Abstract
Rationale
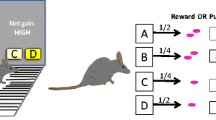
The Iowa Gambling Task (IGT) can be used to quantify impulsive and risky choice behaviors in psychiatric patients, e.g., bipolar disorder (BD) sufferers. Although developing treatments for these behaviors is important, few predictive animal models exist. Inhibition of the dopamine transporter (DAT) can model profiles of altered motor activity and exploration seen in patients with BD. The effect of DAT inhibition on impulsive choices related to BD has received limited study however. We used a rodent IGT to elucidate the effects of similarly acting drugs on risky choice behavior.
Objectives
We hypothesized that (1) C57BL/6 mice could adopt the “safe” choice options in the IGT and (2) DAT inhibition would alter risk preference.
Methods
Mice were trained in the IGT to a stable risk-preference and then administered the norepinephrine/DAT inhibitor amphetamine, or the more selective DAT inhibitors modafinil or GBR12909.
Results
Mice developed a preference for the “safe” option, which was potentiated by amphetamine administration. GBR12909 or modafinil administration increased motor impulsivity, motivation significantly, and risk preference subtly.
Conclusions
The rodent IGT can measure different impulse-related behaviors and differentiate similarly acting BD-related drugs. The contrasting effects of amphetamine and modafinil in mice are similar to effects in rats and humans in corresponding IGT tasks, supporting the translational validity of the task. GBR12909 and modafinil elicited similar behaviors in the IGT, likely through a shared mechanism. Future studies using a within-session IGT are warranted to confirm the suitability of DAT inhibitors to model risk-preference in BD.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adida M, Clark L, Pomietto P, Kaladjian A, Besnier N, Azorin JM, Jeanningros R, Goodwin GM (2008) Lack of insight may predict impaired decision making in manic patients. Bipolar Disord 10:829–837
Adida M, Jollant F, Clark L, Besnier N, Guillaume S, Kaladjian A, Mazzola-Pomietto P, Jeanningros R, Goodwin GM, Azorin JM, Courtet P (2011) Trait-related decision-making impairment in the three phases of bipolar disorder. Biol Psychiatry 70:357–365
Anand A, Barkay G, Dzemidzic M, Albrecht D, Karne H, Zheng QH, Hutchins GD, Normandin MD, Yoder KK (2011) Striatal dopamine transporter availability in unmedicated bipolar disorder. Bipolar Disord 13:406–413
Arban R, Maraia G, Brackenborough K, Winyard L, Wilson A, Gerrard P, Large C (2005) Evaluation of the effects of lamotrigine, valproate and carbamazepine in a rodent model of mania. Behav Brain Res 158:123–132
Bechara A, Damasio AR, Damasio H, Anderson SW (1994) Insensitivity to future consequences following damage to human prefrontal cortex. Cognition 50:7–15
Bechara A, Damasio H, Tranel D, Damasio AR (1997) Deciding advantageously before knowing the advantageous strategy. Science 275:1293–1295
Bechara A, Damasio H, Damasio AR, Lee GP (1999) Different contributions of the human amygdala and ventromedial prefrontal cortex to decision-making. J Neurosci 19:5473–5481
Bechara A, Damasio H, Tranel D, Damasio AR (2005) The Iowa Gambling Task and the somatic marker hypothesis: some questions and answers. Trends Cogn Sci 9:159–162, discussion 162–4
Berggren U, Tallstedt L, Ahlenius S, Engel J (1978) The effect of lithium on amphetamine-induced locomotor stimulation. Psychopharmacol (Berl) 59:41–45
Cardinal RN, Robbins TW, Everitt BJ (2000) The effects of d-amphetamine, chlordiazepoxide, alpha-flupenthixol and behavioural manipulations on choice of signalled and unsignalled delayed reinforcement in rats. Psychopharmacol (Berl) 152:362–375
Cassidy F, Ahearn EP, Carroll BJ (2002) Symptom profile consistency in recurrent manic episodes. Compr Psychiatry 43:179–181
Clark L, Iversen SD, Goodwin GM (2001) A neuropsychological investigation of prefrontal cortex involvement in acute mania. Am J Psychiatry 158:1605–1611
de Visser L, Homberg JR, Mitsogiannis M, Zeeb FD, Rivalan M, Fitoussi A, Galhardo V, van den Bos R, Winstanley CA, Dellu-Hagedorn F (2011) Rodent versions of the iowa gambling task: opportunities and challenges for the understanding of decision-making. Front Neurosci 5:109
Evenden JL (1999) Varieties of impulsivity. Psychopharmacol (Berl) 146:348–361
