Abstract
Rationale
Cannabinoid CB1 receptors in the brain are targets of both endocannabinoid signalling and the psychoactive compounds of the hemp plant. They mediate neuronal effects of their ligands in various corticolimbic and striatal circuits by presynaptic regulation of transmitter release.
Objectives/Methods
This study investigates acute systemic effects of the full CB1 receptor agonist WIN 55,212-2 (WIN) on prepulse inhibition (PPI) of the acoustic startle response (ASR), locomotor activity and spatial memory retrieval in an eight-arm radial-maze task. Furthermore, we tested the effect of local intra-cerebral micro-infusions of WIN into the nucleus accumbens (NAc), ventral tegmental area (VTA), dorsal (dHIP) and ventral (vHIP) hippocampus and medial prefrontal cortex (mPFC).
Results
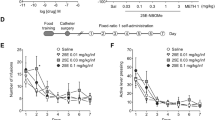
Systemic WIN (1.2 mg/kg) reduced PPI without affecting ASR, had no effect on locomotion in the open field, but impaired retrieval of spatial memory. Infusions of 5 μg/0.3 μl WIN into either NAc (core or shell), dHIP or VTA did not affect PPI and locomotion immediately afterwards. However, PPI was significantly reduced after intra-mPFC and intra-vHIP infusion of WIN. Furthermore, WIN infusion into dHIP increased the number of reference memory errors in the maze, suggesting impairment of memory retrieval.
Conclusions
Our data support the notion that CB1 receptor stimulation impairs sensorimotor gating most likely by modulation of neurotransmitter release in mPFC and vHIP. The lack of effects of local WIN infusions in NAc and VTA might be due to low receptor abundance in these regions. Additionally, CB1 receptor activation in dHIP impairs spatial memory retrieval. Taken together, cortico-hippocampal cannabinoid receptors play an essential role in the regulation of cognitive and behavioural processes.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ameri A (1999) The effects of cannabinoids on the brain. Prog Neurobiol 58:315–348
Auclair N, Otani S, Soubrie P, Crepel F (2000) Cannabinoids modulate synaptic strength and plasticity at glutamatergic synapses of rat prefrontal cortex pyramidal neurons. J Neurophysiol 83:3287–3293
Bakshi VP, Geyer MA (1998) Multiple limbic regions mediate the disruption of prepulse inhibition produced in rats by the noncompetitive NMDA antagonist dizocilpine. J Neurosci 18:8394–8401
Bast T, Feldon J (2003) Hippocampal modulation of sensorimotor processes. Prog Neurobiol 70:319–345
Bast T, Zhang WN, Feldon J (2001) Hyperactivity, decreased startle reactivity, and disrupted prepulse inhibition following disinhibition of the rat ventral hippocampus by the GABA(A) receptor antagonist picrotoxin. Psychopharmacology 156:225–233
Becker JT, Walker JA, Olton DS (1980) Neuroanatomical bases of spatial memory. Brain Res 200:307–320
Bortolato M, Aru GN, Frau R, Orru M, Luckey GC, Boi G, Gessa GL (2005) The CB receptor agonist WIN 55,212–2 fails to elicit disruption of prepulse inhibition of the startle in Sprague–Dawley rats. Psychopharmacology 177:264–271
Breivogel CS, Childers SR (1998) The functional neuroanatomy of brain cannabinoid receptors. Neurobiol Dis 5:417–431
Caine SB, Geyer MA, Swerdlow NR (1992) Hippocampal modulation of acoustic startle and prepulse inhibition in the rat. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 43:1201–1208
Carta G, Nava F, Gessa GL (1998) Inhibition of hippocampal acetylcholine release after acute and repeated delta9-tetrahydrocannabinol in rats. Brain Res 809:1–4
Chaperon F, Thiebot MH (1999) Behavioral effects of cannabinoid agents in animals. Crit Rev Neurobiol 13:243–281
Cheer JF, Kendall DA, Mason R, Marsden CA (2003) Differential cannabinoid-induced electrophysiological effects in rat ventral tegmentum. Neuropharmacology 44:633–641
