Abstract
Rationale
The locus coeruleus (LC) is the source of norepinephrine (NE) in the prefrontal cortex (PFC) and hippocampus and may influence cognitive functions of these areas. Chronic effects of LC-NE lesions do not correspond consistently with acute effects of systemic or intracortical injections of adrenergic agents.
Objective
These studies aim to manipulate LC activity pharmacologically and study acute effects on measures of attention and memory that depend on the PFC and hippocampus.
Methods
Rats were trained to criterion for one of three tasks: visuospatial reaction time (VSRT), a measure of attention sensitive to PFC lesions, delayed matching trained with retractable levers (DM-RL), and delayed nonmatching trained in radial mazes (DNM-RM), measures of spatial working memory sensitive to PFC and hippocampal lesions, respectively. LC activity was manipulated with bilateral 0.5-μl injections of the alpha-2 agonist clonidine (0, 1.1, 4.5, and 18 nmol).
Results
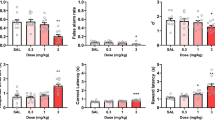
Clonidine produced significant dose-dependent impairments of VSRT, affecting choice response time at the 18-nmol dose and choice accuracy at the 4.5- and 18-nmol doses. Clonidine had no effect on DMRL or DNM-RM at any of the doses tested.
Conclusions
Reversible reduction of LC-NE activity by clonidine impaired measures of visuospatial attention sensitive to PFC lesions but were insufficient to affect PFC- or hippocampal-dependent measures of spatial working memory. These results are consistent with reports that LC-NE lesions produce chronic deficits in attention with little or no effect on measures of working memory.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aghajanian GK, Wang YY (1987) Common alpha 2- and opiate effector mechanisms in the locus coeruleus: intracellular studies in brain slices. Neuropharmacology 26:793–799
Arnsten AFT (1997) Catecholamine regulation of the prefrontal cortex. J Psychopharmacol 11:151–162
Arnsten AFT (2000) Stress impairs prefrontal cortical function in rats and monkeys: role of dopamine D1 and norepinephrine α-1 receptor mechanisms. Prog Brain Res 126:183–192
Arnsten AFT (2004) Adrenergic targets for the treatment of cognitive deficits in schizophrenia. Psychopharmacology 174:25–31
Arnsten AFT, Contant TA (1992) Alpha-2 adrenergic agonists decrease distractibility in aged monkeys performing a delayed response task. Psychopharmacology 108:159–169
Arnsten AFT, Goldman-Rakic PS (1985) α-2 adrenergic mechanisms in prefrontal cortex associated with cognitive decline in aged nonhuman primates. Science 230:1274–1276
Arnsten AFT, Cai JX, Goldman-Rakic PS (1988) The α-2 adrenergic agonist guanfacine improves memory in aged monkeys without sedative or hypotensive side effects: evidence for α-2 receptor subtypes. J Neurosci 8:4287–4298
Aston-Jones G, Rajkowski J, Kubiak P, Alexinsky T (1994) Locus coeruleus neurons in the monkey are selectively activated by attended stimuli in a vigilance task. J Neurosci 14:4467–4490
Aston-Jones G, Rajkowski J, Cohen J (2000) Locus coeruleus and regulation of behavioral flexibility and attention. Prog Brain Res 126:165–182
Bailey KR, Mair RG (2004) Dissociable effects of frontal cortical lesions on measures of visuospatial attention and spatial working memory in the rat. Cereb Cortex 14:974–985
Berridge CW, Abercrombie ED (1999) Relationship between locus coeruleus discharge rates and rates of norepinephrine release within neocortex. Neuroscience 93:1263–1270
Berridge CW, Foote SL (1991) Effects of locus coeruleus activation on electrophysiologic activity in neocortex and hippocampus. J Neurosci 11:3135–3145
Berridge CW, Waterhouse BD (2003) The locus coeruleus–noradrenergic system: modulation of behavioral state and state-dependent cognitive processes. Brain Res Rev 42:33–84
Berridge CW, Page ME, Valentino RJ, Foote SL (1993) Effects of locus coeruleus inactivation on electroencephalographic activity in neocortex and hippocampus. Neuroscience 55:381–393
Burk JA, Mair RG (2001) Thalamic amnesia reconsidered: excitotoxic lesions of the intralaminar nuclei, but not the mediodorsal nucleus disrupt place DMTS performance in the rat (Rattus norvegicus). Behav Neurosci 112:54–67
Burk JA, Mair RG (2001) Effects of intralaminar thalamic lesions on sensory attention and motor intention in the rat: a comparison with lesions involving frontal cortex and hippocampus. Behav Brain Res 123:49–63
Carli M, Robbins TW, Evenden JL, Everitt BJ (1983) Effects of lesions to ascending noradrenergic neurones on performance of a 5-choice serial reaction task in rats; implications for theories of dorsal noradrenergic bundle function based on selective attention and arousal. Behav Brain Res 9:361–380
