Abstract
Rationale
Neuroactive steroids and benzodiazepines can positively modulate GABA by acting at distinct binding sites on synaptic GABAA receptors. Although these receptors are thought to mediate the behavioral effects of both benzodiazepines and neuroactive steroids, other receptors (e.g., extrasynaptic GABAA, N-methyl-d-aspartate (NMDA), σ1, or 5-HT3 receptors) might contribute to the effects of neuroactive steroids, accounting for differences among positive modulators.
Objective
The current study established the neuroactive steroid pregnanolone as a discriminative stimulus to determine whether actions in addition to positive modulation of synaptic GABAA receptors might contribute to its discriminative stimulus effects.
Methods
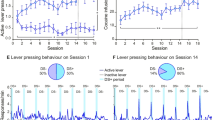
Four rhesus monkeys discriminated 5.6 mg/kg pregnanolone while responding under a fixed-ratio 10 schedule of stimulus-shock termination.
Results
Positive modulators acting at benzodiazepine, barbiturate, or neuroactive steroid sites produced ≥80 % pregnanolone-lever responding, whereas drugs acting primarily at receptors other than synaptic GABAA receptors, such as extrasynaptic GABAA, NMDA, σ1, and 5-HT3 receptors, produced vehicle-lever responding. Flumazenil antagonized the benzodiazepines midazolam and flunitrazepam, with Schild analyses yielding slopes that did not deviate from unity and pA2 values of 7.39 and 7.32, respectively. Flumazenil did not alter the discriminative stimulus effects of pregnanolone.
Conclusion
While these results do not exclude the possibility that pregnanolone acts at receptors other than synaptic GABAA receptors, they indicate a primary and possibly exclusive role of synaptic GABAA receptors in its discriminative stimulus effects. Reported differences in the effects of benzodiazepines and neuroactive steroids are not due to differences in their actions at synaptic GABAA receptors.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arunlakshana O, Schild HO (1959) Some quantitative uses of drug antagonists. Br J Pharmacol 14:48–58
Ator NA (1990) Drug discrimination and drug stimulus generalization with anxiolytics. Drug Dev Res 20:189–204
Ator NA, Grant KA, Purdy RH, Paul SM, Griffiths RR (1993) Drug discrimination analysis of endogenous neuroactive steroids in rats. Eur J Pharmacol 241:237–243
Ator NA (1999) High-dose discrimination training with midazolam: context determines generalization profile. Pharmacol, Biochem Behav 64:237–243
Ator NA (2003) Selectivity in generalization to GABAergic drugs in midazolam-trained baboons. Pharmacol, Biochem Behav 75:435–445
Bai X, Gerak LR (2011) Comparing the discriminative stimuli produced by either the neuroactive steroid pregnanolone or the benzodiazepine midazolam in rats. Psychopharmacology 214:427–435
Dantzer R, Pério A (1982) Behavioural evidence for partial agonist properties of RO 15–1788, a benzodiazepine receptor antagonist. Eur J Pharmacol 81:655–658
de la Garza R, Johanson CE (1987) Discriminative stimulus properties of intragastrically administered d-amphetamine and pentobarbital in rhesus monkeys. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 243:955–962
Dubrovsky BO (2005) Steroids, neuroactive steroids and neurosteroids in psychopathology. Prog NeuroPsychopharmacol Biol Psych 29:169–192
Engel SR, Purdy RH, Grant KA (2001) Characterization of discriminative stimulus effects of the neuroactive steroid pregnanolone. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 297:489–495
Eppolito AK, Gerak LR (2010) Tolerance to the rate-increasing and not rate-decreasing effects of pregnanolone in rats. Behav Pharmacol 21:736–744
Eppolito AK, Bai X, Gerak LR (2012) Discriminative stimulus effects of pregnanolone in rats: role of training dose in determining mechanism of action. Psychopharmacology 223:139–147
Evans SM, Johanson CE (1989) Discriminative stimulus properties of midazolam in the pigeon. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 248:29–38
