Abstract
Rationale
Previous studies have demonstrated an interaction between opioids and noncompetitive antagonists at N-methyl-d-aspartate (NMDA) receptors, but few studies have examined the utility of these medications for treating opioid dependence.
Objective
In this 8-week inpatient study, participants were maintained on the low-affinity, noncompetitive NMDA receptor antagonist memantine (0, 30, and 60 mg per day, PO) and under each maintenance dose condition, the effects of intranasal heroin (0, 12.5, and 50 mg, IN) were examined.
Methods
During the first week after admission to the hospital, participants were detoxified from heroin. All of the volunteers received all of the memantine and heroin dose combinations. Participants (N = 8) first sampled a dose of heroin and $20. During a subsequent choice session, participants could self-administer heroin and/or money. Responses, which consisted of finger presses on a computer mouse, were made under a modified progressive ratio schedule (PR 50, 100, 200, 400, 800, 1,200, 1,600, 2,000, 2,400, and 2,800) during a ten-trial self-administration task. Subjective, performance, and physiological effects were measured repeatedly during laboratory sessions.
Results
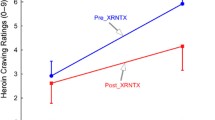
Memantine produced modest reductions in subjective ratings of drug quality, liking, willingness to pay for the drug, and craving for heroin. However, memantine produced few changes in the reinforcing effects of heroin.
Conclusions
These data demonstrate that memantine was well tolerated and modestly effective in reducing the subjective but not the reinforcing effects of heroin. Although it is unlikely that memantine will be useful as a stand-alone maintenance medication for opioid dependence, it may have some utility as an adjunct treatment medication.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allen RM, Dykstra LA (2001) N-methyl-d-aspartate receptor antagonists potentiate the antinociceptive effects of morphine in squirrel monkeys. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 298(1):288–297
Allen RM, Granger AL, Dykstra LA (2001) The competitive N-methyl-d-aspartate receptor antagonist (-)-6-phosphonomethyl-deca-hydroisoquinoline-3-carboxylic acid (LY235959) potentiates the antinociceptive effects of opioids that vary in efficacy at the mu-opioid receptor. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 307(2):785–792
Bisaga A, Evans SM (2004) Acute effects of memantine in combination with alcohol in moderate drinkers. Psychopharmacology 172:16–24
Bulka A, Wiesenfeld-Hallin Z, Xu XJ (2002) Differential antinociception by morphine and methadone in two sub-strains of Sprague-Dawley rats and its potentiation by dextromethorphan. Brain Res 942:95–100
Chen SL, Huang EY, Chow LH, Tao PL (2005) Dextromethorphan differentially affects opioid antinociception in rats. Br J Pharmacol 144(3):400–404
Collins ED, Ward AS, McDowell DM, Foltin RW, Fischman MW (1998) The effects of memantine on the subjective, reinforcing and cardiovascular effects of cocaine in humans. Behav Pharmacol 9:587–598
Collins ED, Vosburg SK, Ward AS, Haney M, Foltin RW (2006) Memantine increases cardiovascular but not behavioral effects of cocaine in methadone-maintained humans. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 83:47–55
Comer SD, Collins ED, MacArthur RB, Fischman MW (1999) Comparison of intranasal and intravenous heroin self-administration by morphine-maintained humans. Psychopharmacology 143:327–338
Craft RM, Lee DA (2005) NMDA antagonist modulation of morphine antinociception in female vs. male rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 80:639–649
Elliott K, Hynansky A, Inturrisi CE (1994) Dextromethorphan attenuates and reverses analgesic tolerance to morphine. Pain 59:361–368
Evans SM, Foltin RW, Levin FR, Fischman MW (1995) Behavioral and subjective effects of DN-2327 (pazinaclone) and alprazolam in normal volunteers. Behav Pharmacol 6:176–186
