Abstract
Rationale and objective
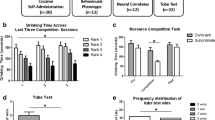
Group-housed male rats form social hierarchies, and under these conditions, it has been reported that subordinate (SUB) rats consume more alcohol than dominant (DOM) rats. We tested the hypothesis that a history of drinking alcohol would cause SUB rats to consume even greater amounts of alcohol.
Methods
Male Long–Evans rats were trained to drink 10% alcohol or a sucrose/quinine solution equal in calories for 1 h/day using a sucrose-fading procedure. Subsequently, rats were housed in colonies (four males, two females) in a visible burrow system (VBS) for 14 days. Individual control male rats were housed in a tub cage with one female. Rats were removed from the VBS (or control environment) daily and given 1 h to drink alcohol or sucrose/quinine.
Results
Colonies given daily access to sucrose/quinine formed clear DOM/SUB relationships in all measured parameters. Alcohol-drinking colonies failed to establish a dominance hierarchy and displayed little aggression, with an average of 14.6 ± 6.1 offensive attacks compared with 58.5 ± 12.3 attacks carried out by DOM sucrose/quinine rats. During VBS housing, alcohol and sucrose/quinine intake decreased independent of housing environment or social status.
Conclusions
Contrary to prior reports of the effect of alcohol on aggressive behavior, moderate daily alcohol intake before and during VBS housing reduced aggression and precluded the formation of a dominance hierarchy in rats.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Albeck DS, McKittrick CR, Blanchard DC, Blanchard RJ, Nikulina J, McEwen BS, Sakai RR (1997) Chronic social stress alters levels of corticotropin-releasing factor and arginine vasopressin mRNA in rat brain. J Neurosci 17:4895–4903
Anisman H, Waller TG (1974) Effects of inescapable shock and shock-produced conflict on self selection of alcohol in rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 2:27–33
Anthenelli RM, Schuckit MA (1993) Affective and anxiety disorders and alcohol and drug dependence: diagnosis and treatment. J Addict Dis 12:73–87
Blanchard DC, Spencer RL, Weiss SM, Blanchard RJ, McEwen B, Sakai RR (1995) Visible burrow system as a model of chronic social stress: behavioral and neuroendocrine correlates. Psychoneuroendocrinology 20:117–134
Blanchard RJ, Hori K, Flannelly K, Blanchard DC (1987a) The effects of ethanol on the offense and defensive behaviors of male and female rats during group formation. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 26:61–64
Blanchard RJ, Hori K, Tom P, Blanchard DC (1987b) Social structure and ethanol consumption in the laboratory rat. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 28:437–442
Blanchard RJ, Flores T, Magee L, Weiss S, Blanchard CD (1992) Pregrouping aggression and defense scores influence alcohol consumption for dominant and subordinate rats in visible burrow systems. Aggress Behav 18:459–467
Bond NW (1978) Shock induced alcohol consumption in rats: role of initial preference. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 9:39–42
Bowen RC, Cipywnyk D, D’Arcy C, Keegan D (1984) Alcoholism, anxiety disorders, and agoraphobia. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 8:48–50
Chester JA, De Paula Barrenha G, DeMaria A, Finegan A (2006) Different effects of stress on alcohol drinking behaviour in male and female mice selectively bred for high alcohol preference. Alcohol Alcohol 41:44–53
Cicero TJ, Bernstein D, Badger TM (1978) Effects of acute alcohol administration on reproductive endocrinology in the male rat. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 2:249–254
Conger JJ (1956) Alcoholism: theory, problem and challenge. II. Reinforcement theory and the dynamics of alcoholism. Q J Stud Alcohol 17:296–305
Croft AP, Brooks SP, Cole J, Little HJ (2005) Social defeat increases alcohol preference of C57BL/10 strain mice; effect prevented by a CCKB antagonist. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 183:163–170