Garcha HS, Rose IC, Stolerman IP (1985) Midazolam cue in rats: generalization tests with anxiolytic and other drugs. Psychopharmacology 87:233–237
Gerak LR, McMahon LR, France CP (2008a) Acute cross tolerance to midazolam, and not pentobarbital and pregnanolone, after a single dose of chlordiazepoxide in monkeys discriminating midazolam. Behav Pharmacol 19:796–804
Gerak LR, Winsauer PJ, Moerschbaecher JM (2008b) Overlapping, but not identical, discriminative stimulus effects of the neuroactive steroid pregnanolone and ethanol. Pharmacol, Biochem Behav 89:473–479
Gerak LR, France CP (2011) Chronic benzodiazepine treatment does not alter interactions between positive GABAA modulators and flumazenil or pentylenetetrazole in monkeys. Behav Pharmacol 22:49–57
Gerak LR, France CP (2012) Quantitative analyses of antagonism: combinations of midazolam and either flunitrazepam or pregnanolone in rhesus monkeys discriminating midazolam. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 340:742–749
Gonsalves SF, Gallagher DW (1987) Time course for development of anticonvulsant tolerance and GABAergic subsensitivity after chronic diazepam. Brain Res 405:94–99
Hosie AM, Wilkins ME, da Silva HM, Smart TG (2006) Endogenous neurosteroids regulate GABAA receptors through two discrete transmembrane sites. Nature 444:486–489
Kenakin T (1993) Pharmacologic analysis of drug–receptor interaction, 2nd edn. Raven Press, New York
Koek W, Assié MB, Zernig G, France CP (2000) In vivo estimates of efficacy at 5-HT1A receptors: effects of EEDQ on the ability of agonists to produce lower-lip retraction in rats. Psychopharmacology 149:377–387
Kokate TG, Svensson BE, Rogawski MA (1994) Anticonvulsant activity of neurosteroids: correlation with gamma-aminobutyric acid-evoked chloride current potentiation. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 270:1223–1229
Kokate TG, Yamaguchi S, Pannell LK, Rajamani U, Carroll DM, Grossman AB, Rogawski MA (1998) Lack of anticonvulsant tolerance to the neuroactive steroid pregnanolone in mice. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 287:553–558
Korpi ER, Sinkkonen ST (2006) GABAA receptors subtypes as targets for neuropsychiatric drug development. Pharmacol Ther 109:12–32
Lancel M (1999) Role of GABAA receptors in the regulation of sleep: initial sleep responses to peripherally administered modulators and agonists. Sleep 22:33–42
Lelas S, Gerak LR, France CP (1999) Discriminative-stimulus effects of triazolam and midazolam in rhesus monkeys. Behav Pharmacol 10:39–50
Lelas S, Gerak LR, France CP (2000) Antagonism of the discriminative stimulus effects of positive γ-aminobutyric acidA modulators in rhesus monkeys discriminating midazolam. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 294:902–908
Löscher W, Rundfeldt C, Hönack D, Ebert U (1996) Long-term studies on anticonvulsant tolerance and withdrawal characteristics of benzodiazepine receptor ligands in different seizure models in mice. I. Comparison of diazepam, clonazepam, clobazam and abecarnil. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 279:561–572
Maurice T, Urani A, Phan VL, Romieu P (2001) The interaction between neuroactive steroids and the sigma1 receptor function: behavioral consequences and therapeutic opportunities. Brain Res Brain Res Rev 37:116–132
McKernan RM, Whiting PJ (1996) Which GABAA-receptor subtypes really occur in the brain? TINS 19:139–143
McMahon LR, Gerak LR, France CP (2001) Potency of positive γ-aminobutyric acidA modulators to substitute for a midazolam discriminative stimulus in untreated monkeys does not predict potency to attenuate a flumazenil discriminative stimulus in diazepam-treated monkeys. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 298:1227–1235
McMahon LR, France CP (2002a) Acute and chronic effects of the neuroactive steroid pregnanolone on schedule-controlled responding in rhesus monkeys. Behav Pharmacol 13:545–555
McMahon LR, France CP (2002b) Daily treatment with diazepam differentially modifies sensitivity to the effects of γ-aminobutyric acidA modulators on schedule-controlled responding in rhesus monkeys. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 300:1017–1025
