Abstract
Rationale
Marijuana use in adolescents is a highly social activity, and interacting endocannabinoid and opioid systems may modulate social reward. However, cannabinoid exposure has been reported to reduce social behavior.
Objectives
The aim of this study was to elucidate the mechanisms underlying the paradoxical relationship between cannabinoid exposure and sociability.
Materials and methods
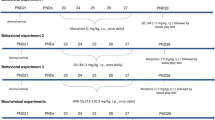
We investigated the effect of cannabinoid agonists with a different mechanism of action on social play behavior in adolescent rats. In addition, we examined whether endocannabinoid neurotransmission interacts with opioid and dopaminergic neurotransmission in the modulation of social play behavior.
Results
The direct CB1 cannabinoid receptor agonist WIN55,212-2 reduced social play. However, the indirect cannabinoid agonist URB597, which inhibits the hydrolysis of the endocannabinoid anandamide, enhanced social play. This effect of URB597 depended upon stimulation of opioid and dopamine receptors. The well-known stimulatory effect of morphine on social play was attenuated by the CB1 cannabinoid receptor antagonist SR141716A, but independent of dopamine receptor stimulation. Combined treatment with ineffective doses of URB597 and morphine increased social play.
Conclusions
Cannabinoid neurotransmission can both enhance and inhibit social interaction in adolescent rats depending on how the endocannabinoid system is stimulated. Activation of cannabinoid receptors throughout the brain, which occurs during cannabis use, inhibits sociability. In contrast, on-demand release of endocannabinoids facilitates social interaction, which is magnified by indirect cannabinoid agonists through an interaction with opioid and dopaminergic neurotransmission. These results shed light on the paradoxical relationship between cannabis exposure and sociability and suggest that endocannabinoid degradation inhibitors hold promise for the treatment of social dysfunctions.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adolphs R (2003) Cognitive neuroscience of human social behaviour. Nat Rev Neurosci 4:165–178
American Psychiatric Association (1994) Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders, 4th edn. American Psychiatric Press, Washington, DC
Andreasson S, Allebeck P, Engstrom A, Rydberg U (1987) Cannabis and schizophrenia. A longitudinal study of Swedish conscripts. Lancet 26:1483–1486
Balfour ME, Yu L, Coolen LM (2004) Sexual behavior and sex-associated environmental cues activate the mesolimbic system in male rats. Neuropsychopharmacology 29:718–730
Beatty WW, Costello KB (1982) Naloxone and play fighting in juvenile rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 17:905–907
Beatty WW, Costello KB, Berry SL (1984) Suppression of play fighting by amphetamine: effects of catecholamine antagonists, agonists and synthesis inhibitors. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 20:747–755
Berridge KC (2003) Pleasures of the brain. Brain Cogn 52:106–128
Berridge KC (2007) The debate over dopamine’s role in reward: the case for incentive salience. Psychopharmacology 191:391–431
Calcagnetti DJ, Schechter MD (1992) Place conditioning reveals the rewarding aspect of social interaction in juvenile rats. Physiol Behav 51:667–672
Caza PA, Spear LP (1980) Ontogenesis of morphine-induced behavior in the rat. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 13:45–50
Crowder WF, Hutto CW Jr (1992) Operant place conditioning measures examined using two nondrug reinforcers. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 41:817–824
Darmani NA (2001) The cannabinoid CB1 receptor antagonist SR 141716A reverses the antiemetic and motor depressant actions of WIN 55, 212-2. Eur J Pharmacol 430:49–58
Depue RA, Morrone-Strupinsky JV (2005) A neurobehavioral model of affiliative bonding: implications for conceptualizing a human trait of affiliation. Behav Brain Sci 28:313–395
De Vries TJ, Hogenboom F, Mulder AH, Schoffelmeer ANM (1990) Ontogeny of μ-, δ- and κ-opioid receptors mediating inhibition of neurotransmitter release and adenylate cyclase activity in rat brain. Dev Brain Res 54:63–69
Douglas LA, Varlinskaya EI, Spear LP (2004) Rewarding properties of social interactions in adolescent and adult male and female rats: impact of social versus isolate housing of subjects and partners. Dev Psychobiol 45:153–162
Drews E, Schneider M, Koch M (2005) Effects of the cannabinoid receptor agonist WIN 55,212-2 on operant behavior and locomotor activity in rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 80:145–150
D’Souza (2007) Cannabinoids and psychosis. Int Rev Neurobiol 78:289–326
Egerton A, Allison C, Brett RR, Pratt JA (2006) Cannabinoids and prefrontal cortical function: insights from preclinical studies. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 30:680–695
