Abstract
Introduction
We have previously found that a disruption to prepulse inhibiton (PPI) induced by methamphetamine (METH) is associated with impaired functioning of pallidotegmental neurons, which play a crucial role in PPI of the startle reflex, through the activation of gamma-aminobutyric acid type B receptors in pedunculopontine tegmental neurons in mice.
Objectives
Here, we examined the effect of nicotine on METH-induced impairment of PPI of the startle reflex focusing on dysfunctional pallidotegmental neurons and the neural system.
Results
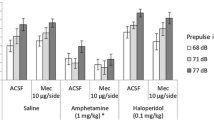
Nicotine (0.15–0.5 mg/kg) ameliorated the deficit in PPI induced by acute METH, and the ameliorating effect of nicotine was antagonized by nicotinic receptor antagonists such as methyllycaconitine and dihydro-β-erythroidine. The acute METH-induced disruption of PPI was accompanied by suppression of c-Fos expression in the lateral globus pallidus (LGP) as well as its induction in the caudal pontine reticular nucleus (PnC) in mice subjected to the PPI test. Nicotine-induced amelioration of PPI deficits in METH-treated mice was accompanied by a reversal of the changes in c-Fos expression in both the LGP and PnC to the basal level.
Conclusions
Nicotine is effective in ameliorating the impairment of PPI caused by METH, which may be associated with normalization of the pallidotegmental neurons.





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- Ach:
-
Acetylcholine
- ADHD:
-
Attention deficit hyperactivity disorders
- DHβE:
-
Dihydro-β-erythroidine
- DRN:
-
Dorsal raphe nucleus
- GABA:
-
gamma-aminobutyric acid
- LGP:
-
Lateral globus pallidus
- METH:
-
Methamphetamine
- nAChRs:
-
Nicotinic acetylcholine receptors
- PFA:
-
Paraformaldehyde
- PnC:
-
Caudal pontine reticular nucleus
- PPI:
-
Prepulse inhibiton
- PPTg:
-
Pedunculopontine tegmental neurons
References
Acri JB, Brown KJ, Saah MI, Grunberg NE (1995) Strain and age differences in acoustic startle responses and effects of nicotine in rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 50:191–198
Adler LE, Hoffer LJ, Griffith J, Waldo MC, Freedman R (1992) Normalization by nicotine of deficient auditory sensory gating in the relatives of schizophrenics. Biol Psychiatry 32:607–616
Adler LE, Hoffer LD, Wiser A, Freedman R (1993) Normalization of auditory physiology by cigarette smoking in schizophrenic patients. Am J Psychiatry 150:1856–1861
Arai S, Takuma K, Mizoguchi H, Ibi D, Nagai T, Takahashi K, Kamei H, Nabeshima T, Yamada K (2008) Involvement of pallidotegmental neurons in methamphetamine- and MK-801-induced impairment of prepulse inhibition of the acoustic startle reflex in mice: reversal by GABA(B) receptor agonist baclofen. Neuropsychopharmacology 33:3164–3175
Bosch D, Schmid S (2006) Activation of muscarinic cholinergic receptors inhibits giant neurons in the caudal pontine reticular nucleus. Eur J NeuroSci 24:1967–1975
Castellanos FX, Fine EJ, Kaysen DL, Kozuch PL, Hamburger SD, Rapoport JL, Hallett M (1996) Sensorimotor gating in boys with Tourette’s syndrome and ADHD. Biol Psychiatry 39:33–41
Cilia J, Cluderay JE, Robbins MJ, Reavill C, Southam E, Kew JN, Jones DN (2002) Reversal of isolation-rearing-induced PPI deficits by an alpha7 nicotinic receptor agonist. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 159:248–257
Dai H, Okuda H, Iwabuchi K, Sakurai E, Chen Z, Kato M, Iinuma K, Yanai K (2004) Social isolation stress significantly enhanced the disruption of prepulse inhibition in mice repeatedly treated with methamphetamine. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1025:257–266
Dani JA, De Biasi M (2002) Cellular mechanisms of nicotine addiction. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 70:439–446
Davis M (1988) Apomorphine, d-amphetamine, strychnine and yohimbine do not alter prepulse inhibition of the acoustic startle reflex. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 95:151–156
Ellenbroek BA, Lubbers LJ, Cools AR (2002) The role of hippocampal dopamine receptors in prepulse inhibition. Eur J NeuroSci 15:1237–1243
Exley R, Clements MA, Hartung H, McIntosh JM, Cragg SJ (2008) Alpha6-containing nicotinic acetylcholine receptors dominate the nicotine control of dopamine neurotransmission in nucleus accumbens. Neuropsychopharmacology 33:2158–2166
Fendt M, Koch M (1999) Cholinergic modulation of the acoustic startle response in the caudal pontine reticular nucleus of the rat. Eur J Pharmacol 370:101–107
