Abstract
Rationale
Clinical observations indicate that atypical antipsychotics, especially clozapine, induce obsessive–compulsive (OC) symptoms in schizophrenia patients. Recent data from neuroimaging and clinical trials suggest a role for altered glutamate neurotransmission in the etiology of OC disorder (OCD), and SLC1A1, GRIN2B, and GRIK2 have all been reported to regulate glutamate transmission and affect OCD pathophysiology.
Objectives
This study aimed to determine whether SLC1A1, GRIN2B, and GRIK2 are associated with clozapine-induced OC symptoms.
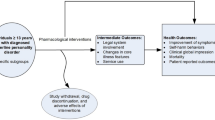
Methods
A total of 250 clinically stable schizophrenia patients receiving clozapine treatment were recruited. The Yale-Brown Obsessive Compulsive Scale (Y-BOCS) was used to evaluate the severity of OC symptoms. Based on their Y-BOCS scores, 250 patients were divided into the OC and non-OC groups (patients with or without OC symptoms, respectively). Additionally, three reported OCD susceptibility polymorphisms, SLC1A1 (rs2228622), GRIN2B (rs890), and GRIK2 (rs1556995), were genotyped.
Results
Trends of association with OC symptoms were observed in rs2228622A and rs890T alleles. SLC1A1 and GRIN2B interaction was found in the significant two-locus gene–gene interaction model (p = 0.0021), using the multifactor dimensionality reduction method. Further analysis showed a significant interaction between SLC1A1 and GRIN2B on the Y-BOCS score (F 6, 137 = 7.650, p < 0.001), and individuals with AA/TT genotypes had a significantly higher mean Y-BOCS score than those with other genotypes, except AG/TT.
Conclusions
These results suggest that SLC1A1, GRIN2B, and interactions between the two may potentially confer a susceptibility to OC symptoms in schizophrenia patients receiving clozapine.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arnold PD, Rosenberg DR, Mundo E, Tharmalingam S, Kennedy JL, Richter MA (2004) Association of a glutamate (NMDA) subunit receptor gene (GRIN2B) with obsessive-compulsive disorder: a preliminary study. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 174:530–538
Arnold PD, Sicard T, Burroughs E, Richter MA, Kennedy JL (2006) Glutamate transporter gene SLC1A1 associated with obsessive-compulsive disorder. Arch Gen Psychiatry 63:769–776
Arnold PD, Macmaster FP, Hanna GL, Richter MA, Sicard T, Burroughs E, Mirza Y, Easter PC, Rose M, Kennedy JL, Rosenberg DR (2009) Glutamate system genes associated with ventral prefrontal and thalamic volume in pediatric obsessive-compulsive disorder. Brain Imaging Behav 3:64–76
Asenjo Lobos C, Komossa K, Rummel-Kluge C, Hunger H, Schmid F, Schwarz S, Leucht S (2010) Clozapine versus other atypical antipsychotics for schizophrenia. Cochrane Database Syst Rev CD006633
Atmaca M, Yildirim H, Ozdemir H, Aydin A, Tezcan E, Ozler S (2006) Volumetric MRI assessment of brain regions in patients with refractory obsessive-compulsive disorder. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 30:1051–1057
Chakrabarty K, Bhattacharyya S, Christopher R, Khanna S (2005) Glutamatergic dysfunction in OCD. Neuropsychopharmacology 30:1735–1740
Conne B, Stutz A, Vassalli JD (2000) The 3′ untranslated region of messenger RNA: a molecular ‘hotspot’ for pathology? Nat Med 6:637–641
de Haan L, Linszen DH, Gorsira R (1999) Clozapine and obsessions in patients with recent-onset schizophrenia and other psychotic disorders. J Clin Psychiatry 60:364–365