Fattore L, Deiana S, Spano SM, Cossu G, Fadda P, Scherma M, Fratta W (2005) Endocannabinoid system and opioid addiction: behavioural aspects. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 81:343–359
Freund TF, Katona I, Piomelli D (2003) Role of endogenous cannabinoids in synaptic signaling. Physiol Rev 83:1017–1066
Genn RF, Tucci S, Marco EM, Viveros MP, File SE (2004) Unconditioned and conditioned anxiogenic effects of the cannabinoid receptor agonist CP 55,940 in the social interaction test. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 77:567–573
Gobbi G, Bambico FR, Mangieri R, Bortolato M, Campolongo P, Solinas M, Cassano T, Morgese MG, Debonnel G, Duranti A, Tontini A, Tarzia G, Mor M, Trezza V, Goldberg SR, Cuomo V, Piomelli D (2005) Antidepressant-like activity and modulation of brain monoaminergic transmission by blockade of anandamide hydrolysis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102:18620–18625
Goldstein A, Naidu A (1989) Multiple opioid receptors: ligand selectivity profiles and binding site signatures. Mol Pharmacol 36:265–272
Goode E (1970) The marijuana smokers. Basic Books, New York
Hol T, Van den Berg C, Van Ree JM, Spruijt BM (1999) Isolation during the play period in infancy decreases adult social interactions in rats. Behav Brain Res 100:91–97
Humphreys AP, Einon DF (1981) Play as a reinforcer for maze learning in juvenile rats. Anim Behav 29:259–270
Johnson SW, North RA (1992) Opioids excite dopamine neurons by hyperpolarization of local interneurons. J Neurosci 12:483–488
Kathuria S, Gaetani S, Fegley D, Valino F, Duranti A, Tontini A, Mor M, Tarzia G, La Rana G, Calignano A, Giustino A, Tattoli M, Palmery M, Cuomo V, Piomelli D (2003) Modulation of anxiety through blockade of anandamide hydrolysis. Nat Med 9:76–81
Kelley AE, Baldo BA, Pratt WE, Will MJ (2005) Corticostriatal–hypothalamic circuitry and food motivation: integration of energy, action and reward. Physiol Behav 86:773–795
Klitenick MA, DeWitte P, Kalivas PW (1992) Regulation of somatodendritic dopamine release in the ventral tegmental area by opioids and GABA: an in vivo microdialysis study. J Neurosci 12:2623–2632
Kornblum HI, Hurlbut DE, Leslie FM (1987) Postnatal development of multiple opioid receptors in rat brain. Dev Brain Res 37:21–41
Lupica CR, Riegel AC (2005) Endocannabinoid release from midbrain dopamine neurons: a potential substrate for cannabinoid receptor antagonist treatment of addiction. Neuropharmacology 48:1105–1116
Maldonado R, Valverde O, Berrendero F (2006) Involvement of the endocannabinoid system in drug addiction. Trends Neurosci 29:225–232
Manzanares J, Corchero J, Romero J, Fernandez-Ruiz JJ, Ramos JA, Fuentes JA (1999) Pharmacological and biochemical interactions between opioids and cannabinoids. Trends Pharmacol Sci 20:287–294
McLaughlin CR, Abood ME (1993) Developmental expression of cannabinoid receptor mRNA. Dev Brain Res 76:75–78
McMahon LR (2006) Characterization of cannabinoid agonists and apparent pA2 analysis of cannabinoid antagonists in rhesus monkeys discriminating Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 319:1211–1218
Niesink RJM, Van Ree JM (1989) Involvement of opioid and dopaminergic systems in isolation-induced pinning and social grooming of young rats. Neuropharmacology 28:411–418
Normansell L, Panksepp J (1990) Effects of morphine and naloxone on play-rewarded spatial discrimination in juvenile rats. Dev Psychobiol 23:75–83
O’Shea M, McGregor IS, Mallet PE (2006) Repeated cannabinoid exposure during perinatal, adolescent or early adult ages produces similar longlasting deficits in object recognition and reduced social interaction in rats. J Psychopharmacol 20:611–621
Panksepp J, Siviy S, Normansell L (1984) The psychobiology of play: theoretical and methodological perspectives. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 8:465–492
Panksepp J, Jalowiec J, DeEskinazi FG, Bishop P (1985) Opiates and play dominance in juvenile rats. Behav Neurosci 99:441–453
Pellis SM (1988) Agonistic versus amicable targets of attack and defense: consequences for the origin, function and descriptive classification of play-fighting. Aggress Behav 14:85–104
Pellis SM, Pellis V (1987) Play-fighting differs from serious fighting in both target of attack and tactics of fighting in the laboratory rat Rattus norvegicus. Aggress Behav 13:227–242
Pertwee RG (1999) Pharmacology of cannabinoid receptor ligands. Curr Med Chem 6:635–664
Pierce RC, Kumaresan V (2006) The mesolimbic dopamine system: the final common pathway for the reinforcing effect of drugs of abuse? Neurosci Biobehav Rev 30:215–238
Rodríguez de Fonseca F, Ramos JA, Bonnin A, Fernández-Ruiz JJ (1993) Presence of cannabinoid binding sites in the brain from early postnatal ages. NeuroReport 4:135–138
