Abstract
Rationale
Previous studies have suggested the involvement of neuronal nitric oxide synthase (nNOS) in the development of sensitization to psychostimulants. Ontogeny-dependent differences in the response to psychostimulants have been reported.
Objective
The objectives were to investigate (a) the short- and long-term consequences of adolescent and adult cocaine exposure on behavioral sensitization and (b) the role of the nNOS gene in behavioral sensitization in adolescent and adult mice.
Materials and methods
Adolescent and adult wild type (WT) and nNOS knockout (KO) mice received saline or cocaine (20 mg/kg) for 5 days and then were challenged with cocaine (20 mg/kg) after a drug-free period of 10 or 30 days. Locomotor activity was recorded by infrared beam interruptions. nNOS immunoreactive (ir) neurons in the dorsal and ventral striatum were quantified 24 h after repeated administration of cocaine to adolescent and adult WT mice.
Results
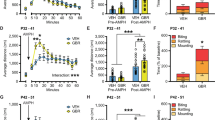
Repeated administration of cocaine to either WT or nNOS KO mice during adolescence resulted in locomotor sensitization, which persisted into adulthood. WT but not KO adult mice developed long-term sensitization to cocaine. Repeated cocaine administration resulted in a 96% increase in the expression of nNOS-ir neurons in the dorsal striatum of adult but not adolescent WT mice.
Conclusions
The nNOS gene is essential for the induction of behavioral sensitization to cocaine in adulthood but not in adolescence. The increased expression of nNOS-ir neurons in the dorsal striatum may underlie the induction of behavioral sensitization in adulthood. Thus, the NO-signaling pathway has an ontogeny-dependent role in the neuroplasticity underlying cocaine behavioral sensitization.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arancio O, Antonova I, Gambaryan S, Lohmann SM, Wood JS, Lawrence DS, Hawkins RD (2001) Presynaptic role of cGMP-dependent protein kinase during long-lasting potentiation. J Neurosci 21(1):143–149
Balda MA, Anderson KL, Itzhak Y (2006) Adolescent and adult responsiveness in the incentive value of cocaine reward in mice: role of neuronal nitric oxide synthase (nNOS) gene. Neuropharmacology 51(2):341–349
Bolanos CA, Glatt SJ, Jackson D (1998) Subsensitivity to dopaminergic drugs in periadolescent rats: a behavioral and neurochemical analysis. Dev Brain Res 111(1):25–33
Borgkvist A, Fisone G (2007) Psychoactive drugs and regulation of the cAMP/PKA/DARPP-32 cascade in striatal medium spiny neurons. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 31(1):79–88
Carlsson M, Carlsson A (1990) Interactions between glutamatergic and monoaminergic systems within the basal ganglia—implications for schizophrenia and Parkinson’s disease. Trends Neurosci 13(7):272–276
Carretero J, Weruaga E, Hernández E, Burks D, Riesco JM, Rubio M, Briñón JG, Aijón J, Vázquez R, Alonso JR (2003) Dopaminergic modulation of nNOS expression in the pituitary gland of male rat. Anat Embryol (Berl) 207(4–5):381–388
Caster JM, Walker QD, Kuhn CM (2005) Enhanced behavioral response to repeated-dose cocaine in adolescent rats. Psychopharmacology 183(2):218–225
Caster JM, Walker QD, Kuhn CM (2007) A single high dose of cocaine induces differential sensitization to specific behaviors across adolescence. Psychopharmacology 193(2):247–260
Collins SL, Izenwasser S (2002) Cocaine differentially alters behavior and neurochemistry in periadolescent versus adult rats. Dev Brain Res 138(1):27–34
Garthwaite J (1991) Glutamate, nitric oxide and cell–cell signaling in the nervous system. Trends Neurosci 14(2):60–67
Hotsenpiller G, Wolf ME (2002) Conditioned locomotion is not correlated with behavioral sensitization to cocaine: an intra-laboratory multi-sample analysis. Neuropsychopharmacology 27(6):924–929
Huang PL, Dawson TM, Bredt DS, Snyder SH, Fishman MC (1993) Targeted disruption of the neuronal nitric oxide synthase gene. Cell 75(7):1273–1286
Itzhak Y (1997) Modulation of cocaine- and methamphetamine-induced behavioral sensitization by inhibition of brain nitric oxide synthase. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 282(2):521–527
Itzhak Y, Anderson KL (2007) Memory reconsolidation of cocaine-associated context requires nitric oxide signaling. Synapse 61(12):1002–1005
Itzhak Y, Ali SF, Martin JL, Black MD, Huang PL (1998) Resistance of neuronal nitric oxide synthase-deficient mice to cocaine-induced locomotor sensitization. Psychopharmacology 140(3):378–386
Kalivas PW, Stewart J (1991) Dopamine transmission in the initiation and expression of drug- and stress-induced sensitization of motor activity. Brain Res Rev 16(3):223–244
Kalivas PW, Duffy P (1993) Time course of extracellular dopamine and behavioral sensitization to cocaine. I. Dopamine axon terminals. J Neurosci 13(1):266–275
Karler R, Calder LD, Chaudhry IA, Turkanis SA (1989) Blockade of “reverse tolerance” to cocaine and amphetamine by MK-801. Life Sci 45(7):599–606
Kiss JP (2000) Role of nitric oxide in the regulation of monoaminergic neurotransmission. Brain Res Bull 52(6):459–466
Laviola G, Wood RD, Kuhn C, Francis R, Spear LP (1995) Cocaine sensitization in periadolescent and adult rats. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 275(1):345–357