Chen J, Marmur R, Pulles A, Paredes W, Gardner EL (1993) Ventral tegmental microinjection of delta 9-tetrahydrocannabinol enhances ventral tegmental somatodendritic dopamine levels but not forebrain dopamine levels: evidence for local neural action by marijuana’s psychoactive ingredient. Brain Res 621:65–70
Childers SR (2006) Activation of G-proteins in brain by endogeneous and exogeneous cannabinoids. AAPS J 8:112–117
Collins DR, Pertwee RG, Davies SN (1995) Prevention by the cannabinoid antagonist SR141716A, of cannabinoid-mediated blockade of long-term potentiation in the rat hippocampal slice. Br J Pharmacol 115:869–870
Davies SN, Pertwee RG, Riedel G (2002) Functions of cannabinoid receptors in the hippocampus. Neuropharmacology 42:993–1007
Devane WA, Hanus L, Breuer A, Pertwee RG, Stevenson LA, Griffin G, Gibson D, Mandelbaum A, Etinger A, Mechoulam R (1992) Isolation and structure of a brain constituent that binds to the cannabinoid receptor. Science 258:1946–1949
Domenici MR, Azad SC, Marsicano G, Schierloh A, Wotjak CT, Dodt HU, Zieglgansberger W, Lutz B, Rammes G (2006) Cannabinoid receptor type 1 located on presynaptic terminals of principal neurons in the forebrain controls glutamatergic synaptic transmission. J Neurosci 26:5794–5799
Drews E, Schneider M, Koch M (2005) Effects of the cannabinoid receptor agonist WIN 55,212–2 on operant behavior and locomotor activity in rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 80:145–150
Egashira N, Mishima K, Iwasaki K, Fujiwara M (2002) Intracerebral microinjection of D9-tetrahydrocannabinol: search for the impairment of spatial memory in the eight- arm radial maze in rats. Brain Res 952:239–245
Elphick MR, Egertova M (2001) The neurobiology and evolution of cannabinoid signalling. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci 356:381–408
Fernandez-Ruiz JJ, Berrendero F, Hernandez ML, Romero J, Ramos JA (1999) Role of endocannabinoids in brain development. Life Sci 65:725–736
Ferrari F, Ottani A, Vivoli R, Giuliani D (1999) Learning impairment produced in rats by the’ cannabinoid agonist HU 210 in a water-maze task. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 64:555–561
Fortin DA, Levine ES (2007) Differential effects of endocannabinoids on glutamatergic and GABAergic inputs to layer 5 pyramidal neurons. Cereb Cortex 17:163–174
French ED, Dillon K, Wu X (1997) Cannabinoids excite dopamine neurons in the ventral tegmentum and substantia nigra. Neuroreport 8:649–652
Gessa GL, Melis M, Muntoni AL, Diana M (1998) Cannabinoids activate mesolimbic dopamine neurons by an action on cannabinoid CB1 receptors. Eur J Pharmacol 341:39–44
Geyer MA, Krebs-Thomson K, Braff DL, Swerdlow NR (2001) Pharmacological studies of prepulse inhibition models of sensorimotor gating deficits in schizophrenia: a decade in review. Psychopharmacology 156:117–154
Gold PE (2003) Acetylcholine modulation of neural systems involved in learning and memory. Neurobiol Learn Mem 80:194–210
Hajos N, Katona I, Naiem SS, Mackie K, Ledent C, Mody I, Freund TF (2000) Cannabinoids inhibit hippocampal GABAergic transmission and network oscillations. Eur J Neuosci 12:3239–3249
Hampson RE, Deadwyler SA (1999) Cannabinoids, hippocampal function and memory. Life Sci 65:715–723
Herkenham M, Lynn AB, Little MD, Johnson MR, Melvin LS, De Costa BR, Rice KC (1990) Cannabinoid receptor localization in brain. Proc Nat Acad Sci USA 87:1932–1936
Herkenham M, Lynn AB, Johnson MR, Melvin LS, De Costa BR, Rice KC (1991) Characterization and localization of cannabinoid receptors in rat brain: a quantitative in vitro autoradiographic study. J Neurosci 11:563–583