Rushworth MF, Behrens TE, Rudebeck PH, Walton ME (2007) Contrasting roles for cingulate and orbitofrontal cortex in decisions and social behaviour. Trends Cogn Sci 11:168–176
Salamone JD, Correa M, Mingote SM, Weber SM (2005) Beyond the reward hypothesis: alternative functions of nucleus accumbens dopamine. Curr Opin Pharmacol 5:34–41
Schneider M, Koch M (2002) The cannabinoid agonist WIN 55,212-2 reduces sensorimotor gating and recognition memory in rats. Behav Pharmacol 13:29–37
Schneider M, Koch M (2005) Deficient social and play behavior in juvenile and adult rats after neonatal cortical lesion: effects of chronic pubertal cannabinoid treatment. Neuropsychopharmacology 30:944–957
Schultz W (2002) Getting formal with dopamine and reward. Neuron 36:241–263
Siviy SM, Panksepp J (1987) Sensory modulation of juvenile play in rats. Dev Psychobiol 20:39–55
Siviy SM, Fleischhauer AE, Kerrigan LA, Kuhlman SJ (1996) D2 dopamine receptor involvement in the rough-and-tumble play behavior of juvenile rats. Behav Neurosci 110:1168–1176
Solinas M, Goldberg SR (2005) Motivational effects of cannabinoids and opioids on food reinforcement depend on simultaneous activation of cannabinoid and opioid systems. Neuropsychopharmacology 30:2035–2045
Sundram S (2006) Cannabis and neurodevelopment: implications for psychiatric disorders. Hum Psychopharmacol 21:245–254
Tanda G, Goldberg SR (2003) Cannabinoids: reward, dependence, and underlying neurochemical mechanisms—a review of recent preclinical data. Psychopharmacology 169:115–134
Tanda G, Pontieri FE, Di Chiara G (1997) Cannabinoid and heroin activation of mesolimbic dopamine transmission by a common μ1 opioid receptor mechanism. Science 276:2048–2050
Van den Berg CL, Hol T, Van Ree JM, Spruijt BM, Everts H, Koolhaas JM (1999a) Play is indispensable for an adequate development of coping with social challenges in the rat. Dev Psychobiol 34:129–138
Van den Berg CL, Pijlman FTA, Koning HAM, Diergaarde L, Van Ree JM, Spruijt BM (1999b) Isolation changes the incentive value of sucrose and social behaviour in juvenile and adult rats. Behav Brain Res 106:133–142
Vanderschuren LJMJ, Niesink RJM, Spruijt BM, Van Ree JM (1995a) Effects of morphine on different aspects of social play in juvenile rats. Psychopharmacology 117:225–231
Vanderschuren LJMJ, Niesink RJM, Spruijt BM, Van Ree JM (1995b) Mu- and kappa-opioid receptor-mediated opioid effects on social play in juvenile rats. Eur J Pharmacol 276:257–266
Vanderschuren LJMJ, Spruijt BM, Hol T, Niesink RJM, Van Ree JM (1995c) Sequential analysis of social play behavior in juvenile rats: effects of morphine. Behav Brain Res 72:89–95
Vanderschuren LJMJ, Stein EA, Wiegant VM, Van Ree JM (1995d) Social play alters regional brain opioid receptor binding in juvenile rats. Brain Res 680:148–156
Vanderschuren LJMJ, Niesink RJM, Van Ree JM (1997) The neurobiology of social play behavior in rats. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 21:309–326
Van Furth WR, Wolterink G, Van Ree JM (1995) Regulation of masculine sexual behavior: involvement of brain opioids and dopamine. Brain Res Rev 21:162–184
Van Ree JM, Niesink RJM, Nir I (1984) Δ1-Tetrahydrocannabinol but not cannabidiol reduces contact and aggressive behavior of rats tested in dyadic encounters. Psychopharmacology 84:561–565
Van Ree JM, Gerrits MAFM, Vanderschuren LJMJ (1999) Opioids, reward and addiction: an encounter of biology, psychology, and medicine. Pharmacol Rev 51:341–396
Verkooijen KT, Nielsen GA, de Vries NK (2007) Youth crowds and substance use: the impact of perceived group norm and multiple group identification. Psychol Addict Behav 21:55–61
Wiley JL, Barrett RL, Lowe J, Balster RL, Martin BR (1995) Discriminative stimulus effects of CP 55,940 and structurally dissimilar cannabinoids in rats. Neuropharmacology 34:669–676
Wise RA (2004) Dopamine, learning and motivation. Nat Rev Neurosci 5:483–494
Young LJ, Wang Z (2004) The neurobiology of pair bonding. Nat Neurosci 7:1048–1054
Zangen A, Solinas M, Ikemoto S, Goldberg SR, Wise RA (2006) Two brain sites for cannabinoid reward. J Neurosci 26:4901–4907
Acknowledgments
We thank Drs. J.M. Van Ree, H.M.B. Lesscher and P. Campolongo for thoughtful comments on this manuscript and M.H. Broekhoven and R. Damsteegt for practical assistance. V. Trezza was a visiting scientist from the Department of Human Physiology and Pharmacology, University of Rome ‘Sapienza’, Rome, Italy, supported by a fellowship from the Italian Ministry of Scientific Research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Trezza, V., Vanderschuren, L.J.M.J. Bidirectional cannabinoid modulation of social behavior in adolescent rats. Psychopharmacology 197, 217–227 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-007-1025-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-007-1025-3