Abstract
Rationale and objectives
Amphetamine-induced sensitization is thought to involve dopamine D1 receptors. Using mice lacking dopamine D1 receptors (D −/−1 ), we found that they exhibited blunted sensitization to low doses of amphetamine, while others using different treatment and testing regimens reported inconsistent results. We investigated whether experimental variables, alteration in gene expression or cholinergic input played a role in amphetamine-induced responses.
Methods
D −/−1 and wild-type (D +/+1 ) mice pretreated with amphetamine (1 mg/kg, 3–7 days) or various doses of nicotine (chronically but intermittently) were challenged with amphetamine (0.7 and/or 1 mg/kg) after short and long abstinence periods. Expression of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) and phosphorylated c-AMP response element binding protein (p-CREB) genes were measured under basal conditions and after acute or repeated amphetamine treatments.
Results
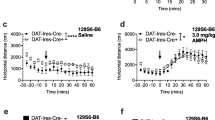
D −/−1 mice failed to exhibit amphetamine-induced sensitization following short-term treatments and long abstinence periods, but expressed sensitization following prolonged amphetamine treatment or a shorter abstinence period. Basal expression of p-CREB (but not BDNF) was higher in D −/−1 than D +/+1 mice and was reduced after amphetamine treatment. Prolonged nicotine pretreatment augmented locomotor responses to amphetamine in both genotypes and restored sensitization in D −/−1 mice.
Conclusions
D1 receptors were necessary for induction, but may not be necessary for expression of amphetamine-induced sensitization at low doses. The manifestation of amphetamine sensitization depended on the duration of treatment and length of the withdrawal period. Cholinergic–nicotinic stimulation restored amphetamine-induced sensitization in D −/−1 mice. Enhanced basal expression of p-CREB in D −/−1 mice may represent an adaptive mechanism related to lack of D1 receptors.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Acquas E, Wilson C, Fibiger HC (1997) Nonstriatal dopamine D1 receptors regulate striatal acetylcholine release in vivo. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 281:360–368
Bickerdike MJ, Abercrombie ED (1997) Striatal acetylcholine release correlates with behavioral sensitization in rats withdrawn from chronic amphetamine. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 282:818–826
Birrell CE, Balfour DJ (1998) The influence of nicotine pretreatment on mesoaccumbens dopamine overflow and locomotor responses to d-amphetamine. Psychopharmacology 140:142–149
Boileau I, Dagher A, Leyton M, Gunn RN, Baker GB, Diksic M, Benkelfat C (2006) Modeling sensitization to stimulants in humans: an [11C] raclopride/positron emission tomography study in healthy men. Arch Gen Psychiatry 63:1386–1395
Choe ES, Wang JQ (2002) CaMKII regulates amphetamine-induced ERK1/2 phosphorylation in striatal neurons. NeuroReport 13:1013–1016
Choe ES, Chung KT, Mao L, Wang JQ (2002) Amphetamine increases phosphorylation of extracellular signal-regulated kinase and transcription factors in the rat striatum via group I metabotropic glutamate receptors. Neuropsychopharmacology 27:565–575
Clarke PB, Kumar R (1983) The effects of nicotine on locomotor activity in non-tolerant and tolerant rats. B J Pharmacol 78:329–337
Cole RL, Konradi C, Douglass J, Hyman SE (1995) Neuronal adaptation to amphetamine and dopamine: molecular mechanisms of prodynorphin gene regulation in rat striatum. Neuron 14:813–823
Crawford CA, Drago J, Watson JB, Levine MS (1997) Effects of repeated amphetamine treatment on the locomotor activity of the dopamine D1A-deficient mouse. NeuroReport 8:2523–2527
DeBoer P, Abercrombie ED (1996) Physiological release of striatal acetylcholine in vivo: modulation by D1 and D2 dopamine receptor subtypes. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 277:775–783
de Rover M, Mansvelder HD, Lodder JC, Wardeh G, Schoffelmeer ANM, Brussaard A (2004) Long-lasting nicotinic modulation of GABAergic synaptic transmission in the rat nucleus accumbens associated with behavioral sensitization to amphetamine. Eur J NeuroSci 19:2859–2870
Di Chiara G, Imperato A (1988) Drugs abused by humans preferentially increase synaptic dopamine concentrations in the mesolimbic system of freely moving rats. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 85:5274–5278
