Abstract
Rationale
Despite established links between nicotine dependence and depression, little research has examined the effects of nicotine on depression symptoms.
Objective
This study evaluated the acute and chronic effects of transdermal nicotine in nonsmokers with baseline depression symptoms during a 4-week, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial.
Methods
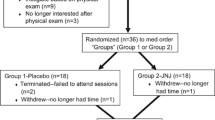
Nonsmokers with scores ≥10 on the Center for Epidemiological Studies Depression scale (CES-D) were recruited from the community. Mood and cognitive performance were measured at baseline (day 0) and at 1, 8, 21, and 28 days. Participants were randomly assigned to wear a placebo or nicotine patch for 4 weeks (3.5 mg/day during weeks 1 and 4; 7 mg/day during weeks 2 and 3). The final sample consisted of 11 nonsmokers with a mean baseline CES-D score of 27.36 (SD=10.53).
Results
Salivary nicotine levels indicated the majority of participants were compliant with treatment. Acute nicotine did not alter mood. After adjusting for baseline values, chronic nicotine resulted in a significant decline in CES-D scores at day 8 (3.5 mg/day), but returned to placebo levels by the last visit. This return to baseline levels was coincident with a decrease in nicotine administration from 7 to 3.5 mg/day. A similar trend for improved response inhibition as measured by the Conners Continuous Performance Task was also observed. Reported side effects were infrequent and minimal.
Conclusion
These findings suggest a role for nicotinic receptor systems in the pathophysiology of depression and that nicotinic compounds should be evaluated for treating depression symptoms.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anda RF, Williamson DF, Escobedo LG, Mast EE, Giovino GA, Remington PL (1990) Depression and the dynamics of smoking. A national perspective. JAMA 264:1541–1545
Audrain-McGovern J, Lerman C, Wileyto EP, Rodriguez D, Shields PG (2004) Interacting effects of genetic predisposition and depression on adolescent smoking progression. Am J Psychiatry 161:1224–1230
Bearden CE, Glahn DC, Monkul ES, Barrett J, Najt P, Villarreal V, Soares JC (2006) Patterns of memory impairment in bipolar disorder and unipolar major depression. Psychiatry Res 142:139–150
Belluardo N, Blum M, Mudo G, Andbjer B, Fuxe K (1998) Acute intermittent nicotine treatment produces regional increases of basic fibroblast growth factor messenger RNA and protein in the tel- and diencephalon of the rat. Neuroscience 83:723–740
Belluardo N, Mudo G, Blum M, Amato G, Fuxe K (2000) Neurotrophic effects of central nicotinic receptor activation. J Neural Transm Suppl:227–245
Belluardo N, Olsson PA, Mudo G, Sommer WH, Amato G, Fuxe K (2005) Transcription factor gene expression profiling after acute intermittent nicotine treatment in the rat cerebral cortex. Neuroscience 133:787–796
Castagnoli K, Steyn SJ, Magnin G, Van Der Schyf CJ, Fourie I, Khalil A, Castagnoli N Jr (2002) Studies on the interactions of tobacco leaf and tobacco smoke constituents and monoamine oxidase. Neurotox Res 4:151–160
Conners CK (1994) The Conners Continuous Performance Test. Multi-Health Systems, Inc., Toronto, Canada
Conners CK, Levin ED, Sparrow E, Hinton SC, Erhardt D, Meck WH, Rose JE, March J (1996) Nicotine and attention in adult attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD). Psychopharmacol Bull 32:67–73
Covey LS, Glassman AH, Stetner F (1997) Major depression following smoking cessation. Am J Psychiatry 154:263–265
Cox LS, Patten CA, Krahn LE, Hurt RD, Croghan IT, Wolter TD, Schroeder DR, Tri D, Offord KP (2003) The effect of nicotine patch therapy on depression in nonsmokers: a preliminary study. J Addict Dis 22:75–85
Djuric VJ, Dunn E, Overstreet DH, Dragomir A, Steiner M (1999) Antidepressant effect of ingested nicotine in female rats of Flinders resistant and sensitive lines. Physiol Behav 67:533–537
Duman RS, Monteggia LM (2006) A neurotrophic model for stress-related mood disorders. Biol Psychiatry 59:1116–1127
Dursun SM, Kutcher S (1999) Smoking, nicotine and psychiatric disorders: evidence for therapeutic role, controversies and implications for future research. Med Hypotheses 52:101–109