Fischer BD, Carrigan KA, Dykstra LA (2005) Effects of N-methyl-d-aspartate receptor antagonists on acute morphine-induced and l-methadone-induced antinociception in mice. J Pain 6(7):425–433
Foltin RW, Fischman MW (1992) The cardiovascular and subjective effects of intravenous cocaine and morphine combinations in humans. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 261:623–632
Fraser HF, Van Horn GD, Martin WR, Wolbach AB, Isbell H (1961) Methods for evaluating addiction liability. (A) “Attitude” of opiate addicts toward opiate-like drugs, (B) A short-term “direct” addiction test. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 133:371–387
Hamdy MM, Noda Y, Miyazaki M, Mamiya T, Nozaki A, Nita A, Sayed M, Assi AA, Gomaa A, Nabeshima T (2004) Molecular mechanisms in dizocilpine-induced attenuation of development of morphine dependence: an association with cortical Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent signal cascade. Behav Brain Res 152:263–270
Handelsman L, Cochrane KJ, Aronson MJ, Ness R, Rubinstein KJ, Kanof PD (1987) Two new rating scales for opiate withdrawal. Am J Drug Alcohol Abuse 13:93–308
Hart CL, Haney M, Foltin RW, Fischman MW (2002) Effects of the NMDA antagonist memantine on human methamphetamine discrimination. Psychopharmacology 164:376–384
Herman BH, Vocci F, Bridge P (1995) The effects of NMDA receptor antagonists and nitric oxide synthase inhibitors on opioid tolerance and dependence: Medication development issues for opiate addiction. Neuropsychopharmacology 13:269–293
Huang EY-K, Liu T-C, Tao P-L (2003) Co-administration of dextromethorphan with morphine attenuates morphine rewarding effect and related dopamine releases at the nucleus accumbens. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg’s Arch Pharmacol 368:386–392
Kelly TH, Foltin RW, Emurian CS, Fischman MW (1993) Performance-based testing for drugs of abuse: Dose and time profiles of marijuana, amphetamine, alcohol, and diazepam. J Anal Toxicol 17:264–272
Kim H-S, Jang C-G, Park W-K (1996) Inhibition by MK-801 of morphine-induced conditioned place preference and postsynaptic dopamine receptor supersensitivity in mice. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 55:11–17
Kornhuber J, Quack G (1995) Cerebrospinal fluid and serum concentrations of the N-methyl-d-aspartate (NMDA) receptor antagonist memantine in man. Neurosci Lett 195:137–139
Kornhuber J, Weller M, Schoppmeyer K, Riederer P (1994) Amantadine and memantine are NMDA receptor antagonists with neuroprotective properties. J Neural Transm 43(Suppl):91–104
Lipton SA (2006) Paradigm shift in neuroprotection by NMDA receptor blockade: memantine and beyond. Nat Rev Drug Discov 5(2):160–170
Mao J, Price DD, Caruso FS, Mayer DJ (1996) Oral administration of dextromethorphan prevents the development of morphine tolerance and dependence in rats. Pain 67:361–368
Marek P, Ben-Eliyahu S, Gold M, Liebeskind JC (1991) Excitatory amino acid antagonists (kynurenic acid and MK-801) attenuate the development of morphine tolerance in the rat. Brain Res 547:77–81
McLeod DR, Griffiths RR, Bigelow GE, Yingling J (1982) An automated version of the Digit Symbol Substitution Test (DSST). Behav Res Meth Instrum 14:463–466
Miller TP, Taylor JL, Tinklenberg JR (1988) A comparison of assessment techniques measuring the effects of methylphenidate, secobarbital, diazepam and diphenhydramine in abstinent alcoholics. Neuropsychobiology 19:90–96
Mobius HJ (2003) Memantine: An update on the current evidence. Int J Geriatr Psychiatry 18:S47–S54
Parsons CG, Danysz W, Quack G (2000) Memantine and the amino-alkyl-cylcohexane MRZ 2/579 are moderate affinity uncompetitive NMDA receptor antagonists—in vitro characterization. Amino Acids 19:157–166