Flaisher-Grinberg S, Overgaard S, Einat H (2009) Attenuation of high sweet solution preference by mood stabilizers: a possible mouse model for the increased reward-seeking domain of mania. J Neurosci Methods 177:44–50
Floresco SB, St Onge JR, Ghods-Sharifi S, Winstanley CA (2008) Cortico–limbic–striatal circuits subserving different forms of cost–benefit decision making. Cogn Affect Behav Neurosci 8:375–389
Frey BN, Valvassori SS, Reus GZ, Martins MR, Petronilho FC, Bardini K, Dal-Pizzol F, Kapczinski F, Quevedo J (2006) Effects of lithium and valproate on amphetamine-induced oxidative stress generation in an animal model of mania. J Psychiatry Neurosci 31:326–332
Gould TD, Einat H (2007) Animal models of bipolar disorder and mood stabilizer efficacy: a critical need for improvement. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 31:825–831
Gould TJ, Keith RA, Bhat RV (2001) Differential sensitivity to lithium's reversal of amphetamine-induced open-field activity in two inbred strains of mice. Behav Brain Res 118:95–105
Granon S, Passetti F, Thomas KL, Dalley JW, Everitt BJ, Robbins TW (2000) Enhanced and impaired attentional performance after infusion of D1 dopaminergic receptor agents into rat prefrontal cortex. J Neurosci 20:1208–1215
Greenwood TA, Alexander M, Keck PE, McElroy S, Sadovnick AD, Remick RA, Kelsoe JR (2001) Evidence for linkage disequilibrium between the dopamine transporter and bipolar disorder. Am J Med Genet 105:145–151
Greenwood TA, Schork NJ, Eskin E, Kelsoe JR (2006) Identification of additional variants within the human dopamine transporter gene provides further evidence for an association with bipolar disorder in two independent samples. Molecular Psychiatry 11:125–133
Grottick AJ, Higgins GA (2002) Assessing a vigilance decrement in aged rats: effects of pre-feeding, task manipulation, and psychostimulants. Psychopharmacology 164:33–41
Han DD, Gu HH (2006) Comparison of the monoamine transporters from human and mouse in their sensitivities to psychostimulant drugs. BMC Pharmacol 6:6
Harrison AA, Everitt BJ, Robbins TW (1997) Central 5-HT depletion enhances impulsive responding without affecting the accuracy of attentional performance: interactions with dopaminergic mechanisms. Psychopharmacol (Berl) 133:329–342
Heikkila RE, Manzino L (1984) Behavioral properties of GBR 12909, GBR 13069 and GBR 13098: specific inhibitors of dopamine uptake. Eur J Pharmacol 103:241–248
Helms CM, Reeves JM, Mitchell SH (2006) Impact of strain and d-amphetamine on impulsivity (delay discounting) in inbred mice. Psychopharmacol (Berl) 188:144–151
Homberg JR, van den Bos R, den Heijer E, Suer R, Cuppen E (2008) Serotonin transporter dosage modulates long-term decision-making in rat and human. Neuropharmacology 55:80–84
Horschitz S, Hummerich R, Lau T, Rietschel M, Schloss P (2005) A dopamine transporter mutation associated with bipolar affective disorder causes inhibition of transporter cell surface expression. Mol Psychiatry 10:1104–1109
Kelley AE, Lang CG (1989) Effects of GBR 12909, a selective dopamine uptake inhibitor, on motor activity and operant behavior in the rat. Eur J Pharmacol 167:385–395
Kim SW, Grant JE, Eckert ED, Faris PL, Hartman BK (2006) Pathological gambling and mood disorders: clinical associations and treatment implications. J Affect Disord 92:109–116
Lapin IP (1993) Anxiogenic effect of phenylethylamine and amphetamine in the elevated plus-maze in mice and its attenuation by ethanol. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 44:241–243
Loos M, Staal J, Schoffelmeer AN, Smit AB, Spijker S, Pattij T (2010) Inhibitory control and response latency differences between C57BL/6J and DBA/2J mice in a Go/No-Go and 5-choice serial reaction time task and strain-specific responsivity to amphetamine. Behav Brain Res 214:216–224
Madras BK, Xie Z, Lin Z, Jassen A, Panas H, Lynch L, Johnson R, Livni E, Spencer TJ, Bonab AA, Miller GM, Fischman AJ (2006) Modafinil occupies dopamine and norepinephrine transporters in vivo and modulates the transporters and trace amine activity in vitro. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 319:561–569
Manji HK, Quiroz JA, Payne JL, Singh J, Lopes BP, Viegas JS, Zarate CA (2003) The underlying neurobiology of bipolar disorder. World Psychiatry 2:136–146
Merikangas KR, Jin R, He JP, Kessler RC, Lee S, Sampson NA, Viana MC, Andrade LH, Hu C, Karam EG, Ladea M, Medina-Mora ME, Ono Y, Posada-Villa J, Sagar R, Wells JE, Zarkov Z (2011) Prevalence and correlates of bipolar spectrum disorder in the world mental health survey initiative. Arch Gen Psychiatry 68:241–251