Ferguson SM, Brodkin JD, Lloyd GK, Menzaghi F (2000) Antidepressant-like effects of the subtype-selective nicotinic acetylcholine receptor agonist, SIB-1508Y, in the learned helplessness rat model of depression. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 152:295–303
Fowler JS, Volkow ND, Wang GJ, Pappas N, Logan J, MacGregor R, Alexoff D, Shea C, Schlyer D, Wolf AP, Warner D, Zezulkova I, Cilento R (1996a) Inhibition of monoamine oxidase B in the brains of smokers. Nature 379:733–736
Fowler JS, Volkow ND, Wang GJ, Pappas N, Logan J, Shea C, Alexoff D, MacGregor RR, Schlyer DJ, Zezulkova I, Wolf AP (1996b) Brain monoamine oxidase A inhibition in cigarette smokers. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 93:14065–14069
Gilbert DG, McClernon FJ, Rabinovich NE, Plath LC, Jensen RA, Meliska CJ (1998) Effects of smoking abstinence on mood and craving in men: influences of negative-affect-related personality traits, habitual nicotine intake and repeated measurements. Pers Individ Differ 25:399–423
Gilbert DG, Crauthers DM, Mooney DK, McClernon FJ, Jensen RA (1999) Effects of monetary contingencies on smoking relapse: influences of trait depression, personality, and habitual nicotine intake. Exp Clin Psychopharmacol 7:174–181
Gilbert DG, McClernon FJ, Rabinovich NE, Plath LC, Masson CL, Anderson AE, Sly KF (2002) Mood disturbance fails to resolve across 31 days of cigarette abstinence in women. J Consult Clin Psychol 70:142–152
Glassman AH, Covey LS, Stetner F, Rivelli S (2001) Smoking cessation and the course of major depression: a follow-up study. Lancet 357:1929–1932
Hannay HJ, Levin HS (1985) Selective Reminding Test: an examination of the equivalence of four forms. J Clin Exp Neuropsychol 7:251–263
Heishman SJ (1998) What aspects of human performance are truly enhanced by nicotine? Addiction 93:317–320
Heishman SJ, Henningfield JE (2000) Tolerance to repeated nicotine administration on performance, subjective, and physiological responses in nonsmokers. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 152:321–333
Heishman SJ, Taylor RC, Henningfield JE (1994) Nicotine and smoking: a review of effects on human performance. Exp Clin Psychopharmacol 2:345
Jacob P 3rd, Wilson M, Benowitz NL (1981) Improved gas chromatographic method for the determination of nicotine and cotinine in biologic fluids. J Chromatogr 222:61–70
Jamner LD, Shapiro D, Jarvik ME (1999) Nicotine reduces the frequency of anger reports in smokers and nonsmokers with high but not low hostility: an ambulatory study. Exp Clin Psychopharmacol 7:454–463
Kelton MC, Kahn HJ, Conrath CL, Newhouse PA (2000) The effects of nicotine on Parkinson’s disease. Brain Cogn 43:274–282
Kendler KS, Neale MC, MacLean CJ, Heath AC, Eaves LJ, Kessler RC (1993) Smoking and major depression. A causal analysis. Arch Gen Psychiatry 50:36–43
Kleykamp BA, Jennings JM, Blank MD, Eissenberg T (2005) The effects of nicotine on attention and working memory in never-smokers. Psychol Addict Behav 19:433–438
Lasser K, Boyd JW, Woolhandler S, Himmelstein DU, McCormick D, Bor DH (2000) Smoking and mental illness: a population-based prevalence study. JAMA 284:2606–2610
Lerman C, Caporaso N, Main D, Audrain J, Boyd NR, Bowman ED, Shields PG (1998) Depression and self-medication with nicotine: the modifying influence of the dopamine D4 receptor gene. Health Psychol 17:56–62
Levin ED, Conners CK, Silva D, Canu W, March J (2001) Effects of chronic nicotine and methylphenidate in adults with attention deficit/hyperactivity disorder. Exp Clin Psychopharmacol 9:83–90
Levin ED, McClernon FJ, Rezvani AH (2006) Nicotinic effects on cognitive function: behavioral characterization, pharmacological specification, and anatomic localization. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 184:523–539
Lorr M, McNair D (1984) Manual: Profile of Mood States. Educational and Industrial Testing Service, San Diego, CA
Maggio R, Riva M, Vaglini F, Fornai F, Molteni R, Armogida M, Racagni G, Corsini GU (1998) Nicotine prevents experimental parkinsonism in rodents and induces striatal increase of neurotrophic factors. J Neurochem 71:2439–2446
