Abstract
Background
Previous findings have shown that intra-accumbens injection of naltrexone, a non-selective opioid antagonist, blocks the acquisition of rapid tolerance to ethanol in rats. This study investigates the effects of intra-accumbens injection of the selective mu-, delta-, and kappa-opioid antagonists, respectively, naloxonazine, naltrindole, and nor-binaltorphimine, on rapid tolerance to ethanol.
Methods
Male Wistar rats with guide cannulae directed to the shell or the core portions of the nucleus accumbens received a microinjection of naloxonazine (2–4 μg), naltrindole (2–4 μg), nor-binaltorphimine (2.5–5 μg), or vehicle. After 5 min, each group was divided in two groups that received ethanol (2.7 g/kg i.p.) or saline. Rats were then tested for motor coordination on the tilting plane apparatus. Twenty four hours later, all rats received a challenge dose of ethanol (2.7 g/kg i.p.) and were tested on the tilt plane again.
Results
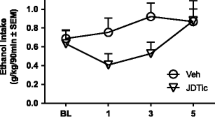
Repeated injections of ethanol caused a reduction in motor impairment suggesting the development of tolerance. However, rats injected with 4 μg naloxonazine into either core or shell portions of the nucleus accumbens did not exhibit tolerance when challenged with ethanol on day 2. Rats treated with 5 μg nor-binaltorphimine into accumbens core plus intraperitoneal saline on day 1 showed reduced motor impairment when challenged with ethanol on day 2, suggesting cross-tolerance to ethanol.
Conclusions
Taken together, our results suggests that mu-opioid receptors in both shell and core portions of the nucleus accumbens, and possibly kappa-opioid in the core, participate in the modulation of rapid tolerance to ethanol.





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- NLZ:
-
Naloxonazine
- NTD:
-
Naltrindole
- BNI:
-
Nor-binaltorphimine
- VEH:
-
Vehicle
- E:
-
Ethanol
- S:
-
Saline
- NMDA:
-
N-methyl-d-aspartic acid
- GABA:
-
γ-Aminobutyric acid
References
Acquas E, Meloni M, Di Chiara G (1993) Blockade of delta-opioid receptors in the nucleus accumbens prevents ethanol-induced stimulation of dopamine release. Eur J Pharmacol 230:239–241
Altman J, Everitt BJ, Glautier S, Markou A, Nutt D, Oretti R, Phillips GD, Robbins TW (1996) The biological, social and clinical bases of drug addiction: commentary and debate. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 125:285–345
Arvola A, Sammalisto L, Wallgren H (1958) A test for level of alcohol intoxication in the rat. Q J Stud Alcohol 19:563–572
Batista LC, Prediger RD, Morato GS, Takahashi RN (2005) Blockade of adenosine and dopamine receptors inhibits the development of rapid tolerance to ethanol in mice. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 181:714–721
Benjamin D, Grant ER, Pohorecky LA (1993) Naltrexone reverses ethanol-induced dopamine release in the nucleus accumbens in awake, freely moving rats. Brain Res 621:137–140
Bertoglio LJ, Carobrez AP (2002) Anxiolytic effects of ethanol and phenobarbital are abolished in test-experienced rats submitted to the elevated plus maze. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 73:963–969
Bitran M, Kalant H (1993) Development of rapid tolerance to pentobarbital and cross-tolerance to ethanol on a motor performance test with intoxicated practice. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 44:981–983
Bodnar RJ, Glass MJ, Ragnauth A, Cooper ML (1995) General, mu and kappa opioid antagonists in the nucleus accumbens alter food intake under deprivation, glucoprivic and palatable conditions. Brain Res 700(1–2):205–212
Brick J, Horowitz GP (1983) Tolerance and cross-tolerance to morphine and ethanol in mice selectively bred for differential sensitivity to ethanol. J Stud Alcohol 44:770–779
Butelman ER, Negus SS, Ai Y, de Costa BR, Woods JH (1993) Kappa opioid antagonist effects of systemically administered nor-binaltorphimine in a thermal antinociception assay in rhesus monkeys. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 267(3):1269–1276
Chandler LJ, Harris RA, Crews FT (1998) Ethanol tolerance and synaptic plasticity. Trends Pharmacol Sci 19:491–495
Chefer VI, Czyzyk T, Bolan EA, Moron J, Pintar JE, Shippenberg TS (2005) Endogenous kappa-opioid receptor systems regulate mesoaccumbal dopamine dynamics and vulnerability to cocaine. J Neurosci 25:5029–5037