Minassian A, Henry BL, Geyer MA, Paulus MP, Young JW, Perry W (2010) The quantitative assessment of motor activity in mania and schizophrenia. J Affect Disord 120:200–206
Navarra R, Graf R, Huang Y, Logue S, Comery T, Hughes Z, Day M (2008) Effects of atomoxetine and methylphenidate on attention and impulsivity in the 5-choice serial reaction time test. Prog Neuro-Psychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 32:34–41
Onaivi ES, Martin BR (1989) Neuropharmacological and physiological validation of a computer-controlled two-compartment black and white box for the assessment of anxiety. Prog Neuro-Psychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 13:963–976
Paine TA, Tomasiewicz HC, Zhang K, Carlezon WA Jr (2007) Sensitivity of the five-choice serial reaction time task to the effects of various psychotropic drugs in Sprague–Dawley rats. Biol Psychiatry 62:687–693
Pattij T, Janssen MC, Vanderschuren LJ, Schoffelmeer AN, van Gaalen MM (2007) Involvement of dopamine D1 and D2 receptors in the nucleus accumbens core and shell in inhibitory response control. Psychopharmacol (Berl) 191:587–598
Perry W, Minassian A, Paulus MP, Young JW, Kincaid MJ, Ferguson EJ, Henry BL, Zhuang X, Masten VL, Sharp RF, Geyer MA (2009) A reverse-translational study of dysfunctional exploration in psychiatric disorders: from mice to men. Arch Gen Psychiatry 66:1072–1080
Perry W, Minassian A, Henry B, Kincaid M, Young JW, Geyer MA (2010) Quantifying over-activity in bipolar and schizophrenia patients in a human open field paradigm. Psychiatry Res 178:84–91
Pinsonneault JK, Han DD, Burdick KE, Kataki M, Bertolino A, Malhotra AK, Gu HH, Sadee W (2011) Dopamine transporter gene variant affecting expression in human brain is associated with bipolar disorder. Neuropsychopharmacology 36(8):1644–1655
Qu WM, Huang ZL, Xu XH, Matsumoto N, Urade Y (2008) Dopaminergic D1 and D2 receptors are essential for the arousal effect of modafinil. J Neurosci 28:8462–8469
Rivalan M, Ahmed SH, Dellu-Hagedorn F (2009) Risk-prone individuals prefer the wrong options on a rat version of the Iowa Gambling Task. Biol Psychiatry 66(8):743–749
Rivalan M, Coutureau E, Fitoussi A, Dellu-Hagedorn F (2011) Inter-individual decision-making differences in the effects of cingulate, orbitofrontal, and prelimbic cortex lesions in a rat gambling task. Front Behav Neurosci 5:22
Robbins TW (2002) The 5-choice serial reaction time task: behavioural pharmacology and functional neurochemistry. Psychopharmacol (Berl) 163:362–380
Robinson ES, Eagle DM, Mar AC, Bari A, Banerjee G, Jiang X, Dalley JW, Robbins TW (2008) Similar effects of the selective noradrenaline reuptake inhibitor atomoxetine on three distinct forms of impulsivity in the rat. Neuropsychopharmacology 33:1028–1037
Rothman RB, Baumann MH (2003) Monoamine transporters and psychostimulant drugs. Eur J Pharmacol 479:23–40
Sevy S, Burdick KE, Visweswaraiah H, Abdelmessih S, Lukin M, Yechiam E, Bechara A (2007) Iowa gambling task in schizophrenia: a review and new data in patients with schizophrenia and co-occurring cannabis use disorders. Schizophr Res 92:74–84
Silverstone PH, Pukhovsky A, Rotzinger S (1998) Lithium does not attenuate the effects of d-amphetamine in healthy volunteers. Psychiatry Res 79:219–226
Swann AC, Steinberg JL, Lijffijt M, Moeller FG (2008) Impulsivity: differential relationship to depression and mania in bipolar disorder. J Affect Disord 106:241–248
Swann AC, Lijffijt M, Lane SD, Steinberg JL, Moeller FG (2009) Increased trait-like impulsivity and course of illness in bipolar disorder. Bipolar Disord 11:280–288
van den Bos R, Lasthuis W, den Heijer E, van der Harst J, Spruijt B (2006) Toward a rodent model of the Iowa gambling task. Behav Res Methods 38:470–478
van den Buuse M, de Jong W (1989) Differential effects of dopaminergic drugs on open-field behavior of spontaneously hypertensive rats and normotensive Wistar–Kyoto rats. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 248:1189–1196
van der Plas EA, Crone EA, van den Wildenberg WP, Tranel D, Bechara A (2008) Executive control deficits in substance-dependent individuals: a comparison of alcohol, cocaine, and methamphetamine and of men and women. J Clin Exp Neuropsychol: 1–14