Drago J, Gerfen CR, Lachowicz JE, Steiner H, Hollon TR, Love PE, Ooi GT, Grinberg A, Lee EJ, Huang SP, Bartlettii PF, Jose PA, Sibley DR, Westphal H (1994) Altered striatal function in a mutant mouse lacking D1A dopamine receptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 91:12564–12568
Driscoll P (1976) Nicotine-like behavioral effect after small doses of mecamylamine in Roman high-avoidance rats. Psychopharmacologia 46:119–121
Driscoll P, Bättig K (1973a) Cigarette smoke and behavior: some recent developments. Rev Environ Health 1:113–133
Driscoll P, Bättig K (1973b) The effect of small doses of mecamylamine on shuttlebox behavior in the guinea-pig. Experientia 29:991–993
El-Ghundi M, Fletcher PJ, Drago J, Ashby P, O’Dowd BF, George SR (1997) Dopamine D1 knockout mice are less sensitive to the locomotor effect of alcohol and amphetamine. Society for Neuroscience Abstract 165.15
El-Ghundi M, George SR, Drago J, Fletcher PJ, Fan T, Nguyen LC, Sibley DR, Westphal H, O’Dowd BF (1998) Disruption of dopamine D1 receptor gene expression attenuates alcohol-seeking behavior. Eur J Pharmacol 353:149–158
Fedele E, Varnier G, Ansaldo MA, Raiteri M (1998) Nicotine administration stimulates the in vivo N-methyl-d-aspartate receptor/nitric oxide/cyclic GMP pathway in rat hippocampus through glutamate release. Br J Pharmacol 125:1042–1048
Ferger B, Kropf W, Kuschinsky K (1994) Studies on electroencephalogram (EEG) in rats suggest that moderate doses of cocaine or d-amphetamine activate dopamine D1 rather than D2 receptors. Psychopharmacology 114:297–308
Flores C, Samaha AN, Stewart J (2000) Requirement of endogenous basic fibroblast growth factor for sensitization to amphetamine. J Neurosci 20:R55
Forster GL, Blaha CD (2000) Laterodorsal tegmental stimulation elicits dopamine efflux in the rat nucleus accumbens by activation of acetylcholine and glutamate receptors in the ventral tegmental area. Eur J NeuroSci 12:3596–3604
Giordano TP III, Satpute SS, Striessnig J, Kosofsky BE, Rajadhyaksha AM (2006) Up-regulation of dopamine D(2)L mRNA levels in the ventral tegmental area and dorsal striatum of amphetamine-sensitized C57BL/6 mice: role of Ca(v)1.3L-type Ca(2+) channels. J Neurochem 99:1197–1206
Gray R, Rajan AS, Radcliffe KA, Yakehiro M, Dani JA (1996) Hippocampal synaptic transmission enhanced by low concentrations of nicotine. Nature 383:713–716
Heidbreder CA, Shippenberg TS (1996) Evidence for an involvement of muscarinic cholinergic systems in the induction but not expression of behavioral sensitization to cocaine. Synapse 24:182–192
Hu XT, Koeltzow TE, Cooper DC, Robertson GS, White FJ, Vezina P (2002) Repeated ventral tegmental area amphetamine administration alters dopamine D1 receptor signaling in the nucleus accumbens. Synapse 45:159–170
Kalivas PW, Stewart J (1991) Dopamine transmission in the initiation and expression of drug- and stress-induced sensitization of motor activity. Brain Res Rev 16:223–244
Karler R, Calder LD, Bedingfield JB (1996) A novel nicotinic-cholinergic role in behavioral sensitization to amphetamine-induced stereotypy in mice. Brain Res 725:192–198
Karlsson RM, Hefner KR, Sibley DR, Holmes A (2008) Comparison of dopamine D1 and D5 receptor knockout mice for cocaine locomotor sensitization. Psychopharmacology 200:117–127
Karper PE, De La Rosa H, Newman ER, Krall CM, Nazarian A, McDougall SA, Crawford CA (2002) Role of D1-like receptors in amphetamine-induced behavioral sensitization: a study using D1A receptor knockout mice. Psychopharmacology 159:407–414
Kelly MA, Low MJ, Rubinstein M, Phillips TJ (2008) Role of dopamine D1-like receptors in methamphetamine locomotor responses of D2 receptor knockout mice. Genes Brain Behav 7:568–577
Keys AS, Mark GP (1998) D1 and D2 dopamine receptor mediation of amphetamine-induced acetylcholine release in nucleus accumbens. Neuroscience 86:521–531
Konradi C, Cole RL, Heckers S, Hyman SE (1994) Amphetamine regulates gene expression in rat striatum via transcription factor CREB. J Neurosci 14:5623–5634
Kuribara H (1995) Inhibition of methamphetamine sensitization by post-methamphetamine treatment with SCH 23390 or haloperidol. Psychopharmacology 119:34–38
Kuribara H (1999) Does nicotine modify the psychotoxic effect of methamphetamine? Assessment in terms of locomotor sensitization in mice. J Toxicol Sci 24:55–62