Chen CS (1968) A study of the alcohol-tolerance effect and an introduction of a new behavioural technique. Psychopharmacologia 12:433–440
Ciccocioppo R, Martin-Fardon R, Weiss F (2002) Effect of selective blockade of mu(1) or delta opioid receptors on reinstatement of alcohol-seeking behavior by drug-associated stimuli in rats. Neuropsychopharmacology 27:391–399
Colombo G, Agabio R, Lobina C, Reali R, Fadda F, Gessa GL (1995) Cross-tolerance to ethanol and gamma-hydroxybutyric acid. Eur J Pharmacol 273:235–238
Crabbe JC, Rigter H, Uijlen J, Strijbos C (1979) Rapid development of tolerance to the hypothermic effect of ethanol in mice. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 208:128–133
Dalley JW, Everitt BJ (2009) Dopamine receptors in the learning, memory and drug reward circuitry. Semin Cell Dev Biol. in press, corrected. doi:10.1016/jsemcdb.2009.10.002
da Silva GE, Morato GS, Takahashi RN (2001) Rapid tolerance to Delta(9)-tetrahydrocannabinol and cross-tolerance between ethanol and Delta(9)-tetrahydrocannabinol in mice. Eur J Pharmacol 431:201–207
David HN, Ansseau M, Abraini JH (2005) Dopamine-glutamate reciprocal modulation of release and motor responses in the rat caudate-putamen and nucleus accumbens of “intact” animals. Brain Res Brain Res Rev 50:336–360
Dawson GR, Crawford SP, Stanhope KJ, Iversen SD, Tricklebank MD (1994) One-trial tolerance to the effects of chlordiazepoxide on the elevated plus maze may be due to locomotor habituation, not repeated drug exposure. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 113:570–572
Di Chiara G (2002) Nucleus accumbens shell and core dopamine: differential role in behavior and addiction. Behav Brain Res 137:75–114
File SE, Mabbutt PS, Hitchcott PK (1990) Characterisation of the phenomenon of “one-trial tolerance” to the anxiolytic effect of chlordiazepoxide in the elevated plus-maze. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 102:98–101
Froehlich JC (1996) The neurobiology of ethanol–opioid interactions in ethanol reinforcement. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 20:181A–186A
Gonzales RA, Weiss F (1998) Suppression of ethanol-reinforced behavior by naltrexone is associated with attenuation of the ethanol-induced increase in dialysate dopamine levels in the nucleus accumbens. J Neurosci 18:10663–10671
Gonzales RA, Job MO, Doyon WM (2004) The role of mesolimbic dopamine in the development and maintenance of ethanol reinforcement. Pharmacol Ther 103:121–146
Heinz A, Beck A, Grüsser SM, Grace AA, Wrase J (2009) Identifying the neural circuitry of alcohol craving and relapse vulnerability. Addict Biol 14(1):108–118
Holloway FA, King DA, Michaelis RC, Harland RD, Bird DC (1989) Tolerance to ethanol's disruptive effects on operant behavior in rats. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 99:479–485
Holstein SE, Pastor R, Meyer PJ, Phillips TJ (2005) Naloxone does not attenuate the locomotor effects of ethanol in FAST, SLOW, or two heterogeneous stocks of mice. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 182:277–289
Honkanen A, Vilamo L, Wegelius K, Sarviharju M, Hyytia P, Korpi ER (1996) Alcohol drinking is reduced by a mu 1- but not by a delta-opioid receptor antagonist in alcohol-preferring rats. Eur J Pharmacol 304:7–13
Hyytia P, Kiianmaa K (2001) Suppression of ethanol responding by centrally administered CTOP and naltrindole in AA and Wistar rats. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 25:25–33
Ikemoto S (2007) Dopamine reward circuitry: two projection systems from the ventral midbrain to the nucleus accumbens-olfactory tubercle complex. Brain Res Rev 56:27–78
Iordanova MD, McNally GP, Westbrook RF (2006) Opioid receptors in the nucleus accumbens regulate attentional learning in the blocking paradigm. J Neurosci 26(15):4036–4045
Juarez J, Eliana Bde T (2007) Alcohol consumption is enhanced after naltrexone treatment. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 31:260–264
June HL, McCane SR, Zink RW, Portoghese PS, Li TK, Froehlich JC (1999) The delta 2-opioid receptor antagonist naltriben reduces motivated responding for ethanol. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 147:81–89