Laviola G, Adriani W, Terranova ML, Gerra G (1999) Psychobiological risk factors for vulnerability to psychostimulants in human adolescents and animal models. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 23(7):993–1010
Lu YF, Kandel ER, Hawkins RD (1999) Nitric oxide signaling contributes to late-phase LTP and CREB phosphorylation in the hippocampus. J Neurosci 19(23):10250–10261
Moll GH, Mehnert C, Wicker M, Bock N, Rothenberger A, Ruther E, Huether G (2000) Age-associated changes in the densities of presynaptic monoamine transporters in different regions of the rat brain from early juvenile life to late adulthood. Dev Brain Res 119(2):251–257
Murrin LC, Zeng WY (1990) Ontogeny of dopamine D1 receptors in rat forebrain: a quantitative autoradiographic study. Dev Brain Res 57(1):7–13
Paule MG (1997) Age-related sensitivity to the acute behavioral effects of cocaine and amphetamine in monkeys. Neurotoxicol Teratol 19(3):240–241
Pulvirenti L, Berrier R, Kreifeldt M, Koob GF (1994) Modulation of locomotor activity by NMDA receptors in the nucleus accumbens core and shell regions of the rat. Brain Res 664(1–2):231–236
Puzzo D, Palmeri A, Arancio O (2006) Involvement of the nitric oxide pathway in synaptic dysfunction following amyloid elevation in Alzheimer’s disease. Rev Neurosci 17(5):497–523
Ritz MC, Lamb RJ, Goldberg SR, Kuhar MJ (1987) Cocaine receptors on dopamine transporters are related to self-administration of cocaine. Science 237(4819):1219–1223
Sasaki M, Gonzalez-Zulueta M, Huang H, Herring WJ, Ahn S, Ginty DD, Dawson VL, Dawson TM (2000) Dynamic regulation of neuronal NO synthase transcription by calcium influx through a CREB family transcription factor-dependent mechanism. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97(15):8617–8622
Snyder SH (1994) Nitric oxide. More jobs for that molecule. Nature 372(6506):504–505
Spear LP, Brake SC (1983) Periadolescence: age-dependent behavior and psychopharmacological responsitivity in rats. Dev Psychobiol 16(2):83–109
Sterio DC (1984) The unbiased estimation of number and sizes of arbitrary particles using the disector. J Microsc 134(Pt 2):127–136
Stewart J, Badiani A (1993) Tolerance and sensitization to the behavioral effects of drugs. Behav Pharmacol 4(4):289–312
Tarazi FI, Tomasini EC, Baldessarini RJ (1999) Postnatal development of dopamine D1-like receptors in rat cortical and striatolimbic brain regions: an autoradiographic study. Dev Neurosci 21(1):43–49
Teicher MH, Andersen SL, Hostetter JC Jr (1995) Evidence for dopamine receptor pruning between adolescence and adulthood in striatum but not nucleus accumbens. Dev Brain Res 89(2):167–172
Tirelli E, Laviola G, Adriani W (2003a) Ontogenesis of behavioral sensitization and conditioned place preference induced by psychostimulants in laboratory rodents. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 27(1–2):163–178
Tirelli E, Tambour S, Michel A (2003b) Sensitised locomotion does not predict conditioned locomotion in cocaine-treated mice: further evidence against the excitatory conditioning model of context-dependent sensitisation. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol 13(4):289–296
Tirelli E, Michel A, Brabant C (2005) Cocaine-conditioned activity persists for a longer time than cocaine-sensitized activity in mice: implications for the theories using Pavlovian excitatory conditioning to explain the context-specificity of sensitization. Behav Brain Res 165(1):18–25
Vanderschuren LJMJ, Kalivas PW (2000) Alterations in dopaminergic and glutamatergic transmission in the induction and expression of behavioral sensitization: a critical review of preclinical studies. Psychopharmacology 151(2–3):99–120
Wang JQ, Lau YS (2001) Dose-related alteration in nitric oxide synthase mRNA expression induced by amphetamine and the full D1 dopamine receptor agonist SKF-82958 in mouse striatum. Neurosci Lett 311(1):5–8
Weibel ER (1981) Stereological methods in cell biology: where are we—where are we going? J Histochem Cytochem 29(9):1043–1052
West MJ, Gundersen HJ (1990) Unbiased stereological estimation of the number of neurons in the human hippocampus. J Comp Neurol 296(1):1–22
Wolf ME, Jeziorski M (1993) Coadministration of MK-801 with amphetamine, cocaine or morphine prevents rather than transiently masks the development of behavioral sensitization. Brain Res 613(2):291–294
Wolf ME, White FJ, Hu XT (1994) MK-801 prevents alterations in the mesoaccumbens dopamine system associated with behavioral sensitization to amphetamine. J Neurosci 14(3 Pt 2):1735–1745
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by awards RO1 DA019107 (YI) and F30 DA022847-01 (MB) from the National Institute on Drug Abuse. The authors are thankful to Dr. Chuanhui Dong, Dept. of Psychiatry & Behavioral Sciences, University of Miami School of Medicine, for his assistance in the statistical analysis.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Balda, M.A., Anderson, K.L. & Itzhak, Y. Differential role of the nNOS gene in the development of behavioral sensitization to cocaine in adolescent and adult B6;129S mice. Psychopharmacology 200, 509–519 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-008-1228-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-008-1228-2