Malberg JE, Duman RS (2003) Cell proliferation in adult hippocampus is decreased by inescapable stress: reversal by fluoxetine treatment. Neuropsychopharmacology 28:1562–1571
McClernon FJ, Gilbert DG, Radtke R (2003) Effects of transdermal nicotine on lateralized identification and memory interference. Hum Psychopharmacol 18:339–343
Perkins KA, Gerlach D, Vender J, Grobe J, Meeker J, Hutchison S (2001) Sex differences in the subjective and reinforcing effects of visual and olfactory cigarette smoke stimuli. Nicotine Tob Res 3:141–150
Poltavski DV, Petros T (2006) Effects of transdermal nicotine on attention in adult non-smokers with and without attentional deficits. Physiol Behav 85:833–843
Potter A, Corwin J, Lang J, Piasecki M, Lenox R, Newhouse PA (1999) Acute effects of the selective cholinergic channel activator (nicotinic agonist) ABT-418 in Alzheimer’s disease. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 142:334–342
Radloff LS (1977) The CES-D scale: a self-report depression scale for research in the general population. Appl Psychol Meas 1:385–401
Reeves D, Kane R, Winter K (1995) Automated Neuropsychological Assessment Metrics (ANAM): test administrators guide version 3.11. National Cognitive Recovery Foundation, San Diego, CA
Rose JE, Levin ED, Benowitz N (1993) Saliva nicotine as an index of plasma levels in nicotine skin patch users. Ther Drug Monit 15:431–435
Salin-Pascual RJ (2002) Relationship between mood improvement and sleep changes with acute nicotine administration in non-smoking major depressed patients. Rev Invest Clin 54:36–40
Salin-Pascual RJ, Drucker-Colin R (1998) A novel effect of nicotine on mood and sleep in major depression. Neuroreport 9:57–60
Salin-Pascual RJ, Rosas M, Jimenez-Genchi A, Rivera-Meza BL, Delgado-Parra V (1996) Antidepressant effect of transdermal nicotine patches in nonsmoking patients with major depression. J Clin Psychiatry 57:387–389
Smith RC, Singh A, Infante M, Khandat A, Kloos A (2002) Effects of cigarette smoking and nicotine nasal spray on psychiatric symptoms and cognition in schizophrenia. Neuropsychopharmacology 27:479–497
Terracciano A, Costa PT Jr (2004) Smoking and the five-factor model of personality. Addiction 99:472–481
Tizabi Y, Overstreet DH, Rezvani AH, Louis VA, Clark E Jr, Janowsky DS, Kling MA (1999) Antidepressant effects of nicotine in an animal model of depression. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 142:193–199
Watkins SS, Koob GF, Markou A (2000) Neural mechanisms underlying nicotine addiction: acute positive reinforcement and withdrawal. Nicotine Tob Res 2:19–37
Watson D, Clark LA, Tellegen A (1988) Development and validation of brief measures of positive and negative affect: the PANAS scales. J Pers Soc Psychol 54:1063–1070
White HK, Levin ED (1999) Four-week nicotine skin patch treatment effects on cognitive performance in Alzheimer’s disease. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 143:158–165
White HK, Levin ED (2004) Chronic transdermal nicotine patch treatment effects on cognitive performance in age-associated memory impairment. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 171:465–471
Wilens TE, Biederman J, Spencer TJ, Bostic J, Prince J, Monuteaux MC, Soriano J, Fine C, Abrams A, Rater M, Polisner D (1999) A pilot controlled clinical trial of ABT-418, a cholinergic agonist, in the treatment of adults with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder. Am J Psychiatry 156:1931–1937
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by a Young Investigator Award from the National Alliance for Research on Schizophrenia and Depression. Dr. Rose is an inventor named on several nicotine patch patents and receives royalties from sales of certain nicotine patches.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
McClernon, F.J., Hiott, F.B., Westman, E.C. et al. Transdermal nicotine attenuates depression symptoms in nonsmokers: a double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Psychopharmacology 189, 125–133 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-006-0516-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-006-0516-y