Lee SP, So CH, Rashid AJ, Varghese G, Cheng R, Lanca AJ, O'Dowd BF, George SR (2004) Dopamine D1 and D2 receptor co-activation generates a novel phospholipase C-mediated calcium signal. J Biol Chem 279:35671–3568
Licata SC, Pierce RC (2003) The roles of calcium/calmodulin-dependent and Ras/mitogen-activated protein kinases in the development of psychostimulant-induced behavioral sensitization. J Neurochem 85:14–22
Lu Y, Grady S, Marks MJ, Picciotto M, Changeux JP, Collins AC (1998) Pharmacological characterization of nicotinic receptor-stimulated GABA release from mouse brain synaptosomes. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 287:648–657
Marshall DL, Redfern PH, Wonnacott S (1997) Presynaptic nicotinic modulation of dopamine release in the three descending pathways studied by in vivo microdialysis: comparisons of naïve and chronic nicotine-treated rats. J Neurochem 68:1511–1519
McGhee DS, Heath MJS, Gelber S, Devay P, Role LW (1995) Nicotine enhancement of fast excitatory synaptic transmission in CNS by pre-synaptic receptors. Science 269:1692–1696
McPherson CS, Featherby T, Krstew E, Andrew JL (2007) Quantification of phosphorylated cAMP-response element-binding protein expression throughout the brain of amphetamine-sensitized rats: activation of hypothalamic orexin A-containing neurons. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 323:805–812
Meredith GE, Callen S, Scheuer DA (2002) Brain-derived neurotrophic factor expression is increased in the rat amygdala, piriform cortex and hypothalamus following repeated amphetamine administration. Brain Res 949:218–227
Miner LL, Drago J, Ghamberlain PM, Donovan D, Uhl GR (1995) Retained cocaine conditioned place preference in D1 receptor deficient mice. NeuroReport 6:2314–2316
O’Neill MF, Shaw G (1999) Comparison of dopamine receptor antagonists on hyperlocomotion induced by cocaine, amphetamine, MK-801 and the dopamine D1 agonist C-APB in mice. Psychopharmacology 145:237–250
Oliverio A (1966) Effects of mecamylamine on avoidance conditioning and maze learning of mice. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 154:350–356
Paulson PE, Robinson TE (1995) Amphetamine-induced time-dependent sensitization of dopamine neurotransmission in the dorsal and ventral striatum: a microdialysis study in behaving rats. Synapse 19:56–65
Pierce RC, Born B, Adams M, Kalivas PW (1996) Repeated intra-ventral tegmental area administration of SKF-38393 induces behavioral and neurochemical sensitization to a subsequent cocaine challenge. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 278:384–392
Rashid AJ, So CH, Kong MM, Furtak T, El-Ghundi M, Cheng R, O’Dowd BF, George SR (2007) D1–D2 dopamine receptor heterooligomers with unique pharmacology are coupled to rapid activation of Gq/11 in the striatum. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104:654–659
Reid MS, Fox L, Ho LB, Berger SP (2000) Nicotine stimulation of extracellular glutamate levels in the nucleus accumbens: neuropharmacological characterization. Synapse 35:129–136
Robinson TE, Berridge KC (1993) The neural basis of drug craving: an incentive-sensitization theory of addiction. Brain Res Brain Res Rev 18:247–291
Rodgers RJ (1979) Effects of nicotine, mecamylamine, and hexamethonium on shock-induced fighting, pain reactivity, and locomotor behaviour in rats. Psychopharmacology 66:93–98
Rodrigues TB, Granado N, Ortiz O, Cerdán S, Moratalla R (2007) Metabolic interactions between glutamatergic and dopaminergic neurotransmitter systems are mediated through D(1) dopamine receptors. J Neurosci Res 85:3284–3293
Ross SB, Jackson DM, Edwards SR (1989) The involvement of dopamine D1 and D2 receptors in the locomotor stimulation produced by (+)-amphetamine in naive and dopamine-depleted mice. Pharmacol Toxicol 64:72–77
Schoffelmeer ANM, De Vries TJ, Wardeh G, van de Ven HWM, Vanderschuren LJMJ (2002) Psychostimulant-induced behavioral sensitization depends on nicotinic receptor activation. J Neurosci 22:3269–3276
Shim I, Javaid JI, Wirtshafter D, Jang SY, Shim KH, Lee HJ, Chung YC, Chun BG (2001) Nicotine-induced behavioral sensitization is associated with extracellular dopamine release and expression of c-fos in the striatum and nucleus accumbens of the rat. Behav Brain Res 121:137–147