Delorme R, Krebs MO, Chabane N, Roy I, Millet B, Mouren-Simeoni MC, Maier W, Bourgeron T, Leboyer M (2004) Frequency and transmission of glutamate receptors GRIK2 and GRIK3 polymorphisms in patients with obsessive compulsive disorder. Neuroreport 15:699–702
Dickel DE, Veenstra-VanderWeele J, Cox NJ, Wu X, Fischer DJ, Van Etten-Lee M, Himle JA, Leventhal BL, Cook EH Jr, Hanna GL (2006) Association testing of the positional and functional candidate gene SLC1A1/EAAC1 in early-onset obsessive-compulsive disorder. Arch Gen Psychiatry 63:778–785
Ertugrul A, Anil Yagcioglu AE, Eni N, Yazici KM (2005) Obsessive-compulsive symptoms in clozapine-treated schizophrenic patients. Psychiatry Clin Neurosci 59:219–222
Evins AE, Amico ET, Shih V, Goff DC (1997) Clozapine treatment increases serum glutamate and aspartate compared to conventional neuroleptics. J Neural Transm 104:761–766
Fenton WS, McGlashan TH (1986) The prognostic significance of obsessive-compulsive symptoms in schizophrenia. Am J Psychiatry 143:437–441
Goodman WK, Price LH, Rasmussen SA, Mazure C, Fleischmann RL, Hill CL, Heninger GR, Charney DS (1989) The Yale-Brown obsessive compulsive scale. I. Development, use, and reliability. Arch Gen Psychiatry 46:1006–1011
Hahn LW, Ritchie MD, Moore JH (2003) Multifactor dimensionality reduction software for detecting gene–gene and gene–environment interactions. Bioinformatics 19:376–382
Hollmann M, Heinemann S (1994) Cloned glutamate receptors. Annu Rev Neurosci 17:31–108
Jamain S, Betancur C, Quach H, Philippe A, Fellous M, Giros B, Gillberg C, Leboyer M, Bourgeron T (2002) Linkage and association of the glutamate receptor 6 gene with autism. Mol Psychiatry 7:302–310
Kayahan B, Ozturk O, Veznedaroglu B, Eraslan D (2005) Obsessive-compulsive symptoms in schizophrenia: prevalence and clinical correlates. Psychiatry Clin Neurosci 59:291–295
Khullar A, Chue P, Tibbo P (2001) Quetiapine and obsessive–compulsive symptoms (OCS): case report and review of atypical antipsychotic-induced OCS. J Psychiatry Neurosci 26:55–59
Kwon JS, Joo YH, Nam HJ, Lim M, Cho EY, Jung MH, Choi JS, Kim B, Kang DH, Oh S, Park T, Hong KS (2009) Association of the glutamate transporter gene SLC1A1 with atypical antipsychotics-induced obsessive-compulsive symptoms. Arch Gen Psychiatry 66:1233–1241
Lieberman JA, Stroup TS, McEvoy JP, Swartz MS, Rosenheck RA, Perkins DO, Keefe RS, Davis SM, Davis CE, Lebowitz BD, Severe J, Hsiao JK (2005) Effectiveness of antipsychotic drugs in patients with chronic schizophrenia. N Engl J Med 353:1209–1223
Liu BC, Zhang J, Wang L, Li XW, Wang Y, Ji J, Yang FP, Wan CL, Gao LH, Xu YF, Feng GY, He L, Zhao XZ, He G (2010) No association between EGR gene family polymorphisms and schizophrenia in the Chinese population. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 34:506–509
Marazziti D, Carlini M, Dell'Osso L (2012) Treatment strategies of obsessive-compulsive disorder and panic disorder/agoraphobia. Curr Top Med Chem 12:238–253
McEvoy JP, Lieberman JA, Stroup TS, Davis SM, Meltzer HY, Rosenheck RA, Swartz MS, Perkins DO, Keefe RS, Davis CE, Severe J, Hsiao JK (2006) Effectiveness of clozapine versus olanzapine, quetiapine, and risperidone in patients with chronic schizophrenia who did not respond to prior atypical antipsychotic treatment. Am J Psychiatry 163:600–610
Ongur D, Goff DC (2005) Obsessive–compulsive symptoms in schizophrenia: associated clinical features, cognitive function and medication status. Schizophr Res 75:349–362