June HL, Cummings R, Eiler WJ 2nd, Foster KL, McKay PF, Seyoum R, Garcia M, McCane S, Grey C, Hawkins SE, Mason D (2004) Central opioid receptors differentially regulate the nalmefene-induced suppression of ethanol- and saccharin-reinforced behaviors in alcohol-preferring (P) rats. Neuropsychopharmacology 29(2):285–299
Kalant H (1998) Research on tolerance: what can we learn from history? Alcohol Clin Exp Res 22:67–76
Kelley AE, Bless EP, Swanson CJ (1996) Investigation of the effects of opiate antagonists infused into the nucleus accumbens on feeding and sucrose drinking in rats. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 278(3):1499–1507
Khaimova E, Kandov Y, Israel Y, Cataldo G, Hadjimarkou MM, Bodnar RJ (2004) Opioid receptor subtype antagonists differentially alter GABA agonist-induced feeding elicited from either the nucleus accumbens shell or ventral tegmental area regions in rats. Brain Res 1026(2):284–294
Khanna JM, Mayer JM (1982) An analysis of cross-tolerance among ethanol, other general depressants and opioids. Subst Alcohol Actions Misuse 3:243–257
Khanna JM, Le AD, Kalant H, Leblanc AE (1979) Cross-tolerance between ethanol and morphine with respect to their hypothermic effects. Eur J Pharmacol 59:145–149
Khanna JM, Morato GS, Chau A, Shah G (1995) Influence of nitric oxide synthase inhibition on the development of rapid tolerance to ethanol. Brain Res Bull 37:599–604
Khanna JM, Chau A, Shah G (1996) Characterization of the phenomenon of rapid tolerance to ethanol. Alcohol 13:621–628
Khanna JM, Morato GS, Kalant H (2002) Effect of NMDA antagonists, an NMDA agonist, and serotonin depletion on acute tolerance to ethanol. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 72:291–298
Kim SG, Stromberg MF, Kim MJ, Volpicelli JR, Park JM (2000) The effect of antagonists selective for mu- and delta-opioid receptor subtypes on alcohol consumption in C57BL/6 mice. Alcohol 22:85–90
Lamonte N, Echo JA, Ackerman TF, Christian G, Bodnar RJ (2002) Analysis of opioid receptor subtype antagonist effects upon mu opioid agonist-induced feeding elicited from the ventral tegmental area of rats. Brain Res 929(1):96–100
Larson SJ, Siegel S (1998) Learning and tolerance to the ataxic effect of ethanol. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 61:131–142
LeBlanc AE, Kalant H (1975) Ethanol-induced cross tolerance to several homologous alcohols in the rat. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 32:123–128
Lee YK, Park SW, Kim YK, Kim DJ, Jeong J, Myrick H, Kim YH (2005) Effects of naltrexone on the ethanol-induced changes in the rat central dopaminergic system. Alcohol Alcohol 40:297–301
Lemos JI, Takahashi RN, Morato GS (2007) Effects of SR141716 and WIN 55, 212-2 on tolerance to ethanol in rats using the acute and rapid procedures. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 194:139–149
Li XW, Li TK, Froehlich JC (1998) Enhanced sensitivity of the nucleus accumbens proenkephalin system to alcohol in rats selectively bred for alcohol preference. Brain Res 794:35–47
Linseman MA, Le AD (1997) Effects of opioids on the absorption of alcohol. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 58:79–84
Littleton JM, John GR, Jones PA, Grieve SJ (1980) The rapid onset of functional tolerance to ethanol—role of different neurotransmitters and synaptosomal membrane lipids. Acta Psychiatr Scand Suppl 286:137–51
Maldve RE, Zhang TA, Ferrani-Kile K, Schreiber SS, Lippmann MJ, Snyder GL, Fienberg AA, Leslie SW, Gonzales RA, Morrisett RA (2002) DARPP-32 and regulation of the ethanol sensitivity of NMDA receptors in the nucleus accumbens. Nat Neurosci 5:641–648
Mansfield JG, Benedict RS, Woods SC (1983) Response specificity of behaviorally augmented tolerance to ethanol supports a learning interpretation. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 79:94–98
Mansour A, Hoversten MT, Taylor LP, Watson SJ, Akil H (1995) The cloned mu, delta and kappa receptors and their endogenous ligands: evidence for two opioid peptide recognition cores. Brain Res 700:89–98
Martinez RC, Oliveira AR, Macedo CE, Molina VA, Brandão ML (2008) Involvement of dopaminergic mechanisms in the nucleus accumbens core and shell subregions in the expression of fear conditioning. Neurosci Lett 446(2–3):112–116