So CH, Varghese G, Curley KJ, Kong MM, Alijaniaram M, Ji X, Nguyen T, O'dowd BF, George SR (2005) D1 and D2 dopamine receptors form heterooligomers and cointernalize after selective activation of either receptor. Mol Pharmacol 68:568–578
Stolerman IP, Fink R, Jarvik ME (1973) Acute and chronic tolerance to nicotine measured by activity in rats. Psychopharmacologia 30:329–342
Stolerman IP, Garcha HS, Mirza NR (1995) Dissociations between the locomotor stimulant and depressant effects of nicotinic agonists in rats. Psychopharmacology 117:430–437
Tritto T, McCallum SE, Waddle SA, Hutton SR, Paylor R, Collins AC, Marks MJ (2004) Null mutant analysis of responses to nicotine: deletion of beta2 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor subunit but not alpha7 subunit reduces sensitivity to nicotine-induced locomotor depression and hypothermia. Nicotine Tob Res 6:145–158
Turgeon SM, Pollack AE, Fink JS (1997) Enhanced CREB phosphorylation and changes in c-Fos and FRA expression in striatum accompany amphetamine sensitization. Brain Res 749:120–126
Vanderschuren LJMJ, Kalivas PW (2000) Alterations in dopaminergic and glutamatergic transmission in the induction and expression of behavioral sensitization: a critical review of preclinical studies. Psychopharmacology 151:99–120
Vanderschuren LJMJ, Schmidt ED, De Vries TJ, Van Moorsel CAP, Tilders FJH, Schoffelmeer ANM (1999) A single exposure to amphetamine is sufficient to induce long-term behavioral, neuroendocrine and neurochemical sensitization in rats. J Neurosci 19:9579–9586
Vezina P (1996) D1 dopamine receptor activation is necessary for the induction of sensitization by amphetamine in the ventral tegmental area. J Neurosci 16:2411–2420
Vezina P (2004) Sensitization of midbrain dopamine neuron reactivity and the self-administration of psychomotor stimulant drugs. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 27:827–839
Vezina P, Blanc G, Glowinski J, Tassin JP (1992) Nicotine and morphine differentially activate brain dopamine in prefrontocortical and subcortical terminal fields: effects of acute and repeated injections. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 261:484–490
Waddington JL, Daly SA, Downes RP, Deveney AM, McCauley PG, O’Boyle KM (1995) Behavioural pharmacology of ‘D-1-like’ dopamine receptors: further subtyping, new pharmacological probes and interactions with ‘D-2-like’ receptors. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 19:811–131
White FJ, Kalivas PW (1998) Neuroadaptation involved in amphetamine and cocaine addiction. Drug Alcohol Depend 51:141–153
Wolf ME (1998) The role of excitatory amino acids in behavioral sensitization to psychomotor stimulants. Prog Neurobiol 54:679–720
Wolf ME, White FJ, Nassar R, Brooderson RJ, Khansa MR (1993) Differential development of autoreceptor subsensitivity and enhanced dopamine release during amphetamine sensitization. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 264:249–255
Wolf ME, White FJ, Hu XT (1994) MK-801 prevents alterations in the mesoaccumbens dopamine system associated with behavioral sensitization to amphetamine. J Neurosci 14:1735–1745
Wonnacott S (1997) Presynaptic nicotinic ACh receptors. Trends Neurosci 20:92–98
Wu M, Shanabrough M, Leranth C, Alreja M (2000) Cholinergic excitation of septohippocampal GABA but not cholinergic neurons: implications for learning and memory. J Neurosci 20:3900–3908
Xu M, Guo Y, Vorhees CV, Zhang J (2000) Behavioral responses to cocaine and amphetamine administration in mice lacking the dopamine D1 receptor. Brain Res 852:198–207
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to thank Dr. John Drago, Dr. David Sibley, and Dr. Heiner Westphal for generously providing the D1 receptor knockout mice. This work was supported by the Canadian Institutes of Health Research and the National Institute on Drug Abuse. SRG is the recipient of a Canada Research Chair in Molecular Neuroscience from the CIHR.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
El-Ghundi, M.B., Fan, T., Karasinska, J.M. et al. Restoration of amphetamine-induced locomotor sensitization in dopamine D1 receptor-deficient mice. Psychopharmacology 207, 599–618 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-009-1690-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-009-1690-5