Abstract
Rationale
Unlike adult rats, young rats exhibit context-dependent and context-independent behavioral sensitization when assessed after a single pretreatment injection of cocaine.
Objective
The purpose of this study was to determine whether: (1) the context-dependent and context-independent sensitization of young rats can be dissociated based on the persistence of the sensitized response and (2) the expression of behavioral sensitization is associated with region-specific increases in Fos immunoreactivity (Fos-IR).
Materials and methods
On postnatal day (PD) 19, rats were injected with either saline or cocaine (30 mg/kg) in a novel test chamber or the home cage. After 1, 3, 5, 7, 14, or 61 abstinence days, rats were challenged with 20 mg/kg cocaine and locomotor activity was measured for 60 min. In a separate experiment, rats pretreated on PD 19 were challenged with cocaine (10–30 mg/kg) on PD 80.
Results
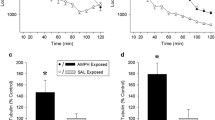
The sensitized responding of young rats persisted for the same length of time (5 days) regardless of whether cocaine pretreatment occurred in a novel environment or the home cage. Behavioral sensitization did not reemerge in adulthood. When assessed after three abstinence days (i.e., on PD 22), acute treatment with cocaine increased Fos-IR in various brain regions, but sensitized responding was associated with elevated Fos expression in only the caudate–putamen (CP) and prefrontal cortex (PFC).
Conclusions
Persistence of the sensitized response cannot be used to dissociate the one-trial context-dependent and context-independent sensitization of young rats. Fos data indicate that the CP and PFC may be involved in the mediation of short-term behavioral sensitization on PD 22.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anagnostaras SG, Schallert T, Robinson TE (2002) Memory processes governing amphetamine-induced psychomotor sensitization. Neuropsychopharmacology 26:703–715
Badiani A, Camp DM, Robinson TE (1997) Enduring enhancement of amphetamine sensitization by drug-associated environmental stimuli. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 282:787–794
Battisti JJ, Chang CH, Uretsky NJ, Wallace LJ (1999) Sensitization of stereotyped behavior to amphetamine is context and response dependent. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 63:263–269
Battisti JJ, Uretsky NJ, Wallace LJ (2000) Importance of environmental context in the development of amphetamine- or apomorphine-induced stereotyped behavior after single and multiple doses. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 66:671–677
Brenhouse HC, Stellar JR (2006) c-Fos and ΔFosB expression are differentially altered in distinct subregions of the nucleus accumbens shell in cocaine-sensitized rats. Neuroscience 137:773–780
Browman KE, Badiani A, Robinson TE (1998a) Modulatory effect of environmental stimuli on the susceptibility to amphetamine sensitization: a dose-effect study in rats. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 287:1007–1014
Browman KE, Badiani A, Robinson TE (1998b) The influence of environment on the induction of sensitization to the psychomotor activating effects of intravenous cocaine in rats is dose-dependent. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 137:90–98
Carey RJ, Gui J (1998) Cocaine conditioning and cocaine sensitization: what is the relationship? Behav Brain Res 92:67–76
Caster JM, Walker QD, Kuhn CM (2007) A single high dose of cocaine induces differential sensitization to specific behaviors across adolescence. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 193:247–260
Conversi D, Bonito-Oliva A, Orsini C, Colelli V, Cabib S (2008) DeltaFosB accumulation in ventro-medial caudate underlies the induction but not the expression of behavioral sensitization by both repeated amphetamine and stress. Eur J Neurosci 27:191–201
Crombag HS, Jedynak JP, Redmond K, Robinson TE, Hope BT (2002) Locomotor sensitization to cocaine is associated with increased Fos expression in the accumbens, but not in the caudate. Behav Brain Res 136:455–462
Day HE, Badiani A, Uslaner JM, Oates MM, Vittoz NM, Robinson TE, Watson SJ Jr, Akil H (2001) Environmental novelty differentially affects c-fos mRNA expression induced by amphetamine or cocaine in subregions of the bed nucleus of the stria terminalis and amygdala. J Neurosci 21:732–740