Pauls DL (2008) The genetics of obsessive compulsive disorder: a review of the evidence. Am J Med Genet C Semin Med Genet 148C:133–139
Rosenberg DR, MacMaster FP, Keshavan MS, Fitzgerald KD, Stewart CM, Moore GJ (2000) Decrease in caudate glutamatergic concentrations in pediatric obsessive-compulsive disorder patients taking paroxetine. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry 39:1096–1103
Ryu S, Oh S, Cho EY, Nam HJ, Yoo JH, Park T, Joo YH, Kwon JS, Hong KS (2011) Interaction between genetic variants of DLGAP3 and SLC1A1 affecting the risk of atypical antipsychotics-induced obsessive–compulsive symptoms. Am J Med Genet B Neuropsychiatr Genet 156B:949–959
Sa AR, Hounie AG, Sampaio AS, Arrais J, Miguel EC, Elkis H (2009) Obsessive-compulsive symptoms and disorder in patients with schizophrenia treated with clozapine or haloperidol. Compr Psychiatry 50:437–442
Sampaio AS, Fagerness J, Crane J, Leboyer M, Delorme R, Pauls DL, Stewart SE (2011) Association between polymorphisms in GRIK2 gene and obsessive-compulsive disorder: a family-based study. CNS Neurosci Ther 17:141–147
Samuels J, Wang Y, Riddle MA, Greenberg BD, Fyer AJ, McCracken JT, Rauch SL, Murphy DL, Grados MA, Knowles JA, Piacentini J, Cullen B, Bienvenu OJ 3rd, Rasmussen SA, Geller D, Pauls DL, Liang KY, Shugart YY, Nestadt G (2011) Comprehensive family-based association study of the glutamate transporter gene SLC1A1 in obsessive-compulsive disorder. Am J Med Genet B Neuropsychiatr Genet 156B:472–477
Schirmbeck F, Zink M (2012) Clozapine-induced obsessive-compulsive symptoms in schizophrenia: a critical review. Curr Neuropharmacol 10:88–95
Schirmbeck F, Esslinger C, Rausch F, Englisch S, Meyer-Lindenberg A, Zink M (2011) Antiserotonergic antipsychotics are associated with obsessive-compulsive symptoms in schizophrenia. Psychol Med 41:2361–2373
Shi YY, He L (2005) SHEsis, a powerful software platform for analyses of linkage disequilibrium, haplotype construction, and genetic association at polymorphism loci. Cell Res 15:97–98
Stewart SE, Fagerness JA, Platko J, Smoller JW, Scharf JM, Illmann C, Jenike E, Chabane N, Leboyer M, Delorme R, Jenike MA, Pauls DL (2007) Association of the SLC1A1 glutamate transporter gene and obsessive-compulsive disorder. Am J Med Genet B Neuropsychiatr Genet 144B:1027–1033
van Grootheest DS, Cath DC, Beekman AT, Boomsma DI (2005) Twin studies on obsessive–compulsive disorder: a review. Twin Res Hum Genet 8:450–458
Wu K, Hanna GL, Rosenberg DR, Arnold PD (2012) The role of glutamate signaling in the pathogenesis and treatment of obsessive–compulsive disorder. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 100:726–735
Zhang C, Li Z, Shao Y, Xie B, Du Y, Fang Y, Yu S (2011) Association study of tryptophan hydroxylase-2 gene in schizophrenia and its clinical features in Chinese Han population. J Mol Neurosci 43:406–411
Acknowledgments
We are deeply grateful to all participants. This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81000581), Shanghai Science & Technology Development Foundation (12140904200), and the National Key Clinical Disciplines at Shanghai Mental Health Center (OMA-MH2011-873).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cai, J., Zhang, W., Yi, Z. et al. Influence of polymorphisms in genes SLC1A1, GRIN2B, and GRIK2 on clozapine-induced obsessive–compulsive symptoms. Psychopharmacology 230, 49–55 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-013-3137-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-013-3137-2