Duncan EA, Proulx K, Woods SC (2005) Central administration of melanin-concentrating hormone increases alcohol and sucrose/quinine intake in rats. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 29:958–964
Ellison G (1987) Stress and alcohol intake: the socio-pharmacological approach. Physiol Behav 40:387–392
Ellison G, Daniel F, Zoraster R (1979) Delayed increases in alcohol consumption occur in rat colonies but not in isolated rats after injections of monoamine neurotoxins. Exp Neurol 65:608–615
Fidler TL, LoLordo VM (1996) Failure to find postshock increases in ethanol preference. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 20:110–121
Gorman DM, Brown GW (1992) Recent developments in life-event research and their relevance for the study of addictions. Br J Addict 87:837–849
Grant KA, Samson HH (1985) Induction and maintenance of ethanol self-administration without food deprivation in the rat. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 86:475–479
Heinrichs SC, Pich EM, Miczek KA, Britton KT, Koob GF (1992) Corticotropin-releasing factor antagonist reduces emotionality in socially defeated rats via direct neurotropic action. Brain Res 581:190–197
Ida Y, Tsujimaru S, Nakamaura K, Shirao I, Mukasa H, Egami H, Nakazawa Y (1992) Effects of acute and repeated alcohol ingestion on hypothalamic–pituitary–gonadal and hypothalamic–pituitary–adrenal functioning in normal males. Drug Alcohol Depend 31:57–64
Jellinek EM (1952) Phases of alcohol addiction. Q J Stud Alcohol 13:673–684
Kratz CM, Levitsky DA, Lustick SL (1978) Long term effects of quinine on food intake and body weight in the rat. Physiol Behav 21:321–324
Krsiak M, Borgesova M (1973) Effect of alcohol on behaviour of pairs of rats. Psychopharmacologia 32:201–209
Kushner MG, Abrams K, Thuras P, Hanson KL, Brekke M, Sletten S (2005) Follow-up study of anxiety disorder and alcohol dependence in comorbid alcoholism treatment patients. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 29:1432–1443
Linsky AS, Straus MA, Colby JP Jr (1985) Stressful events, stressful conditions and alcohol problems in the United States: a partial test of Bales’s theory. J Stud Alcohol 46:72–80
Lucas LR, Celen Z, Tamashiro KL, Blanchard RJ, Blanchard DC, Markham C, Sakai RR, McEwen BS (2004) Repeated exposure to social stress has long-term effects on indirect markers of dopaminergic activity in brain regions associated with motivated behavior. Neuroscience 124:449–457
Lugo JN Jr, Marino MD, Gass JT, Wilson MA, Kelly SJ (2006) Ethanol exposure during development reduces resident aggression and testosterone in rats. Physiol Behav 87:330–337
McKittrick CR, Blanchard DC, Blanchard RJ, McEwen BS, Sakai RR (1995) Serotonin receptor binding in a colony model of chronic social stress. Biol Psychiatry 37:383–393
Merikangas KR, Stevens DE, Fenton B, Stolar M, O’Malley S, Woods SW, Risch N (1998) Co-morbidity and familial aggregation of alcoholism and anxiety disorders. Psychol Med 28:773–788
Miczek KA, Barry H 3rd (1977a) Comparison of the effects of alcohol, chlordiazepoxide, and delta9-tetrahydrocannabinol on intraspecies aggression in rats. Adv Exp Med Biol 85B:251–264
Miczek KA, Barry H 3rd (1977b) Effects of alcohol on attack and defensive-submissive reactions in rats. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 52:231–237
Miczek KA, Weerts EM, Tornatzky W, DeBold JF, Vatne TM (1992) Alcohol and “bursts” of aggressive behavior: ethological analysis of individual differences in rats. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 107:551–563
Mills KC, Bean JW, Hutcheson JS (1977) Shock induced ethanol consumption in rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 6:107–115
Mos J, Olivier B (1988) Differential effects of selected psychoactive drugs on dominant and subordinate male rats housed in a colony. Neurosci Res Commun 2:29–36
Ng Cheong Ton MJ, Brown Z, Michalakeas A, Amit Z (1983) Stress induced suppression of maintenance but not of acquisition of ethanol consumption in rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 18:141–144
Parker LF, Radow BL (1974) Isolation stress and volitional ethanol consumption in the rat. Physiol Behav 12:1–3
