Abstract
Rationale
Adult rats typically exhibit more robust behavioral sensitization than do preweanling rats. A possible explanation for this age-dependent difference is that environmental context may have relatively less impact on the psychostimulant-induced behaviors of preweanling rats.
Objective
The purpose of this study was to assess the importance of environmental context for the development of cocaine-induced sensitization in preweanling and adult rats.
Materials and methods
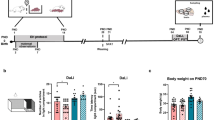
On postnatal day (PD) 19 or PD 79, rats in the context-dependent condition were injected with 30 mg/kg cocaine immediately before being placed in a novel test chamber for 30 min. The same rats were then injected with saline 30 min after being returned to the home cage. Rats in the context-independent condition were injected with saline before being placed in the novel chamber and cocaine in the home age. Control rats were injected with saline at both time points. One day later, adult and preweanling rats were challenged with saline or 10 mg/kg cocaine (experiment 1), or preweanling rats were challenged with 5, 20, or 30 mg/kg cocaine (experiment 2). After being injected, rats were placed in the test chamber, and behavior was measured for 60 min.
Results
Adult rats showed context-dependent locomotor sensitization and conditioned activity, with females exhibiting more locomotor activity than males. Preweanling rats did not exhibit conditioned activity, but they showed robust context-dependent and context-independent sensitization when challenged with 10–30 mg/kg cocaine.
Conclusions
Context did not influence the expression of behavioral sensitization in preweanling rats, suggesting that deficits in associative or memory processes may be responsible for age-dependent differences in behavioral sensitization and conditioned activity.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anagnostaras SG, Robinson TE (1996) Sensitization to the psychomotor stimulant effects of amphetamine: modulation by associative learning. Behav Neurosci 110:1397–1414
Anagnostaras SG, Schallert T, Robinson TE (2002) Memory processes governing amphetamine-induced psychomotor sensitization. Neuropsychopharmacology 26:703–715
Andersen SL (2003) Trajectories of brain development: point of vulnerability or window of opportunity? Neurosci Biobehav Rev 27:3–18
Anderson MJ, Barnes GW, Briggs JF, Ashton KM, Moody EW, Joynes RL, Riccio DC (2004) Effects of ontogeny on performance of rats in a novel object-recognition task. Psychol Rep 94:437–443
Badiani A, Robinson TE (2004) Drug-induced neurobehavioral plasticity: the role of environmental context. Behav Pharmacol 15:327–339
Badiani A, Camp DM, Robinson TE (1997) Enduring enhancement of amphetamine sensitization by drug-associated environmental stimuli. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 282:787–794
Battisti JJ, Chang CH, Uretsky NJ, Wallace LJ (1999) Sensitization of stereotyped behavior to amphetamine is context and response dependent. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 63:263–269
Battisti JJ, Uretsky NJ, Wallace LJ (2000) Importance of environmental context in the development of amphetamine- or apomorphine-induced stereotyped behavior after single and multiple doses. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 66:671–677
Browman KE, Badiani A, Robinson TE (1998a) Modulatory effect of environmental stimuli on the susceptibility to amphetamine sensitization: a dose-effect study in rats. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 287:1007–1014
Browman KE, Badiani A, Robinson TE (1998b) The influence of environment on the induction of sensitization to the psychomotor activating effects of intravenous cocaine in rats is dose-dependent. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 137:90–98
Cailhol S, Mormède P (1999) Strain and sex differences in the locomotor response and behavioral sensitization to cocaine in hyperactive rats. Brain Res 842:200–205
Campbell BA, Jaynes J, Misanin JR (1968) Retention of a light–dark discrimination in rats of different ages. J Comp Physiol Psych 66:467–472
Campbell BA, Misanin JR, White BC, Lytle LD (1974) Species differences in ontogeny of memory: indirect support for neural maturation as a determinant of forgetting. J Comp Physiol Psych 87:193–202
Carey RJ, Gui J (1998) Cocaine conditioning and cocaine sensitization: what is the relationship? Behav Brain Res 92:67–76
Chin J, Sternin O, Wu HB, Burrell S, Lu D, Jenab S, Perrotti LI, Quinones-Jenab V (2002) Endogenous gonadal hormones modulate behavioral and neurochemical responses to acute and chronic cocaine administration. Brain Res 945:123–130