Drew KL, Glick SD (1989) Environment-dependent sensitization to amphetamine-induced circling behavior. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 31:705–708
Fontana D, Post RM, Weiss SRB, Pert A (1993) The role of D1 and D2 dopamine receptors in the acquisition and expression of cocaine-induced conditioned increases in locomotor activity. Behav Pharmacol 4:375–387
Fujiwara Y, Kazahaya Y, Nakashima M, Sato M, Otsuki S (1987) Behavioral sensitization in the rat: an ontogenic study. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 91:316–319
Graybiel AM, Moratalla R, Robertson HA (1990) Amphetamine and cocaine induce drug-specific activation of the c-fos gene in striosome-matrix compartments and limbic subdivisions of the striatum. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 87:6912–6916
Holson RR, Pearce B (1992) Principles and pitfalls in the analysis of prenatal treatment effects in multiparous species. Neurotoxicol Teratol 14:221–228
Hope BT, Simmons DE, Mitchell TB, Kreuter JD, Mattson BJ (2006) Cocaine-induced locomotor activity and Fos expression in nucleus accumbens are sensitized for 6 months after repeated cocaine administration outside the home cage. Eur J Neurosci 24:867–875
Hu M, Becker JB (2003) Effects of sex and estrogen on behavioral sensitization to cocaine in rats. J Neurosci 23:693–699
Jackson HC, Nutt DJ (1993) A single preexposure produces sensitization to the locomotor effects of cocaine in mice. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 45:733–735
Kalivas PW, Stewart J (1991) Dopamine transmission in the initiation and expression of drug- and stress-induced sensitization of motor activity. Brain Res Rev 16:223–244
Kolta MG, Scalzo FM, Ali SF, Holson RR (1990) Ontogeny of the enhanced behavioral response to amphetamine in amphetamine-pretreated rats. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 100:377–382
Leith NJ, Kuczenski R (1982) Two dissociable components of behavioral sensitization following repeated amphetamine administration. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 76:310–315
Mattson BJ, Crombag HS, Mitchell T, Simmons DE, Kreuter JD, Morales M, Hope BT (2007) Repeated amphetamine administration outside the home cage enhances drug-induced Fos expression in rat nucleus accumbens. Behav Brain Res 185:88–98
Mattson BJ, Koya E, Simmons DE, Mitchell TB, Berkow A, Crombag HS, Hope BT (2008) Context-specific sensitization of cocaine-induced locomotor activity and associated neuronal ensembles in rat nucleus accumbens. Eur J Neurosci 27:202–212
McDougall SA, Collins RL, Karper PE, Watson JB, Crawford CA (1999) Effects of repeated methylphenidate treatment in the young rat: sensitization of both locomotor activity and stereotyped sniffing. Exp Clin Psychopharm 7:208–218
McDougall SA, Reichel CM, Cyr MC, Karper PE, Nazarian A, Crawford CA (2005) Importance of D1 receptors for associative components of amphetamine-induced behavioral sensitization and conditioned activity: a study using D1 receptor knockout mice. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 183:20–30
McDougall SA, Baella SA, Stuebner NM, Halladay LM, Crawford CA (2007) Cocaine-induced behavioral sensitization in preweanling and adult rats: effects of a single drug–environment pairing. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 193:323–332
National Research Council (2003) Guidelines for the care and use of mammals in neuroscience and behavioral research. National Academy Press, Washington, DC
Nordquist RE, Vanderschuren LJ, Jonker AJ, Bergsma M, de Vries TJ, Pennartz CM, Voorn P (2008) Expression of amphetamine sensitization is associated with recruitment of a reactive neuronal population in the nucleus accumbens core. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 198:113–126
Ostrander MM, Badiani A, Day HE, Norton CS, Watson SJ, Akil H, Robinson TE (2003) Environmental context and drug history modulate amphetamine-induced c-fos mRNA expression in the basal ganglia, central extended amygdala, and associated limbic forebrain. Neuroscience 120:551–571
Paxinos G, Watson C (1998) The rat brain: in stereotaxic coordinates, 4th edn. Academic, San Diego
Pierce RC, Kalivas PW (1997) A circuitry model of the expression of behavioral sensitization to amphetamine-like psychostimulants. Brain Res Rev 25:192–216
