Abstract
Rationale
It is still common to encounter a partial or no response to antipsychotic treatment in clinical practice, but only individual case reports are currently available concerning the efficacy of long-acting risperidone (RLAI) in treatment-resistant schizophrenia. The relationship between RSP and 9-OH-RSP plasma levels, and clinical response or tolerability has not yet been thoroughly assessed.
Methods
This open-label, non-randomised study involved 30 outpatients with treatment-resistant schizophrenia, who were prescribed RLAI for 6 months, and clinically evaluated using the Brief Psychiatric Rating Scale (BPRS), the Positive and Negative Symptoms Scale (PANSS), the Clinical Global Impression-Improvement Scale (CGI-I), and the Simpson and Angus Scale for Extrapyramidal Side Effects (EPSE). Plasma RSP and 9-OH-RSP levels were determined at steady-state, and the metabolic ratio (MR) was calculated as plasma 9-OH-RSP/RSP levels.
Results
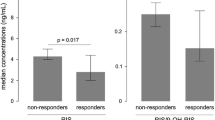
At the end of the study, 60% of the patients responded to RLAI (a ≥20% reduction in the PANSS score). Linear regression analysis showed a significant positive relationship between the RSP dose and active moiety (RSP + 9-OH-RSP) (r = 0.4; p = 0.02). There was a significant positive relationship between active moiety and EPSE scores (r = 0.6; p = 0.00). The BPRS responders had a significantly higher mean MR than the non-responders (3.41 ± 1.87 SD vs 1.60 ± 0.98 SD) (p = 0.00).
Conclusions
Therapeutic drug monitoring seems to be useful in optimising the dose of RLAI, especially in the case of tolerability problems. MR might be a better index of clinical response to RLAI than the value of the active moiety, although this needs to be confirmed by further data.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Albrecht A, Morena PG, Baumann P, Eap CB (2004) High dose of depot risperidone in a nonresponder schizophrenic patients. J Clin Psychopharmacol 24(6):673–674
Altamura AC, Bassetti R, Cattaneo E, Vismara S (2005) Some biological correlates of drug resistance in schizophrenia: a multidimensional approach. World J Biol Psychiatry 6(Suppl 2):23–30
Bondolfi G, Dufour H, Patris M, May JP, Billeter U, Eap CB, Baumann P (1998) Risperidone versus clozapine in treatment-resistant chronic schizophrenia: a randomized double-blind study. Am J Psychiatry 155:499–504
Buur-Rasmussen B, Brosen K (1999) Cytochrome P450 therapeutic drug monitoring with respect to clozapine. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol 9(6):453–459
Castberg I, Spigset O (2005) Serum concentration of risperidone and 9-hydroxyrisperidone after administration of the long-acting injectable form of risperidone. Ther Drug Monitoring 27:103–106
Conley R, Kelly D (2001) Management of treatment resistance in schizophrenia. Biol Psychiatry 50:898–911
Curtis VA, Katsafouros K, Möller HJ, Medori R, Sacchetti E (2008) Long-acting risperidone improves negative symptoms in stable psychotic patients. J Psychopharmacol 23(3):254–261
De Marinis T, Saleem PT, Glue P, Arnoldussen WJ, Teijeiro R, Lex A, Latif MA, Medori R (2007) Switching to long-acting injectable risperidone is beneficial with regard to clinical outcomes, regardless of previous conventional medication in patients with schizophrenia. Pharmacopsychiatry 40:257–263
Dremencov E, El Mansari M, Blier P (2007) Distinct electrophysiological effects of paliperidone and risperidone on the firing activity of rat serotonin and norepinephrine neurons. Psychopharmacology 194(1):63–72
Fleischhacker WW, EErdekens M, Karcher K, Remington G, Llorca PM, Chrzanowski W, Martin S, Gefvert O (2003) Treatment of schizophrenia with long-acting injectable risperidone: a 12-month open-label trial of the fist long-acting second generation antipsychotic. J Clin Psychiatry 64:1250–1257