Fendt M, Li L, Yeomans JS (2001) Brain stem circuits mediating prepulse inhibition of the startle reflex. Psychopharmacol (Berl) 156:216–224
Franklin KBJ, Paxinos G (1997) The mouse brain in stereotaxic coordinates. Academic, NY
Hoffman HS, Searle JL (1968) Acoustic and temporal factors in the evocation of startle. J Acoust Soc Am 43:269–282
Kayadjanian N, Rétaux S, Menétrey A, Besson MJ (1994) Stimulation by nicotine of the spontaneous release of [3H]gamma-aminobutyric acid in the substantia nigra and in the globus pallidus of the rat. Brain Res 649:129–135
Klink R, de Kerchove d’Exaerde A, Zoli M, Changeux JP (2001) Molecular and physiological diversity of nicotinic acetylcholine receptors in the midbrain dopaminergic nuclei. J Neurosci 21:1452–1463
Kobayashi Y, Isa T (2002) Sensory-motor gating and cognitive control by the brainstem cholinergic system. Neural Netw 15:731–741
Koch M, Schnitzler HU (1997) The acoustic startle response in rats–circuits mediating evocation, inhibition and potentiation. Behav Brain Res 89:35–49
Kungel M, Ebert U, Herbert H, Ostwald J (1994) Substance P and other putative transmitters modulate the activity of reticular pontine neurons: an electrophysiological and immunohistochemical study. Brain Res 643:29–39
Lança AJ, Adamson KL, Coen KM, Chow BL, Corrigall WA (2000) The pedunculopontine tegmental nucleus and the role of cholinergic neurons in nicotine self-administration in the rat: a correlative neuroanatomical and behavioral study. Neuroscience 96:735–742
Mihailescu S, Guzmán-Marín R, Drucker-Colín R (2001) Nicotine stimulation of dorsal raphe neurons: effects on laterodorsal and pedunculopontine neurons. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol 11:359–366
Mihailescu S, Guzmán-Marín R, Domínguez Mdel C, Drucker-Colín R (2002) Mechanisms of nicotine actions on dorsal raphe serotoninergic neurons. Eur J Pharmacol 452:77–82
Schreiber R, Dalmus M, De Vry J (2002) Effects of alpha 4/beta 2- and alpha 7-nicotine acetylcholine receptor agonists on prepulse inhibition of the acoustic startle response in rats and mice. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 159:248–257
Shoemaker JM, Saint Marie RL, Bongiovanni MJ, Neary AC, Tochen LS, Swerdlow NR (2005) Prefrontal D1 and ventral hippocampal N-methyl-d-aspartate regulation of startle gating in rats. Neuroscience 135:385–394
Suemaru K, Yasuda K, Umeda K, Araki H, Shibata K, Choshi T, Hibino S, Gomita Y (2004) Nicotine blocks apomorphine-induced disruption of prepulse inhibition of the acoustic startle in rats: possible involvement of central nicotinic alpha7 receptors. Br J Pharmacol 142:843–850
Swerdlow NR, Braff DL, Taaid N, Geyer MA (1994) Assessing the validity of an animal model of deficient sensorimotor gating in schizophrenic patients. Arch Gen Psychiatry 51:139–154
Swerdlow NR, Platten A, Shoemaker J, Pitcher L, Auerbach P (2001) Effects of pergolide on sensorimotor gating of the startle reflex in rats. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 158:230–240
Takahashi K, Nagai T, Kamei H, Maeda K, Matsuya T, Arai S, Mizoguchi H, Yoneda Y, Nabeshima T, Takuma K, Yamada K (2007) Neural circuits containing pallidotegmental GABAergic neurons are involved in the prepulse inhibition of the startle reflex in mice. Biol Psychiatry 62:148–157
Yeomans JS, Lee J, Yeomans MH, Steidl S, Li L (2006) Midbrain pathways for prepulse inhibition and startle activation in rat. Neuroscience 142:921–929
Acknowledgments
This study was supported in part by a Grant-in-aid for Scientific Research (No.19390062) from the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science and by grants for the 21st century COE program from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science, and Technology of Japan; the Smoking Research Foundation, Japan; JSPS and KOSEF under the Japan-Korea Basic Scientific Cooperation Program; the Academic Frontier Project for Private Universities, matching fund subsidy from MEXT, 2007–2011, Research on the Risk of Chemical Substances, Health and Labour Science Research Grants supported by the Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare, and JST, CREST, and GCOE.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mizoguchi, H., Arai, S., Koike, H. et al. Therapeutic potential of nicotine for methamphetamine-induced impairment of sensorimotor gating: involvement of pallidotegmental neurons. Psychopharmacology 207, 235–243 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-009-1651-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-009-1651-z