Hill EL, Gallopin T, Ferezou I, Cauli B, Rossier J, Schweitzer P, Lambolez B (2007) Functional CB1 receptors are broadly expressed in neocortical GABAergic and glutamatergic neurons. J Neurophysiol 97:2580–2589
Howlett AC, Breivogel CS, Childers SR, Deadwyler SA, Hampson RE, Porrino LJ (2004) Cannabinoid physiology and pharmacology: 30 years of progress. Neuropharmacology 47:354–358
Iversen L (2003) Cannabis and the brain. Brain 126:1252–1270
Japha K, Koch M (1999) Picrotoxin in the medial prefrontal cortex impairs sensorimotor gating in rats: reversal by haloperidol. Psychopharmacology 14:347–354
Järbe TUC, Ross T, DiPatrizio NV, Pandarinathan L, Makriyannis A (2006) Effects of CB1R agonist WIN-55,212–2 and the CB1R antagonist SR-141716 and AM-1387: open-field examinations in rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 85:243–252
Katona I, Sperlagh B, Sik A, Kafalvi A, Vizi ES, Mackie K, Freund TF (1999) Presynaptically located CB1 cannabinoid receptors regulate GABA release from axon terminals of specific hippocampal interneurons. J Neurosci 19:4544–4558
Katona I, Sperlagh B, Magloczky Z, Santh E, Kofalvi A, Czirjak S, Mackie K, Vizi ES, Freund TF (2000) GABAergic interneurons are the targets of cannabinoid actions in the human hippocampus. Neuroscience 100:797–804
Katona I, Urban GM, Wallace M, Ledent C, Jung KM, Piomelli D, Mackie K, Freund TF (2006) Molecular composition of the endocannabinoid system at glutamatergic synapses. J Neurosci 26:5628–5637
Koch M (1999) The neurobiology of startle. Prog Neurobiol 59:107–128
Lichtman AH, Martin BR (1996) Delta 9-tetrahydrocannabinol impairs spatial memory through a cannabinoid receptor mechanism. Psychopharmacology 126:125–131
Lichtman AH, Dimen KR, Martin BR (1995) Systemic or intrahippocampal cannabinoid administration impairs spatial memory in rats. Psychopharmacology 119:282–290
Lupica CR, Riegel AC, Hoffman AF (2004) Marijuana and cannabinoid regulation of brain reward circuits. Br J Pharmacol 143:227–234
Mansbach RS, Geyer MA (1989) Effects of phencyclidine and phencyclidine biologs on sensorimotor gating in the rat. Neuropsychopharmacology 2:299–308
Marsicano G, Lutz B (1999) Expression of the cannabinoid receptor CB1 in distinct neuronal subpopulations in the adult mouse forebrain. Eur J Neurosci 11:4213–4225
Martin WJ, Coffin PO, Attias E, Balinsky M, Tsou K, Walker JM (1999) Anatomical basis for cannabinoid-induced antinociception as revealed by intracerebral microinjections. Brain Res 822:237–242
Matsuda LA, Lolait SJ, Brownstein MJ, Young AC, Bonner TI (1990) Structure of a cannabinoid receptor and functional expression of the cloned cDNA. Nature 346:561–564
Mishima K, Egashira N, Hirosawa N, Fujii M, Matsumoto Y, Iwasaki K, Fujiwara M (2001) Characteristics of learning and memory impairment induced by delta9-tetrahydrocannabinol in rats. Jpn J Pharmacol 87:297–308
Misner DL, Sullivan JM (1999) Mechanism of cannabinoid effects on long-term potentiation and depression in hippocampal CA1 neurons. J Neurosci 19:6795–6805
Monhemius R, Azami J, Green DL, Robert MH (2001) CB1 receptor mediated analgesia from the nucleus reticularis gigantocellularis pars alpha is activated in an animal model of neurophatic pain. Brain Res 908:67–74
Munro S, Thomas KL, Abu-Shaar M (1993) Molecular characterization of a peripheral receptor for cannabinoids. Nature 365:61–65
Patel S, Hillard CJ (2003) Cannabinoid-induced Fos expression within A10 dopaminergic neurons. Brain Res 963:15–25
Paxinos G, Watson C (1998) The rat brain in stereotaxic coordinates, 4th edn. Academic, New York
Piomelli D (2003) The molecular logic of endocannabinoid signalling. Nat Rev Neurosci 4:873–884