Rademacher DJ, Napier TC, Meredith GE (2007) Context modulates the expression of conditioned motor sensitization, cellular activation and synaptophysin immunoreactivity. Eur J Neurosci 26:2661–2668
Robertson GS, Jian M (1995) D1 and D2 dopamine receptors differentially increase Fos-like immunoreactivity in accumbal projections to the ventral pallidum and midbrain. Neuroscience 64:1019–1034
Robinson TE, Becker JB (1986) Enduring changes in brain and behavior produced by chronic amphetamine administration: a review and evaluation of animal models of amphetamine psychosis. Brain Res Rev 11:157–198
Sherwood NM, Timiras P (1970) A stereotaxic atlas of the developing rat brain. University of California Press, Berkeley
Sircar R, Kim D (1999) Female gonadal hormones differentially modulate cocaine-induced behavioral sensitization in Fischer, Lewis, and Sprague-Dawley rats. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 289:54–65
Snyder KJ, Katovic NM, Spear LP (1998) Longevity of the expression of behavioral sensitization to cocaine in preweanling rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 60:909–914
Stewart J, Vezina P (1991) Extinction procedures abolish conditioned stimulus control but spare sensitized responding to amphetamine. Behav Pharmacol 2:65–71
Tirelli E, Ferrara M (1997) Neonatal and preweanling rats are able to express short-term behavioral sensitization to cocaine. Eur J Pharmacol 328:103–114
Tirelli E, Terry P (1998) Amphetamine-induced conditioned activity and sensitization: the role of habituation to the test context and the involvement of Pavlovian processes. Behav Pharmacol 9:409–419
Tirelli E, Laviola G, Adriani W (2003a) Ontogenesis of behavioral sensitization and conditioned place preference induced by psychostimulants in laboratory rodents. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 27:163–178
Tirelli E, Tambour S, Michel A (2003b) Sensitised locomotion does not predict conditioned locomotion in cocaine-treated mice: further evidence against the excitatory conditioning model of context-dependent sensitisation. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol 13:289–296
Todtenkopf MS, Mihalakopoulos A, Stellar JR (2002) Withdrawal duration differentially affects c-fos expression in the medial prefrontal cortex and discrete subregions of the nucleus accumbens in cocaine-sensitized rats. Neuroscience 114:1061–1069
Trinh JV, Nehrenberg DL, Jacobsen JP, Caron MG, Wetsel WC (2003) Differential psychostimulant-induced activation of neural circuits in dopamine transporter knockout and wild type mice. Neuroscience 118:297–310
Vanderschuren LJMJ, Kalivas PW (2000) Alterations in dopaminergic and glutamatergic transmission in the induction and expression of behavioral sensitization: a critical review of preclinical studies. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 151:99–120
Vanderschuren LJ, Schoffelmeer AN, Van Leeuwen SD, Hof L, Jonker AJ, Voorn P (2002) Compartment-specific changes in striatal neuronal activity during expression of amphetamine sensitization are the result of drug hypersensitivity. Eur J Neurosci 16:2462–2468
Weiss SRB, Post RM, Pert A, Woodward R, Murman D (1989) Context-dependent cocaine sensitization: differential effect of haloperidol on development versus expression. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 34:655–661
Wolf ME (1998) The role of excitatory amino acids in behavioral sensitization to psychomotor stimulants. Prog Neurobiol 54:679–720
Wood RD, Tirelli E, Snyder KJ, Heyser CJ, LaRocca TM, Spear LP (1998) Evidence for behavioral sensitization to cocaine in preweanling rat pups. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 138:114–123
Zavala AR, Nazarian A, Crawford CA, McDougall SA (2000) Cocaine-induced behavioral sensitization in the young rat. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 151:291–298
Zorrilla EP (1997) Multiparous species present problems (and possibilities) to developmentalists. Dev Psychobiol 30:141–150
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
McDougall, S.A., Charntikov, S., Cortez, A.M. et al. Persistence of one-trial cocaine-induced behavioral sensitization in young rats: regional differences in Fos immunoreactivity. Psychopharmacology 203, 617–628 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-008-1407-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-008-1407-1