Popik P, Danysz W (1997) Inhibition of reinforcing effects of morphine and motivational aspects of naloxone-precipitated opioid withdrawal by N-methyl-d-aspartate receptor antagonist, memantine. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 280:854–865
Popik P, Skolnick P (1996) The NMDA antagonist memantine blocks the expression and maintenance of morphine dependence. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 53(4):791–797
Popik P, Wrobel M, Rygula R, Bisaga A, Bespalov AY (2003) Effects of memantine, an NMDA receptor antagonist, on place preference conditioned with drug and nondrug reinforcers in mice. Behav Pharmacol 14:237–244
Popik P, Wrobel M, Bisaga A (2006) Reinstatement of morphine-conditioned reward is blocked by memantine. Neuropsychopharmacology 31(1):160–170
Redwine KE, Trujillo KA (2003) Effects of NMDA receptor antagonists on acute m-opioid analgesia in the rat. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 76:361–372
Ribeiro Do Couto B, Aguilar MA, Manzanedo C, Rodriguez-Arias M, Minarro J (2005) NMDA glutamate but not dopamine antagonists blocks drug-induced reinstatement of morphine place preference. Brain Res Bull 64(6):493–503
Schuster CR, Greenwald MK, Johanson CE, Heishman S (1995) Measurement of drug craving during naltrexone-precipitated withdrawal in methadone-maintained volunteers. Exp Clin Psychopharmacol 3:424–431
Semenova S, Danysz W, Bespalov A (1999) Low-affinity NMDA receptor channel blockers inhibit acquisition of intravenous morphine self-administration in naïve mice. Eur J Pharmacol 378:1–8
Tiseo PJ, Inturrisi CE (1993) Attenuation and reversal of morphine tolerance by the competitive N-methyl-d-aspartate receptor antagonist LY274614. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 264:1090–1096
Tiseo PJ, Cheng J, Pasternak GW, Inturrisi CE (1994) Modulation of morphine tolerance by the competitive N-methyl-d-aspartate receptor antagonist LY274614: assessment of opioid receptor changes. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 268:195–201
Trujillo KA (1995) Effects of noncompetitive N-methyl-d-aspartate receptor antagonists on opiate tolerance and dependence. Neuropsychopharmacology 13:301–307
Trujillo KA, Akil H (1991) Inhibition of morphine tolerance and dependence by the NMDA receptor antagonist MK-801. Science 251:85–87
Trujillo KA, Akil H (1994) Inhibition of opiate tolerance by non-competitive N-methyl-d-aspartate receptor antagonists. Brain Res 633(1-2):178–188
Tzschentke TM, Schmidt WJ (1995) N-methyl-d-aspartate receptor antagonists block morphine-induced conditioned place preference in rats. Neurosci Lett 193:37–40
Tzschentke TM, Schmidt WJ (2000) Effects of the non-competitive NMDA-receptor antagonist memantine on morphine- and cocaine-induced potentiation of lateral hypothalamic brain stimulation reward. Psychopharmacology 149:225–234
Vosburg SK, Hart CL, Haney M, Foltin RW (2005) An evaluation of the reinforcing effects of memantine in cocaine-dependent humans. Drug Alcohol Depend 79:257–260
Wesnes K, Warburton DM (1983) Effects of smoking on rapid information processing performance. Neuropsychobiology 9:223–229
Xi ZX, Stein EA (2002) Blockade of ionotropic glutamatergic transmission in the ventral tegmental area reduces heroin reinforcement in rat. Psychopharmacology 164(2):144–150
Acknowledgments
The medical assistance of Janet Murray RN and Drs. Adam Bisaga, John Mariani, Benjamin Nordstrom, Shabnam Shakibaie, and Jeanne Manubay is gratefully acknowledged. The technical assistance of Mr. Chaim Kozlovsky also is appreciated. This research was supported by grant DA09236.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Comer, S.D., Sullivan, M.A. Memantine produces modest reductions in heroin-induced subjective responses in human research volunteers. Psychopharmacology 193, 235–245 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-007-0775-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-007-0775-2