Cunningham MG, Bhattacharyya S, Benes FM (2002) Amygdalo-cortical sprouting continues into early adulthood: implications for the development of normal and abnormal function during adolescence. J Comp Neurol 453:116–130
Drew KL, Glick SD (1989) Environment-dependent sensitization to amphetamine-induced circling behavior. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 31:705–708
Ferguson SM, Robinson TE (2004) Amphetamine-evoked gene expression in striatopallidal neurons: regulation by corticostriatal afferents and the ERK/MAPK signaling cascade. J Neurochem 91:337–348
Ferguson SM, Norton CS, Watson SJ, Akil H, Robinson TE (2003) Amphetamine-evoked c-fos mRNA expression in the caudate-putamen: the effects of DA and NMDA receptor antagonists vary as a function of neuronal phenotype and environmental context. J Neurochem 86:33–44
Fontana D, Post RM, Weiss SRB, Pert A (1993) The role of D1 and D2 dopamine receptors in the acquisition and expression of cocaine-induced conditioned increases in locomotor activity. Behav Pharmacol 4:375–387
Fujiwara Y, Kazahaya Y, Nakashima M, Sato M, Otsuki S (1987) Behavioral sensitization in the rat: an ontogenic study. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 91:316–319
Guanowsky V, Misanin JR, Riccio DC (1983) Retention of conditioned taste aversion in weanling, adult, and old-age rats. Behav Neural Biol 37:173–178
Harrod SB, Booze RM, Welch M, Browning CE, Mactutus CF (2005) Acute and repeated intravenous cocaine-induced locomotor activity is altered as a function of sex and gonadectomy. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 82:170–181
Holson RR, Pearce B (1992) Principles and pitfalls in the analysis of prenatal treatment effects in multiparous species. Neurotoxicol Teratol 14:221–228
Hu M, Becker JB (2003) Effects of sex and estrogen on behavioral sensitization to cocaine in rats. J Neurosci 23:693–699
Jackson HC, Nutt DJ (1993) A single preexposure produces sensitization to the locomotor effects of cocaine in mice. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 45:733–735
Kalivas PW, Stewart J (1991) Dopamine transmission in the initiation and expression of drug- and stress-induced sensitization of motor activity. Brain Res Rev 16:223–244
Kolta MG, Scalzo FM, Ali SF, Holson RR (1990) Ontogeny of the enhanced behavioral response to amphetamine in amphetamine-pretreated rats. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 100:377–382
Leith NJ, Kuczenski R (1982) Two dissociable components of behavioral sensitization following repeated amphetamine administration. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 76:310–315
Li Y, Acerbo MJ, Robinson TE (2004) The induction of behavioural sensitization is associated with cocaine-induced structural plasticity in the core (but not shell) of the nucleus accumbens. Eur J Neurosci 20:1647–1654
McDougall SA, Duke MA, Bolanos CA, Crawford CA (1994) Ontogeny of behavioral sensitization in the rat: effects of direct and indirect dopamine agonists. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 116:483−490
McDougall SA, Collins RL, Karper PE, Watson JB, Crawford CA (1999) Effects of repeated methylphenidate treatment in the young rat: sensitization of both locomotor activity and stereotyped sniffing. Exp Clin Psychopharmacol 7:208–218
Michel A, Tambour S, Tirelli E (2003) The magnitude and the extinction duration of the cocaine-induced conditioned locomotion-activated response are related to the number of cocaine injections paired with the testing context in C57BL/6J mice. Behav Brain Res 145:113–123
National Research Council (2003) Guidelines for the Care and Use of Mammals in Neuroscience and Behavioral Research. National Academy Press, Washington, DC
Ostrander MM, Badiani A, Day HE, Norton CS, Watson SJ, Akil H, Robinson TE (2003) Environmental context and drug history modulate amphetamine-induced c-fos mRNA expression in the basal ganglia, central extended amygdala, and associated limbic forebrain. Neuroscience 120:551–571
Partridge B, Schenk S (1999) Context-independent sensitization to the locomotor-activating effects of cocaine. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 63:543–548
Paulson PE, Camp DM, Robinson TE (1991) Time course of transient behavioral depression and persistent behavioral sensitization in relation to regional brain monoamine concentrations during amphetamine withdrawal in rats. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 103:480–492
Pierce RC, Kalivas PW (1997) A circuitry model of the expression of behavioral sensitization to amphetamine-like psychostimulants. Brain Res Rev 25:192–216
