Abstract
Objective
To investigate the effects of Ginko biloba extract (EGb) administration on T lymphocyte subsets and superoxide dismutase (SOD) levels in schizophrenia.
Methods
One hundred and nine schizophrenic inpatients were randomly assigned to 12 weeks of treatment with 360 mg/day of EGb plus a stable dose of 0.25 mg kg−1 day−1 of haloperidol and placebo plus the same dose of haloperidol using a double-blind design. Clinical efficacy was determined using the Brief Psychiatric Rating Scale (BPRS), Scale for Assessment of Positive Symptoms, and Scale for Assessment of Negative Symptoms. T lymphocytes (CD3+), T helper cells (CD4+), T suppressor cells (CD8+), and IL-2-secreting cells were measured using the alkaline phosphatase/antialkaline phosphatase technique; and SOD levels were measured by radioimmunometric assay at baseline and at posttreatment, as compared to 30 sex- and age-matched normal subjects.
Results
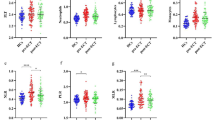
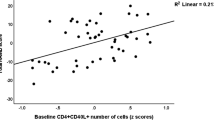
Patients demonstrated significantly lower CD3+, CD4+, and IL-2-secreting cells, together with CD4/CD8 ratio, and significantly higher blood SOD levels than did healthy controls at baseline. There was a significantly negative relationship between SOD and CD4+ cells in the schizophrenic group at baseline. After a 12-week treatment, CD3+, CD4+, and IL-2-secreting cells, together with CD4/CD8 ratio, showed a significant increase, but a significant decrease in SOD levels in the EGb group. There was only a significant increase in CD4+ cells but no change in SOD levels in the placebo group. There was a significant correlation between the change in CD4+ cells at posttreatment vs pretreatment and a reduction of BPRS total score in the whole patient group.
Conclusions
EGb may improve the decreased peripheral immune functions in schizophrenia. The beneficial effects of EGb on the immune systems and the improvement of schizophrenic symptoms may be medicated through its antioxidant activity.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Causo C, Candore G, Cigna D, Colucc AT, Modica MA (1993) Biological significance of soluble IL-2 receptor. Mediators Inflamm 2:3–21
Cosentino M, Fietta A, Caldiroli E, Marino F, Rispoli L, Comelli M, Lecchini S, Frigo G (1996) Assessment of lymphocyte subsets and neutrophil leukocyte function in chronic psychiatric patients on long-term drug therapy. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 20:1117–1129
DeFeudis FV (1991) In vivo studies with EGb761. In: DeFeudis FV (ed) Ginkgo biloba extract (EGb): pharmacological activities and clinical applications. Elsevier, Paris, pp 61–66
Hildeman DA, Mitchell T, Teague TK, Henson P, Day BJ, Kappler J, Marrack PC (1999) Reactive oxygen species regulate activation-induced T cell apoptosis. Immunity 10:735–744
Jacobs BP, Browner WS (2000) Ginkgo biloba: a living fossil. Am J Med 108:341–342
Lohr JB, Kuczenski R, Niculescu AB (2003) Oxidative mechanisms and tardive dyskinesia. CNS Drugs 17:47–62
Maclennan KM, Darlington CL, Smith PF (2002) The CNS effects of Ginkgo biloba extracts and ginkgolide B. Prog Neurobiol 67:235–257
Muller N, Hofschuster E, Ackenheil M, Eckstein R (1993) T cells and psychopathology in schizophrenia: relationship to the outcome of neuroleptic therapy. Acta Psychiatr Scand 87:66–71
Muller N, Riedel M, Ackenheil M, Schwarz MJ (1999) The role of immune function in schizophrenia: an overview. Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci 249(Suppl 4):62–68
Muller N, Riedel M, Gruber R, Ackenheil M, Schwarz MJ (2000) The immune system and schizophrenia. An integrative view. Ann N Y Acad Sci 917:456–467
Puebla-Perez AM, Lozoya X, Villasenor-Garcia MM (2003) Effect of Ginkgo biloba extract, EGb 761, on the cellular immune response in a hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis activation model in the rat. Int Immunopharmacol 3:75–80
Sperner-Unterweger B, Whitworth A, Kemmler G, Hilbe W, Thaler J, Weiss G, Fleischhacker WW (1999) T-cell subsets in schizophrenia: a comparison between drug-naive first episode patients and chronic schizophrenic patients. Schizophr Res 38:61–70
Tian YM, Tian HJ, Zhang GY, Dai YR (2003) Effects of Ginkgo biloba extract (EGb 761) on hydroxyl radical-induced thymocyte apoptosis and on age-related thymic atrophy and peripheral immune dysfunctions in mice. Mech Ageing Dev 124:977–983
Villemain F, Chatenoud L, Galinowski A, Homo-Delarche F, Ginestet D, Loo H, Zarifian E, Bach JF (1989) Aberrant T cell-mediated immunity in untreated schizophrenic patients: deficient interleukin-2 production. Am J Psychiatry 146:609–616
Yao JK, Reddy RD, van Kammen DP (2001) Oxidative damage and schizophrenia: an overview of the evidence and its therapeutic implications. CNS Drugs 15:287–310
Zhang XY, Zhou DF, Zhang PY, Wu GY, Su JM, Cao LY (2001a) A double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of extract of Ginkgo biloba added to haloperidol in treatment-resistant patients with schizophrenia. J Clin Psychiatry 62:878–883
Zhang XY, Zhou DF, Su JM, Zhang PY (2001b) The effect of extract of ginkgo biloba added to haloperidol on superoxide dismutase in inpatients with chronic schizophrenia. J Clin Psychopharmacol 21:85–88
Zhang XY, Zhou DF, Cao LY, Zhang PY, Wu GY (2002) Decreased production of interleukin-2 (IL-2), IL-2 secreting cells and CD4+ cells in medication-free patients with schizophrenia. J Psychiatr Res 36:331–336
Acknowledgement
This study was supported by the Beijing Scientific and Technological New Stars Fund, Beijing, China (Dr. X. Y. Zhang).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, X.Y., Zhou, D.F., Cao, L.Y. et al. The effects of Ginkgo biloba extract added to haloperidol on peripheral T cell subsets in drug-free schizophrenia: a double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Psychopharmacology 188, 12–17 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-006-0476-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-006-0476-2