Mayfield RD, Grant M, Schallert T, Spirduso WW (1992) Tolerance to the effects of ethanol on the speed and success of reaction time responding in the rat: effects of age and intoxicated practice. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 107:78–82
McFarland K, Kalivas PW (2001) The circuitry mediating cocaine-induced reinstatement of drug-seeking behavior. J Neurosci 21(21):8655–8663
Meshul CK, McGinty JF (2000) Kappa opioid receptor immunoreactivity in the nucleus accumbens and caudate-putamen is primarily associated with synaptic vesicles in axons. Neuroscience 96:91–99
Mhatre M, Holloway F (2003) Micro1-opioid antagonist naloxonazine alters ethanol discrimination and consumption. Alcohol 29:109–116
Miceli D, Marfaing-Jallat P, Le Magnen J (1980) Failure of naloxone to affect initial and acquired tolerance to ethanol in rats. Eur J Pharmacol 63:327–333
Middaugh LD, Szumlinski KK, Van Patten Y, Marlowe AL, Kalivas PW (2003) Chronic ethanol consumption by C57BL/6 mice promotes tolerance to its interoceptive cues and increases extracellular dopamine, an effect blocked by naltrexone. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 27:1892–1900
Morgan CJ, Badawy AA, Thomas DR, Dando TG, Kirby A (1989) The [lactate]/[pyruvate] ratio and alcohol metabolism: experiments with naloxone in fasting normal male volunteers. Alcohol Alcohol 24:185–188
Neznanova ON, Blokhina EA, Sukhotina IA, Bespalov AY (2000) Motor impairment produced by ethanol and site-selective NMDA receptor antagonists in mice: tolerance and cross-tolerance. Alcohol 20:31–36
Nielsen CK, Simms JA, Pierson HB, Li R, Saini SK, Ananthan S, Bartlett SE (2008) A novel delta opioid receptor antagonist, SoRI-9409, produces a selective and long-lasting decrease in ethanol consumption in heavy-drinking rats. Biol Psychiatry 64(11):974–981
Olive MF, Koenig HN, Nannini MA, Hodge CW (2001) Stimulation of endorphin neurotransmission in the nucleus accumbens by ethanol, cocaine, and amphetamine. J Neurosci 21:RC184
O'Malley SS, Jaffe AJ, Chang G, Schottenfeld RS, Meyer RE, Rounsaville B (1992) Naltrexone and coping skills therapy for alcohol dependence. A controlled study. Arch Gen Psychiatry 49:881–887
Paxinos G, Watson C (1998) The rat brain in stereotaxic coordinates, 4th edn. Academic, San Diego
Phillips AG, Vacca G, Ahn S (2008) A top-down perspective on dopamine, motivation and memory. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 90(2):236–249
Porrino LJ, Williams-Hemby L, Whitlow C, Bowen C, Samson HH (1998) Metabolic mapping of the effects of oral alcohol self-administration in rats. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 22:176–182
Quintanilla ME, Tampier L (2000) Effect of naltrexone on acute tolerance to ethanol in UChB rats. Alcohol 21:245–249
Ragnauth A, Moroz M, Bodnar RJ (2000) Multiple opioid receptors mediate feeding elicited by mu and delta opioid receptor subtype agonists in the nucleus accumbens shell in rats. Brain Res 876(1–2):76–87
Resch GE, Shridharani S, Millington WR, Garris DR, Simpson CW (2005) Glycyl-glutamine in nucleus accumbens reduces ethanol intake in alcohol preferring (P) rats. Brain Res 1058(1–2):73–81
Sanchis-Segura C, Pastor R, Aragon CM (2004) Opposite effects of acute versus chronic naltrexone administration on ethanol-induced locomotion. Behav Brain Res 153:61–67
Schmidt BL, Tambeli CH, Levine JD, Gear RW (2002) mu/delta Cooperativity and opposing kappa-opioid effects in nucleus accumbens-mediated antinociception in the rat. Eur J Neurosci 15(5):861–868
Schuckit MA (1986) Biological markers in alcoholism. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 10:191–199
Schultz W, Dayan P, Montague PR (1997) A neural substrate of prediction and reward. Science 275:1593–1599
Stratford TR (2005) Activation of feeding-related neural circuitry after unilateral injections of muscimol into the nucleus accumbens shell. Brain Res 1048(1–2):241–250
Stromberg MF, Casale M, Volpicelli L, Volpicelli JR, O'Brien CP (1998) A comparison of the effects of the opioid antagonists naltrexone, naltrindole, and beta-funaltrexamine on ethanol consumption in the rat. Alcohol 15:281–289
