CA, Huganir RL (1992) Identification of the cAMP-dependent protein kinase and protein kinase C phosphorylation sites within the major intracellular domains of the beta 1, gamma 2S, and gamma 2L subunits of the gamma-aminobutyric acid type A receptor. J Biol Chem 267:14470–6
NIAAA (2000) 10th Special report to the US Congress on alcohol and health: highlights from current research, National Institutes of Health: National Institute of Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism, Washington DC
NIDA (2011) NIDA Info Facts. National Institutes of Health - Department of Health.
Nishizuka Y (1992) Intracellular signaling by hydrolysis of phospholipids and activation of protein kinase C. Science 258:607–14
Ohsawa M, Kamei J (1997) Pretreatment with the protein kinase C activator phorbol 12,13-dibutyrate attenuates the ethanol-induced loss of the righting reflex in mice: modification by diabetes. Brain Res 764:244–8
Olsen RW, Sieghart W (2009) GABAA receptors: subtypes provide diversity of function and pharmacology. Neuropharmacology 56:141–8
Paxinos G, Watson CH (2007) The rat brain in stereotaxic coordinates. Elsevier, London, UK
Prenosil GA, Schneider Gasser EM, Rudolph U, Keist R, Fritschy JM, Vogt KE (2006) Specific subtypes of GABAA receptors mediate phasic and tonic forms of inhibition in hippocampal pyramidal neurons. J Neurophysiol 96:846–57
Proctor WR, Poelchen W, Bowers BJ, Wehner JM, Messing RO, Dunwiddie TV (2003) Ethanol differentially enhances hippocampal GABAA receptor-mediated responses in protein kinase C gamma (PKC gamma) and PKC epsilon null mice. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 305:264–70
Qi ZH, Song M, Wallace MJ, Wang D, Newton PM, McMahon T, Chou WH, Zhang C, Shokat KM, Messing RO (2007) Protein kinase C epsilon regulates gamma-aminobutyrate type A receptor sensitivity to ethanol and benzodiazepines through phosphorylation of gamma2 subunits. J Biol Chem 282:33052–63
Ramirez RL, Spear LP (2010) Ontogeny of ethanol-induced motor impairment following acute ethanol: assessment via the negative geotaxis reflex in adolescent and adult rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 95:242–8
Rubin R (1989) Ethanol interferes with collagen-induced platelet activation by inhibition of arachidonic acid mobilization. Arch Biochem Biophys 270:99–113
Russell C, Acevedo-Duncan M (2005) Effects of the PKC inhibitor PD 406976 on cell cycle progression, proliferation, PKC isozymes and apoptosis in glioma and SVG-transformed glial cells. Cell proliferation 38:87–106
Sabria J, Torres D, Pasto M, Peralba JM, Allali-Hassani A, Pares X (2003) Release of neurotransmitters from rat brain nerve terminals after chronic ethanol ingestion: differential effects in cortex and hippocampus. Addict Biol 8:287–94
Shanker G, Hampson RE, Aschner M (2004) Methylmercury stimulates arachidonic acid release and cytosolic phospholipase A2 expression in primary neuronal cultures. Neurotoxicology 25:399–406
Silveri MM, Spear LP (1998) Decreased sensitivity to the hypnotic effects of ethanol early in ontogeny. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 22:670–6
Silveri MM, Spear LP (2002) The effects of NMDA and GABAA pharmacological manipulations on ethanol sensitivity in immature and mature animals. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 26:449–56
Tabakoff B, Nelson E, Yoshimura M, Hellevuo K, Hoffman PL (2001) Phosphorylation cascades control the actions of ethanol on cell cAMP signalling. J Biomed Sci 8:44–51
Terunuma M, Xu J, Vithlani M, Sieghart W, Kittler J, Pangalos M, Haydon PG, Coulter DA, Moss SJ (2008) Deficits in phosphorylation of GABAA receptors by intimately associated protein kinase C activity underlie compromised synaptic inhibition during status epilepticus. J Neurosci 28(2):376–84
Thomson FJ, Johnson MS, Mitchell R, Wolbers WB, Ison AJ, MacEwan DJ (1993) The differential effects of protein kinase C activators and inhibitors on rat anterior pituitary hormone release. Mol Cell Endocrinol 94:223–34
Van Skike CE, Botta P, Chin VS, Tokunaga S, McDaniel JM, Venard J, Diaz-Granados JL, Valenzuela CF, Matthews DB (2010) Behavioral effects of ethanol in cerebellum are age dependent: potential system and molecular mechanisms. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 34:2070–80
Wang J, Chen Q, Zhou J, Wen J, Bian F, Li G, Mu X, Han Y, Xia G, Zhang M (2012) Specific protein kinase C isoforms alpha and betaI are involved in follicle-stimulating hormone-induced mouse follicle-enclosed oocytes meiotic resumption. PloS one 7:e45043
Weiner JL, Valenzuela CF (2006) Ethanol modulation of GABAergic transmission: the view from the slice. Pharmacol Ther 111(3):533–54
Werner DF, Kumar S, Criswell HE, Suryanarayanan A, Fetzer JA, Comerford CE, Morrow AL (2011) PKCgamma is required for ethanol-induced increases in GABAA receptor alpha4 subunit expression in cultured cerebral cortical neurons. J Neurochem 116:554–63
Yeo JF, Ong WY, Ling SF, Farooqui AA (2004) Intracerebroventricular injection of phospholipases A2 inhibitors modulates allodynia after facial carrageenan injection in mice. Pain 112:148–55
Yu ZY, Wang W, Fritschy JM, Witte OW, Redecker C (2006) Changes in neocortical and hippocampal GABAA receptor subunit distribution during brain maturation and aging. Brain Res 1099:73–81
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Institute of Health grants AA017823 and AA019367 and the Developmental Exposure Alcohol Research Center. The authors would like to thank Laura Mickelson for her technical assistance. We would also like to thank Linda Spear and A. Leslie Morrow for their thoughtful comments and discussions during the drafting of this manuscript.
Conflict of interest
The authors have no financial conflicts of interest to disclose.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Santerre, J.L., Gigante, E.D., Landin, J.D. et al. Molecular and behavioral characterization of adolescent protein kinase C following high dose ethanol exposure. Psychopharmacology 231, 1809–1820 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-013-3267-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-013-3267-6