Abstract
Rationale
There is increasing evidence to suggest the possible efficacy of Crocus sativus (saffron) in the management of Alzheimer’s disease (AD).
Objective
The purpose of the present investigation was to assess the efficacy of C. sativus in the treatment of patients with mild-to-moderate AD.
Methods
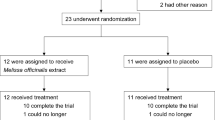
Fifty-four Persian-speaking adults 55 years of age or older who were living in the community were eligible to participate in a 22-week, double-blind study of parallel groups of patients with AD. The main efficacy measures were the change in the Alzheimer’s Disease Assessment Scale—cognitive subscale and Clinical Dementia Rating Scale—Sums of Boxes scores compared with baseline. Adverse events (AEs) were systematically recorded. Participants were randomly assigned to receive a capsule saffron 30 mg/day (15 mg twice per day) or donepezil 10 mg/day (5 mg twice per day).
Results
Saffron at this dose was found to be effective similar to donepezil in the treatment of mild-to-moderate AD after 22 weeks. The frequency of AEs was similar between saffron extract and donepezil groups with the exception of vomiting, which occurred significantly more frequently in the donepezil group.
Conclusion
This phase II study provides preliminary evidence of a possible therapeutic effect of saffron extract in the treatment of patients with mild-to-moderate Alzheimer’s disease. This trial is registered with the Iranian Clinical Trials Registry (IRCT138711051556N1).



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdullaev FI, Espinosa-Aguirre JJ (2004) Biomedical properties of saffron and its potential use in cancer therapy and chemoprevention trials. Cancer Detect Prev 28:426–432
Abe K, Saito H (2000) Effects of saffron extract and its constituent crocin on learning behaviour and long-term potentiation. Phytother Res 14:149–152
Abe K, Sugiura M, Shoyama Y, Saito H (1998) Crocin antagonizes ethanol inhibition of NMDA receptor-mediated responses in rat hippocampal neurons. Brain Res 787:132–138
Akhondzadeh S (1999) Hippocampal synaptic plasticity and cognition. J Clin Pharm Ther 24:241–248
Akhondzadeh S (2007) Herbal medicine in the treatment of psychiatric and neurological Disorders. In: L’Abate L (ed) Low-cost approaches to promote physical and mental health: theory research and practice. Springer, New York, pp 119–138
Akhondzadeh Basti A, Moshiri E, Noorbala AA, Jamshidi AH, Abbasi SH, Akhondzadeh S (2007) Comparison of petal of Crocus sativus L. and fluoxetine in the treatment of depressed outpatients: a pilot double-blind randomized trial. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 31:439–442
Akhondzadeh S, Abbasi SH (2006) Herbal medicine in the treatment of Alzheimer's disease. Am J Alzheimers Dis Other Demen 21:113–118
Akhondzadeh S, Noroozian M, Mohammadi M, Ohadinia S, Jamshidi AH, Khani M (2003a) Salvia officinalis extract in the treatment of patients with mild to moderate Alzheimer's disease: a double blind, randomized and placebo-controlled trial. J Clin Pharm Ther 28:53–59
Akhondzadeh S, Noroozian M, Mohammadi M, Ohadinia S, Jamshidi AH, Khani M (2003b) Melissa officinalis extract in the treatment of patients with mild to moderate Alzheimer's disease: a double blind, randomised, placebo controlled trial. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 74:863–866
Akhondzadeh S, Tahmacebi-Pour N, Noorbala AA, Amini H, Fallah-Pour H, Jamshidi AH, Khani M (2005) Crocus sativus L. in the treatment of mild to moderate depression: a double-blind, randomized and placebo-controlled trial. Phytother Res 19:148–151
Akhondzadeh S, Shafiee Sabet M, Harirchian MH, Togha M, Cheraghmakani H, Razeghi S, Hejazi SS, Yousefi MH, Alimardani R, Jamshidi AH, Zare F, Moradi A (2009) Saffron in the treatment of patients with mild to moderate Alzheimer’s disease: a 16-week, randomized and placebo controlled trial. J Clin Pharm Ther (in press)
Becker RE, Greig NH (2008) Alzheimer's disease drug development in 2008 and beyond: problems and opportunities. Curr Alzheimer Res 5:346–357
Birks J, Grimley A, Evans J (2009) Ginkgo biloba for cognitive impairment and dementia. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 21:CD003120
Citron M (2004) Strategies for disease modification in Alzheimer’s disease. Nat Rev Neurosci 5:677–685
Ernst E (2006) Herbal medicines—they are popular, but are they also safe? Eur J Clin Pharmacol 62:1–2