Freudenreich O, Henderson DC, Walsh JP, Culthane MA, Goff DC (2007) Risperidone augmentation for schizophrenia partially responsive to clozapine: a double-blind, placebo-controlled trials. Schizophr Res 92:90–94
Guy W (1976) Clinical Global Impression. In: US Department of Health and Human Services, Public Health Service, ed. ECDEU assessment manual for psychopharmacology. Rockville 76: 218–220
Honer WG, Thornton AE, Chen EY, Chan RC, Wong JO, Bergmann A, Falkai P, Pomarol-Clotet E, McKenna PJ, Stip E, Williams R, MacEwan GW, Wasan K, Procyshyn R (2006) Clozapine alone versus clozapine and risperidone with refractory schizophrenia. N Engl J Med 354(5):472–482
Josiassen RC, Joseph A, Kohegyi E, Stokes S, Dadvand M, Paing WW, Shaughnessy RA (2005) Clozapine augmented with risperidone in the treatment of schizophrenia: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Am J Psychiatry 162:130–136
Kane J, Honigfeld G, Singer J, Meltzer H (1988) Clozapine for the treatment-resistant schizophrenic. A double-blind comparison with chlorpromazine. Arch Gen Psychiatry 45:789–796
Kapur S, Zipursky RB, Remington G (1999) Clinical and theoretical implications of 5-HT2 and D2 receptors occupancy of clozapine, risperidone, and olanzapine in schizophrenia. Am J Psychiatry 156:286–293
Kay SR, Fizbein A, Opler LA (1987) The Positive and Negative Syndrome Scale (PANSS) for schizophrenia. Schizophr Bull 3:261–276
Kissling W, Heres S, Lloyd K, Sacchetti E, Bouhours P, Medori R, Llorca PM (2005) Direct transition to long-acting risperidone—analysis of long-term efficacy. J Psychopharmacol 19(suppl 5):15–21
Lasser RA, Bossie CA, Gharabawi GM, Turner M (2004) Patients with schizophrenia previously stabilized on conventional depot antipsychotics experience significant clinical improvements following treatment with long-acting risperidone. Eur Psychiatry 19:219–225
Lerma-Carrillo I, Molina JD, Cuevas-Durán T, González-Parra S, Blasco-Fontecilla H, Andrade-Rosa C, López-Muñoz F, Alamo C (2007) Adjunctive treatment with risperidone in clozapine-resistant schizophrenia: a case report and review. Clin Neuropharmacol 30(2):114–121
Lindenmayer JP, Parak M, Gorman JM (2006) Improved long-term outcome with long-acting risperidone treatment of chronic schizophrenia with prior partial response. J Psychiatr Pract 12(1):55–57
Linnet K, Ejsing TB (2008) A review on the impact of P-glycoprotein on the penetration of drugs into the brain. Focus on psychotropic drugs. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol 18:157–169
Llorca PM, Bouhours P, Moreau-Mallet V (2008a) Improved symptom control, functioning and satisfaction in French patients treated with long-acting injectable risperidone. Encéphale 34:170–178
Llorca PM, Sacchetti E, Lloyd K, Kissling W, Medori R (2008b) Long-term remission in schizophrenia and related psyhcosis with long-acting risperidone: results obtained in an open-label study with an observational period of 18 months. Int J Clin Pharmacol Ther 46(1):14–22
Mannaert E, Vermeulen A, Remmerie B, Bouhours P, Levron JC (2005) Pharmacokinetic profile of long-acting injectable risperidone at steady-state: comparison with oral administration. Encéphale 31:609–615
Marino J, Caballero J (2008) Paliperidone extended-release for the treatment of schizophrenia. Pharmacotherapy 28(10):1282–1298
Mauri MC, Laini V, Boscati L, Rudelli R, Salvi V, Orlandi R, Papa P (2001) Long-term treatment of chronic schizophrenia with risperidone: a study with plasma levels. Eur Psychiatry 16:57–63
Mauri MC, Volonteri LS, Dell’Osso B, Regispani F, Papa P, Baldi M, Bareggi SR (2003) Predictors of clinical outcome in schizophrenic patients responding to clozapine. J Clin Psychopharmacol 23(6):660–664