Cole BJ, Robbins TW (1987) Amphetamine impairs discrimination performance of rats with dorsal noradrenergic bundle lesions on a 5-choice serial reaction time task: new evidence for central dopaminergic–noradrenergic interactions. Psychopharmacology 91:458–466
Cole BJ, Robbins RW (1992) Forebrain norepinephrine: role in controlled information processing in the rat. Neuropsychopharmacology 7:129–142
Decker MW, Gallagher M (1987) Scopolamine-disruption of radial arm maze performance: modification by noradrenergic depletion. Brain Res 417:59–69
Foote SL, Morrison JH (1987) Extrathalamic modulation of cortical function. Annu Rev Neurosci 10:67–95
Franowicz JS, Kessler L, Dailey-Borja CM, Kobilka BK, Limbird LE, Arnsten AFT (2002) Mutation of the alpha 2A-adrenoceptor impairs working memory performance and annuls cognitive enhancement by guanfacine. J Neurosci 22:8771–8777
Hagan JJ, Leslie RA, Patel S, Evans ML, Wattam TA, Holmes S, Benham CD, Taylor SG, Routledge C, Hemmati P, Munton RP, Ashmeade TE, Shah AS, Hatcher JP, Hatcher PD, Jones DN, Smith MI, Piper DC, Hunter AJ, Porter RA, Upton N (1999) Orexin A activates locus coeruleus cell firing and increases arousal in the rat. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 96:10911–10916
Ivanov A, Aston-Jones G (1995) Extranuclear dendrites of locus coeruleus neurons: activation by glutamate and modulation of activity by alpha adrenoceptors. J Neurophysiol 74:2427–2436
Jackson WJ, Buccafusco JJ (1991) Clonidine enhances delayed matching-to-sample performance by young and aged monkeys. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 39:79–84
Koger SM, Mair RG (1992) Depletion of cortical norepinephrine in rats by 6-hydroxydompaine does not impair performance of a delayed-nonmatching-to-sample task. Behav Neurosci 106:718–721
Langlais PJ, Connor DJ, Thal L (1993) Comparison of the effects of single and combined neurotoxic lesions of the nucleus basalis magnocellularis and dorsal noradrenergic bundle on learning and memory in the rat. Behav Brain Res 31:81–90
Mair RG, Burk JA, Porter MC (1998) Lesions of the frontal cortex, hippocampus, and intralaminar thalamic nuclei have distinct effects on remembering in rats. Behav Neurosci 112:772–792
Mao Z-M, Arnsten AFT, Li B-M (1999) Local infusion of alpha-1 adrenergic agonist into the prefrontal cortex impairs spatial working memory performance in monkeys. Biol Psychiatry 46:1259–1265
McGaughy J, Sandstrom M, Ruland S, Bruno JP, Sarter M (1997) Lack of effects of lesions of the dorsal noradrenergic bundle on behavioral vigilance. Behav Neurosci 111:646–652
National Research Council (2003) Guidelines for the care and use of mammals in Neuroscience and Behavioral Research. http://www.nap.edu/catalog/10732.html
Paxinos G, Watson C (1998) The rat brain in stereotaxic coordinates, 4th edn. Academic, San Diego
Pisa M, Fibiger HC (1983) Evidence against a role of the rat’s dorsal noradrenergic bundle in selective attention and place memory. Brain Res 272:319–329
Porter MC, Burk JA, Mair RG (2000) A comparison of the effects of hippocampal or prefrontal cortical lesions on three versions of delayed non-matching-to-sample based on positional or spatial cues. Behav Brain Res 109:69–81
Pudovkina OL, Kawahara Y, de Vries J, Westerink BH (2001) The release of noradrenaline in the locus coeruleus and prefrontal cortex studied with dual probe microdialysis. Brain Res 906:38–45
Rajkowski J, Majczynski H, Clayton E, Aston-Jones G (2004) Activation of monkey locus coeruleus neurons varies with difficulty and performance in a target detection task. J Neurophysiol 92:361–371
Rama P, Linnankoski I, Tanila H, Petovaara A, Carlson S (1996) Medetomidine, atipamezole, and guanfacine in delayed response performance of aged monkeys. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 54:1–7
Robbins TW (2002) The 5-choice serial reaction time task: behavioural pharmacology and functional neurochemistry. Psychopharmacology 163:362–380
Robbins TW, Everitt BJ (1995) Central norepinephrine neurons and behavior. In: Bloom FE, Kupfer DJ (eds) Psychopharmacology: the fourth generation of progress. Raven, New York
Tanila H, Rama P, Carlson S (1996) The effects of prefrontal intracortical microinjections of an alpha-2 agonist, alpha-2 antagonist and lidocaine on the delayed alternation performance of aged rats. Brain Res Bull 40:117–119
Woodward DJ, Moises HC, Waterhouse BD, Hoffer BJ, Freedman R (1979) Modulatory actions of norepinephrine in the central nervous system. Fed Proc 38:2109–2116
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mair, R.D., Zhang, Y., Bailey, K.R. et al. Effects of clonidine in the locus coeruleus on prefrontal- and hippocampal-dependent measures of attention and memory in the rat. Psychopharmacology 181, 280–288 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-005-2263-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-005-2263-x