Robinson TE, Becker JB (1986) Enduring changes in brain and behavior produced by chronic amphetamine administration: a review and evaluation of animal models of amphetamine psychosis. Brain Res Rev 11:157–198
Robinson TE, Becker JB, Presty SK (1982) Long-term facilitation of amphetamine-induced rotational behavior and striatal dopamine release produced by a single exposure to amphetamine: sex differences. Brain Res 571:330–337
Sell SL, Scalzitti JM, Thomas ML, Cunningham KA (2000) Influence of ovarian hormones and estrous cycle on the behavioral response to cocaine in female rats. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 293:879–886
Sershen H, Hashim A, Lajtha A (1998) Gender difference in kappa-opioid modulation of cocaine-induced behavior and NMDA-evoked dopamine release. Brain Res 801:67–71
Sircar R, Kim D (1999) Female gonadal hormones differentially modulate cocaine-induced behavioral sensitization in Fischer, Lewis, and Sprague–Dawley rats. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 289:54–65
Snyder KJ, Katovic NM, Spear LP (1998) Longevity of the expression of behavioral sensitization to cocaine in preweanling rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 60:909–914
Spear LP (2000) The adolescent brain and age-related behavioral manifestations. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 24:417–463
Stewart J, Vezina P (1988) Conditioning and sensitization. In: Kalivas PW, Barnes CD (eds) Sensitization in the nervous system. Telford Press, Caldwell, NJ, pp 207–224
Stewart J, Vezina P (1991) Extinction procedures abolish conditioned stimulus control but spare sensitized responding to amphetamine. Behav Pharmacol 2:65–71
Tirelli E, Ferrara M (1997) Neonatal and preweanling rats are able to express short-term behavioral sensitization to cocaine. Eur J Pharmacol 328:103–114
Tirelli E, Terry P (1998) Amphetamine-induced conditioned activity and sensitization: the role of habituation to the test context and the involvement of Pavlovian processes. Behav Pharmacol 9:409–419
Tirelli E, Laviola G, Adriani W (2003a) Ontogenesis of behavioral sensitization and conditioned place preference induced by psychostimulants in laboratory rodents. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 27:163–178
Tirelli E, Tambour S, Michel A (2003b) Sensitised locomotion does not predict conditioned locomotion in cocaine-treated mice: further evidence against the excitatory conditioning model of context-dependent sensitisation. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol 13:289–296
Uslaner J, Badiani A, Norton CS, Day HE, Watson SJ, Akil H, Robinson TE (2001) Amphetamine and cocaine induce different patterns of c-fos mRNA expression in the striatum and subthalamic nucleus depending on environmental context. Eur J Neurosci 13:1977–1983
van Haaren F, Meyer ME (1991) Sex differences in locomotor activity after acute and chronic cocaine administration. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 39:923–927
Vezina P, Stewart J (1990) Amphetamine administered to the ventral tegmental area but not to the nucleus accumbens sensitizes rats to systemic morphine: lack of conditioned effects. Brain Res 516:99–106
Weiss SRB, Post RM, Pert A, Woodward R, Murman D (1989) Context-dependent cocaine sensitization: differential effect of haloperidol on development versus expression. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 34:655–661
White FJ, Joshi A, Koeltzow TE, Hu X-T (1998) Dopamine receptor antagonists fail to prevent induction of cocaine sensitization. Neuropsychopharmacology 18:26–40
Wolf ME (1998) The role of excitatory amino acids in behavioral sensitization to psychomotor stimulants. Prog Neurobiol 54:679–720
Wood RD, Tirelli E, Snyder KJ, Heyser CJ, LaRocca TM, Spear LP (1998) Evidence for behavioral sensitization to cocaine in preweanling rat pups. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 138:114–123
Zavala AR, Nazarian A, Crawford CA, McDougall SA (2000) Cocaine-induced behavioral sensitization in the young rat. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 151:291–298
Zorrilla EP (1997) Multiparous species present problems (and possibilities) to developmentalists. Dev Psychobiol 30:141–150
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
McDougall, S.A., Baella, S.A., Stuebner, N.M. et al. Cocaine-induced behavioral sensitization in preweanling and adult rats: effects of a single drug–environment pairing. Psychopharmacology 193, 323–332 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-007-0788-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-007-0788-x