Mauri MC, Volonteri LS, Colasanti A, Fiorentini A, De Gaspari IF, Bareggi SR (2007) Clinical pharmacokinetics of atypical antipsychotics: a critical review of the relationship between plasma concentrations and clinical response. Clin Pharmacokinet 46(5):359–388
Mauri MC, Turner M, Volonteri LS, Medori R (2009) Dosing patterns in Europe: efficacy and safety of risperidone long-acting injectable in doses of 25, 37.5 and 50 mg. Int J Psychiatry Clin Practice 13(1):36–47
Möller HJ, Llorca PM, Sacchetti E, Martin SD, Medori R, Parellada E, for the StoRMi Study Group (2005) Efficacy and safety of direct transition to risperidone long-acting injectable in patients treated with various antipsychotic therapy. Int Clin Psychopharmacol 20:121–130
Nesvag R, Hendset M, Refsum H, Tanum L (2006) Serum concentration of risperidone and 9-OH risperidone following intramuscular injection of long-acting risperidone compared with oral risperidone medication. Acta Psychiatr Scand 114:21–26
Odou P, Levron JC, Luyckx M (2000) Risperidone drug monitoring. A useful clinical tool? Clin Drug Invest 19:283–292
Olesen OV, Licht RW, Thomsen E, Bruun T, Viftrup JE, Linnet K (1998) Serum concentrations and side effects in psychiatric patients during risperidone therapy. Ther Drug Monit 20:380–384
Overall J, Gorham D (1962) Brief Psychiatric Rating Scale. Psychol Rep 10:799–812
Pani L, Marchese G (2009) Expected clinical benefits of paliperidone extended-release formulation when compared with risperidone immediate-release. Expert Opin Drug Deliv 6(3):319–331
Remington G, Kapur S, Zipursky R (1998) The relationship between risperidone plasma levels and dopamine D2 occupancy: a positron emission tomographic study. J Clin Psychopharmacol 18(1):82–83
Remington G, Mamo D, Labelle A, Reiss J, Shammi C, Mannaert E, Mann S, Kapur S (2006) A PET study evaluating dopamine D2 receptor occupancy for long-acting injectable risperidone. Am J Psychiatry 163:396–401
Richelson E, Souder T (2000) Binding of antipsychotic drugs to human brain receptors. Focus on newer generation compounds. Life Sci 68:29–39
Riedel M, Schwarz MJ, Strassnig M, Spellmann I, Müller-Arends A, Weber K, Zach J, Müller N, Möller HJ (2005) Risperidone plasma levels, clinical response and side-effects. Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci 255:261–268
Schotte A, Janssen PFM, Gommeren W, Luyten WH, Van Gompel P, Lesage AS, De Loore K, Leysen JE (1996) Risperidone compared with new and reference antipsychotic drugs: in vitro and in vivo receptor binding. Psychopharmacology 124:57–73
Seeman P (2005) An update of fast-off dopamine D2 atypical antipsychotics. Am J Psychiatry 162:1984–1985
Simpson RM, Angus JSW (1970) A rating scale for extrapyramidal side effects. Acta Psychiatr Scand 212:11–19
Spina E, Avenoso A, Facciola G, Scordo MG, Ancione M, Madia A (2001) Relationship between plasma risperidone and 9-hydroxyriperidone concentrations and clinical response in patients with schizophrenia. Psychopharmacology 153(2):238–243
Verma SK, Tan CH, Chan YH, Chong SA (2005) Plasma risperidone levels and clinical response in patients with first-episode psychosis. J Clin Psychopharmacol 25(6):609–611
Wang JS, Zhu HJ, Markowitz JS, Donovan JL, De Vane CL (2006) Evaluation of antipsychotic drugs as inhibitors of multidrug resistance transporter P-glycoprotein. Psychopharmacology 187(4):415–423
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Volonteri, L.S., Cerveri, G., De Gaspari, I.F. et al. Long-acting injectable risperidone and metabolic ratio: a possible index of clinical outcome in treatment-resistant schizophrenic patients. Psychopharmacology 210, 489–497 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-010-1852-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-010-1852-5