Pistis M, Porcu G, Melis M, Diana M, Gessa GL (2001) Effects of cannabinoids on prefrontal neuronal responses to ventral tegmental area stimulation. Eur J Neurosci 14:96–102
Prather PL, Martin NA, Breivogel CS, Childers SR (2000) Activation of cannabinoid receptors in rat brain by WIN 55212–2 produces coupling to multiple G protein a-subunits with different potencies. Mol Pharmacol 57:1000–1010
Riedel G, Davies SN (2005) Cannabinoid functionin learning, memory and plasticity. Handb Exp Pharmacol 168:445–477
Rodriguez de Fonseca F, Del Arco I, Martin-Calderon JL, Gorriti MA, Navarro M (1998) Role of the endogenous cannabinoid system in the regulation of motor activity. Neurobiol Dis 5:483–501
Sanudo-Pena MC, Tsou K, Delay ER, Hohman AG, Force M, Walker JM (1997) Endogenous cannabinoids as an aversive or counter-rewarding system in the rat. Neurosci Lett 223:125–128
Sanudo-Pena MC, Romero J, Seale GE, Fernandez-Ruiz JJ, Walker JM (2000) Activational role of cannabinoids on movement. Eur J Pharmacol 391:269–274
Schneider M, Koch M (2002) The cannabinoid agonist WIN 55,212-2 reduces sensorimotor gating and recognition memory in rats. Behav Pharmacol 13:29–37
Sesack SR, Pickel VM (1990) In the rat medial nucleus accumbens, hippocampal and catecholaminergic terminals converge on spiny neurons and are in apposition to each other. Brain Res 527:266–279
Sesack SR, Carr DB (2002) Selective prefrontal cortex inputs to dopamine cells: implications for schizophrenia. Physiol Behav 77:513–517
Shen M, Piser TM, Seybold VS, Thayer SA (1996) Cannabinoid receptor agonists inhibit glutamatergicsynaptic transmission in rat hippocampal cultures. J Neurosci 16:4322–4334
Swerdlow NR, Geyer MA, Braff DL (2001) Neural circuit regulation of prepulse inhibition of startle in the rat: Current knowledge and future challenges. Psychopharmacology 156:194–215
Szabo B, Siemes S, Wallmichrath I (2002) Inhibition of GABAergic neurotransmission in the ventral tegmental area by cannabinoids. Eur J Neurosci 15:2057–2061
Tanda G, Pontieri FE, Di Chiara G (1997) Cannabinoid and heroin activation of mesolimbic dopamine transmission by a common mu1 opiod receptor mechanism. Science 276:2048–2050
Tsou K, Brown S, Sanudo-Pena MC, Mackie K, Walker JM (1998) Immunhistochemical distribution of cannabinoid CB1 receptors in the rat central nervous system. Neuroscience 83:393–411
UNODC (United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime) (2007) World drug report. UNODC, Geneva
Valjent E, Maldonado R (2000) A behavioural model to reveal place preference to delta 9-tetrahydrocannabinol in mice. Psychopharmacology 147:436–438
Wan FJ, Swerdlow NR (1996) Sensorimotor gating in rats is regulated by different dopamine–glutamate interactions in the nucleus accumbens core and shell subregions. Brain Res 722:168–176
Wan FJ, Caine SB, Swerdlow NR (1996) The ventral subiculum modulation of prepulse inhibition is not mediated via dopamine D2 or nucleus accumbens non-NMDA glutamate receptor activity. Eur J Pharmacol 314:9–18
Wenger T, Moldrich G, Furst S (2003) Neuromorphological background of cannabis addiction. Brain Res Bull 61:125–128
Zhang WN, Bast T, Feldon J (2002) Prepulse inhibition in rats with temporary inhibition/inactivation of ventral or dorsal hippocampus. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 73:929–940
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wegener, N., Kuhnert, S., Thüns, A. et al. Effects of acute systemic and intra-cerebral stimulation of cannabinoid receptors on sensorimotor gating, locomotion and spatial memory in rats. Psychopharmacology 198, 375–385 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-008-1148-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-008-1148-1