Pich EM, Heinrichs SC, Rivier C, Miczek KA, Fisher DA, Koob GF (1993) Blockade of pituitary-adrenal axis activation induced by peripheral immunoneutralization of corticotropin-releasing factor does not affect the behavioral response to social defeat stress in rats. Psychoneuroendocrinology 18:495–507
Rivier C (1999) Alcohol rapidly lowers plasma testosterone levels in the rat: evidence that a neural brain-gonadal pathway may be important for decreased testicular responsiveness to gonadotropin. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 23:38–45
Rockman GE, Hall A, Hong J, Glavin GB (1987) Unpredictable cold-immobilization stress effects on voluntary ethanol consumption in rats. Life Sci 40:1245–1251
Schuckit MA, Hesselbrock V (1994) Alcohol dependence and anxiety disorders: what is the relationship? Am J Psychiatry 151:1723–1734
Sclafani A, Ackroff K (1994) Glucose- and fructose-conditioned flavor preferences in rats: taste versus postingestive conditioning. Physiol Behav 56:399–405
Spencer RL, Miller AH, Moday H, McEwen BS, Blanchard RJ, Blanchard DC, Sakai RR (1996) Chronic social stress produces reductions in available splenic type II corticosteroid receptor binding and plasma corticosteroid binding globulin levels. Psychoneuroendocrinology 21:95–109
Swendsen JD, Merikangas KR, Canino GJ, Kessler RC, Rubio-Stipec M, Angst J (1998) The comorbidity of alcoholism with anxiety and depressive disorders in four geographic communities. Compr Psychiatry 39:176–184
Tamashiro KL, Nguyen MM, Fujikawa T, Xu T, Yun Ma L, Woods SC, Sakai RR (2004) Metabolic and endocrine consequences of social stress in a visible burrow system. Physiol Behav 80:683–693
Tolliver GA, Sadeghi KG, Samson HH (1988) Ethanol preference following the sucrose-fading initiation procedure. Alcohol 5:9–13
van Erp AM, Miczek KA (1997) Increased aggression after ethanol self-administration in male resident rats. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 131:287–295
van Erp AM, Miczek KA (2001) Persistent suppression of ethanol self-administration by brief social stress in rats and increased startle response as index of withdrawal. Physiol Behav 73:301–311
van Erp AM, Tachi N, Miczek KA (2001) Short or continuous social stress: suppression of continuously available ethanol intake in subordinate rats. Behav Pharmacol 12:335–342
Vengeliene V, Siegmund S, Singer MV, Sinclair JD, Li TK, Spanagel R (2003) A comparative study on alcohol-preferring rat lines: effects of deprivation and stress phases on voluntary alcohol intake. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 27:1048–1054
Volpicelli JR, Ulm RR, Hopson N (1990) The bidirectional effects of shock on alcohol preference in rats. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 14:913–916
Weerts EM, Tornatzky W, Miczek KA (1993) Prevention of the pro-aggressive effects of alcohol in rats and squirrel monkeys by benzodiazepine receptor antagonists. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 111:144–152
Weiss KJ, Rosenberg DJ (1985) Prevalence of anxiety disorder among alcoholics. J Clin Psychiatry 46:3–5
Widenius TV, Eriksson CJ, Ylikahri RH, Harkonen M (1989) Inhibition of testosterone synthesis by ethanol: role of luteinizing hormone. Alcohol 6:241–244
Wolffgramm J (1990) Free choice ethanol intake of laboratory rats under different social conditions. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 101:233–239
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to Dennis Choi, Dr. Li Yun Ma, and Therese Rider for expert technical assistance. In addition, the authors would like to thank Drs. Ron Jandacek and Patrick Tso for the use of their gas chromatography machine. This research was supported by NIH grant DK 66596, DK 17844, and by NIH training grant T32 DK59803.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Duncan, E.A., Tamashiro, K.L.K., Nguyen, M.M.N. et al. The impact of moderate daily alcohol consumption on aggression and the formation of dominance hierarchies in rats. Psychopharmacology 189, 83–94 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-006-0536-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-006-0536-7