Vawter MP, Freed WJ, Kleinman JE (2000) Neuropathology of bipolar disorder. Biol Psychiatry 48:486–504
Volkow ND, Fowler JS, Logan J, Alexoff D, Zhu W, Telang F, Wang GJ, Jayne M, Hooker JM, Wong C, Hubbard B, Carter P, Warner D, King P, Shea C, Xu Y, Muench L, Apelskog-Torres K (2009) Effects of modafinil on dopamine and dopamine transporters in the male human brain: clinical implications. JAMA 301:1148–1154
Wade TR, de Wit H, Richards JB (2000) Effects of dopaminergic drugs on delayed reward as a measure of impulsive behavior in rats. Psychopharmacol (Berl) 150:90–101
Waters KA, Burnham KE, O'Connor D, Dawson GR, Dias R (2005) Assessment of modafinil on attentional processes in a five-choice serial reaction time test in the rat. J Psychopharmacol 19:149–158
Yan TC, Dudley JA, Weir RK, Grabowska EM, Pena-Oliver Y, Ripley TL, Hunt SP, Stephens DN, Stanford SC (2011) Performance deficits of NK1 receptor knockout mice in the 5-choice serial reaction-time task: effects of d-amphetamine, stress and time of day. PLoS One 6:e17586
Yechiam E, Hayden EP, Bodkins M, O'Donnell BF, Hetrick WP (2008) Decision making in bipolar disorder: a cognitive modeling approach. Psychiatry Res 161:142–152
Young JW, Geyer MA (2010) Action of modafinil—increased motivation via the dopamine transporter inhibition and D1 receptors? Biol Psychiatry 67:784–787
Young JW, Minassian A, Paulus MP, Geyer MA, Perry W (2007) A reverse-translational approach to bipolar disorder: rodent and human studies in the Behavioral Pattern Monitor. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 31:882–896
Young JW, Light GA, Marston HM, Sharp R, Geyer MA (2009) The 5-choice continuous performance test: evidence for a translational test of vigilance for mice. PLoS One 4:e4227
Young JW, Goey AK, Minassian A, Perry W, Paulus MP, Geyer MA (2010a) GBR 12909 administration as a mouse model of bipolar disorder mania: mimicking quantitative assessment of manic behavior. Psychopharmacol (Berl) 208:443–454
Young JW, Goey AK, Minassian A, Perry W, Paulus MP, Geyer MA (2010b) The mania-like exploratory profile in genetic dopamine transporter mouse models is diminished in a familiar environment and reinstated by subthreshold psychostimulant administration. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 96:7–15
Young JW, Henry BL, Geyer MA (2011a) Predictive animal models of mania, hits, misses, and future directions. Br J Pharmacol 164(4):1263–1284
Young JW, Kooistra K, Geyer MA (2011b) Dopamine receptor mediation of the exploratory/hyperactivity effects of modafinil. Neuropsychopharmacology 36:1385–1396
Young JW, van Enkhuizen J, Winstanley CA, Geyer MA (2011c) Increased risk-taking behavior in dopamine transporter knockdown mice: further support for a mouse model of mania. J Psychopharmacol 25:934–943
Zack M, Poulos CX (2009) Effects of the atypical stimulant modafinil on a brief gambling episode in pathological gamblers with high vs. low impulsivity. J Psychopharmacol 23:660–671
Zeeb FD, Winstanley CA (2011) Lesions of the basolateral amygdala and orbitofrontal cortex differentially affect acquisition and performance of a rodent gambling task. J Neurosci 31:2197–2204
Zeeb FD, Robbins TW, Winstanley CA (2009) Serotonergic and dopaminergic modulation of gambling behavior as assessed using a novel rat gambling task. Neuropsychopharmacology 34:2329–2343
Zolkowska D, Jain R, Rothman RB, Partilla JS, Roth BL, Setola V, Prisinzano TE, Baumann MH (2009) Evidence for the involvement of dopamine transporters in behavioral stimulant effects of modafinil. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 329:738–746
Acknowledgements
We thank Dr. Berend Olivier and Mahalah Buell for their support. These studies were supported by NIH grants R01-MH071916, and R21-MH091571, as well as by the Veteran's Administration VISN 22 Mental Illness Research, Education, and Clinical Center. The authors report no conflict of interest. The experiments comply with all US federal and Californian state requirements for animal care and were approved by the American Association for Accreditation of Laboratory Animal Care.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
van Enkhuizen, J., Geyer, M.A. & Young, J.W. Differential effects of dopamine transporter inhibitors in the rodent Iowa gambling task. Psychopharmacology 225, 661–674 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-012-2854-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-012-2854-2