Stromberg MF, Mackler SA, Volpicelli JR, O'Brien CP (2001) Effect of acamprosate and naltrexone, alone or in combination, on ethanol consumption. Alcohol 23:109–116
Tampier L, Mardones J (1999) Differences in ethanol sensitivity and acute tolerance between UChA and UChB rats. J Stud Alcohol 60:168–171
Turchan J, Przewlocka B, Toth G, Lason W, Borsodi A, Przewlocki R (1999) The effect of repeated administration of morphine, cocaine and ethanol on mu and delta opioid receptor density in the nucleus accumbens and striatum of the rat. Neuroscience 91:971–977
Varaschin RK, Wazlawik E, Morato GS (2005) Systemic and intra-accumbens microinjections of naltrexone interfere with tolerance to ethanol in rats. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 182:366–374
Vengeliene V, Bilbao A, Molander A, Spanagel R (2008) Neuropharmacology of alcohol addiction. Br J Pharmacol 154:299–315
Vogel-Sprott M, Rawana E, Webster R (1984) Mental rehearsal of a task under ethanol facilitates tolerance. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 21:329–331
Volpicelli JR, Alterman AI, Hayashida M, O'Brien CP (1992) Naltrexone in the treatment of alcohol dependence. Arch Gen Psychiatry 49:876–880
Volpicelli JR, Rhines KC, Rhines JS, Volpicelli LA, Alterman AI, O'Brien CP (1997) Naltrexone and alcohol dependence. Role of subject compliance. Arch Gen Psychiatry 54:737–742
Waller MB, McBride WJ, Lumeng L, Li TK (1983) Initial sensitivity and acute tolerance to ethanol in the P and NP lines of rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 19:683–686
Wamsley JK, Young WS 3rd, Kuhar MJ (1980) Immunohistochemical localization of enkephalin in rat forebrain. Brain Res 190:153–174
Wazlawik E, Morato GS (2002) Effects of intracerebroventricular administration of 7-nitroindazole on tolerance to ethanol. Brain Res Bull 57:165–170
Wazlawik E, Morato GS (2003) Influence of drugs acting on nitric oxide-dependent pathways on ethanol tolerance in rats. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 170:343–350
Wu PH, Mihic SJ, Liu JF, Le AD, Kalant H (1993) Blockade of chronic tolerance to ethanol by the NMDA antagonist, (+)-MK-801. Eur J Pharmacol 231:157–164
Wu PH, Liu JF, Lanca AJ, Kalant H (1994) Selective involvement of central 5-HT2 receptors in the maintenance of tolerance to ethanol by arginine8-vasopressin. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 270:802–808
Wu PH, Liu JF, Wu WL, Lanca AJ, Kalant H (1996) Development of alcohol tolerance in the rat after a single exposure to combined treatment with arginine8-vasopressin and ethanol. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 276:1283–1291
Xi ZX, Fuller SA, Stein EA (1998) Dopamine release in the nucleus accumbens during heroin self-administration is modulated by kappa opioid receptors: an in vivo fast-cyclic voltammetry study. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 284:151–161
Zaleski MJ, Nunes Filho JR, Lemos T, Morato GS (2001) GABA(B) receptors play a role in the development of tolerance to ethanol in mice. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 153:415–424
Zastawny RL, George SR, Nguyen T, Cheng R, Tsatsos J, Briones-Urbina R, O'Dowd BF (1994) Cloning, characterization, and distribution of a mu-opioid receptor in rat brain. J Neurochem 62:2099–2105
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by the Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico (CNPq; Grant 472829/2003-3). We thank Dr. R.N. Takahashi, Dr. G.A. Rae, and Dr. D.D. Savage for their helpful comments. We also thank Drs. J. Marino-Neto and Z.L. Bouzon for their technical assistance in the histological analyses. R.K. Varaschin received a Studentship from CNPq and G.S. Morato is a Research Fellow of CNPq—Brazil (501007-2003-2). All procedures were carried out in accordance with the Brazilian Society of Neurosciences and Behavior, Animal Care Guidelines and approved by our institutional ethics committee (259/CEUA/UFSC).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Varaschin, R.K., Morato, G.S. Selective mu- and kappa-opioid receptor antagonists administered into the nucleus accumbens interfere with rapid tolerance to ethanol in rats. Psychopharmacology 206, 85–96 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-009-1582-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-009-1582-8