Folstein MF, Folstein SE, McHugh PR (1975) Mini-mental state. A practical method or grading the cognitive state of patients for the clinician. J Psychiatr Res 12:189–198
Golde TE (2005) The Aβ hypothesis: leading us to rationally-designed therapeutic strategies for the treatment or prevention of Alzheimer disease. Brain Pathol 15:84–87
Hughes CP, Berg L, Danziger WL, Coben LA, Martin RL (1982) A new clinical scale for the staging of dementia. Br J Psychiatry 140:566–572
Izzo AA, Capasso F (2006) Herbal medicines to treat Alzheimer’s disease. Trends Pharmacol Sci 28:47–48
Mantle D, Pickering AT, Perry E (2002) Medical plant extracts for treatment of dementia. A review of their pharmacology, efficacy and tolerability. CNS Drugs 13:201–213
McKhann G, Drachman D, Folstein M, Katzman R, Price D, Stadlan EM (1984) Clinical diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease: report of the NINCDS-ADRDA Work Group under the auspices of Department of Health and Human Services Task Force on Alzheimer’s Disease. Neurology 34:939–944
Papandreou MA, Kanakis CD, Polissiou MG, Efthimiopoulos S, Cordopatis P, Margarity M, Lamari FN (2006) Inhibitory activity on amyloid-beta aggregation and antioxidant properties of Crocus sativus stigmas extract and its crocin constituents. J Agric Food Chem 15:8762–8768
Pitsikas N, Zisopoulou S, Tarantilis PA, Kanakis CD, Polissiou MG, Sakellaridis N (2007) Effects of the active constituents of Crocus sativus L. crocins on recognition and spatial rats' memory. Behav Brain Res 183:141–146
Rafii MS, Aisen PS (2009) Recent developments in Alzheimer's disease therapeutics. BMC Med 19:7
Rosen WG, Mohs RC, Davis KL (1984) A new rating scale for Alzheimer’s disease. Am J Psychiatry 141:1356–1364
Schmidt M, Betti G, Hensel A (2007) Saffron in phytotherapy: pharmacology and clinical uses. Wien Med Wochenschr 157:315–319
Starkstein SE, Mizrahi R, Power BD (2008) Depression in Alzheimer's disease: phenomenology, clinical correlates and treatment. Int Rev Psychiatry 20:382–388
Sugiura M, Shoyama Y, Saito H, Nishiyama N (1995a) Crocin improves the ethanol-induced impairment of learning behaviors of mice in passive avoidance tasks. Proc Japan Acad Ser B 1:319–324
Sugiura M, Shoyama Y, Saito H, Abe K (1995b) Ethanol extract of Crocus sativus L. antagonizes the inhibitory action of ethanol on hippocampal long-term potentiation in vivo. Phytother Res 9:100–104
Tedeschi G, Cirillo M, Tessitore A, Cirillo S (2008) Alzheimer's disease and other dementing conditions. Neurol Sci 29(Suppl):301–307
Tsuno N (2009) Donepezil in the treatment of patients with Alzheimer's disease. Expert Rev Neurother 9:591–598
Wake G, Court J, Pickering A, Lewis R, Wilkins R, Perry E (2000) CNS acetylcholine receptor activity in European medicinal plants traditionally used to improve failing memory. J Ethnopharmacol 69:105–114
Acknowledgments
This study was a thesis of Dr. Mehdi Shafiee Sabet toward Iranian Board of Neurology under supervision of Prof. Shahin Akhondzadeh and Dr. Mohammad Hossein Harirchian at Tehran University of Medical Sciences.
Funding
This study was supported by two grants from Tehran University of Medical Sciences and Green Plants of Life Co., IMPIRAN to Prof. Shahin Akhondzadeh (Grant No: 8480).
Ethics approval
The protocol was approved by the Institutional Review Board (IRB) of Tehran University of Medical Sciences (Grant No. 8480).
The trial group
Shahin Akhondzadeh (principal investigator and statistical support, clinical neuropsychopharmacologist from January 2007 to February 2009)
Mansoureh Togha, Mohammad Hossein Harirchian, and Seyyed Shamssedin Hejazi (clinical coordinator, neurologist from January 2007 to February 2009)
Mehdi Shafiee Sabet, Hamed Cheraghmakani (trial programmer, resident of neurology from January 2007 to February 2009)
Aboulghasem Yousefi, Mohammad Hossein Yousefi, Farhad Zare, Atbin Moradi, Roozbeh Alimardani, and Ardalan Vossoughi (trialist, medical doctor from January 2007 to February 2009)
Amir Hossein Jamshidi, Shams-Ali Rezazadeh, and Soodeh Razeghi (pharmacognosist and nutritionist from January 2007 to February 2009)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Akhondzadeh, S., Shafiee Sabet, M., Harirchian, M.H. et al. A 22-week, multicenter, randomized, double-blind controlled trial of Crocus sativus in the treatment of mild-to-moderate Alzheimer’s disease. Psychopharmacology 207, 637–643 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-009-1706-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-009-1706-1