McMahon LR, France CP (2005) Combined discriminative stimulus effects of midazolam with other positive GABAA modulators and GABAA receptor agonists in rhesus monkeys. Psychopharmacology 178:400–409
Morrow AL (2007) Recent developments in the significance and therapeutic relevance of neuroactive steroids—Introduction to the special issue. Pharmacol Ther 116:1–6
Olsen RW, Sieghart W (2009) GABAA receptors: subtypes provide diversity of function and pharmacology. Neuropharmacology 56:141–148
Olsen RW, Hanchar HJ, Meera P, Wallner M (2007) GABAA receptor subtypes: the “one glass of wine” receptors. Alcohol 41:201–209
Reddy DS, Rogawski MA (2000) Chronic treatment with the neuroactive steroid ganaxolone in the rat induces anticonvulsant tolerance to diazepam but not to itself. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 295:1241–1248
Reddy DS, Rogawski MA (2001) Enhanced anticonvulsant activity of neuroactive steroids in a rat model of catamenial epilepsy. Epilepsia 42:337–344
Rowlett JK, Winger G, Carter RB, Wood PL, Woods JH, Woolverton WL (1999) Reinforcing and discriminative stimulus effects of the neuroactive steroids pregnanolone and Co 8–7071 in rhesus monkeys. Psychopharmacology 145:205–212
Rupprecht R, di Michele F, Hermann B, Strohle A, Lancel M, Romeo E, Holsboer F (2001) Neuroactive steroids: molecular mechanisms of action and implications for neuropsychopharmacology. Brain Res 37:59–67
Shannon EE, Porcu P, Purdy RH, Grant KA (2005a) Characterization of the discriminative stimulus effects of the neuroactive steroid pregnanolone in DBA/2J and C57BL/6J inbred mice. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 314:675–685
Shannon EE, Purdy RG, Grant KA (2005b) Discriminative stimulus effects of 5.6 mg/kg of pregnanolone in DBA/2J and C57BL/6J inbred mice. Alcohol 32:35–45
Spealman RD (1985) Discriminative stimulus effects of midazolam in squirrel monkeys: comparison with other drugs and antagonism by Ro 15–1788. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 235:456–462
Vanover KE (1997) Discriminative stimulus effects of the endogenous neuroactive steroid pregnanolone. Eur J Pharmacol 327:97–101
Vanover KE, Suruki M, Robledo S, Huber M, Wieland S, Lan NC, Gee KW, Wood PL, Carter RB (1999) Positive allosteric modulators of the GABAA receptor: differential interaction of benzodiazepines and neuroactive steroids with ethanol. Psychopharmacology 141:77–82
Vanover KE (2000) Effects of benzodiazepine receptor ligands and ethanol in rats trained to discriminate pregnanolone. Pharmacol, Biochem Behav 67:483–487
Wafford KA (2005) GABAA receptor subtypes: any clues to the mechanism of benzodiazepine dependence? Curr Opin Pharmacol 5:47–52
Wieland S, Belluzzi J, Hawkinson JE, Hogenkamp D, Upasani R, Stein L, Wood PL, Gee KW, Lan NC (1997) Anxiolytic and anticonvulsant activity of a synthetic neuroactive steroid Co 3–0593. Psychopharmacology 134:46–54
Woudenberg F, Slangen JL (1989) Discriminative stimulus properties of midazolam: comparison with other benzodiazepines. Psychopharmacology 97:466–470
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to thank T. Andrews, B. Blaylock, B. Harrington, A. Hernandez, Victoria Hill, Victoria Le, J. Pressly and S. Schirmer for their excellent technical assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
These studies were supported by the National Institutes of Health National Institute on Drug Abuse [Grant DA009157] and a Senior Scientist Award to CPF [Grant K05 DA17918]. The content is solely the responsibility of the authors and does not necessarily represent the official views of the National Institute on Drug Abuse or the National Institutes of Health.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gerak, L.R., France, C.P. Discriminative stimulus effects of pregnanolone in rhesus monkeys. Psychopharmacology 231, 181–190 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-013-3218-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-013-3218-2