Abstract
Rationale
In previous studies, we have demonstrated that mice of the inbred strain C57BL/6J (C57) are more susceptible to amphetamine-induced conditioned place preference (CPP) than DBA/2J (DBA) mice. Moreover, we also observed parallel strain differences for the locomotor-stimulant effects of the drug. However, other studies have reported either no difference or opposite strain differences for cocaine- and morphine-induced CPP as well as for the locomotor effects of these drugs, suggesting that amphetamine-related behavioral phenotypes might depend on a specific pharmacological action of the psychostimulant.
Objectives
This study was aimed at testing strain differences for cocaine- and morphine-related behavioral phenotypes in the same experimental protocol and conditions previously used for amphetamine.
Methods
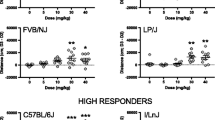
C57 and DBA mice were tested for CPP induced by cocaine (0, 5, 10, and 20 mg/kg) and morphine (0, 5, 7.5, and 10 mg/kg). Locomotor activity data were simultaneously obtained by measuring distance moved during all different CPP phases and unconditioned locomotor activity, behavioral sensitization and conditioned hyperactivity were measured together with CPP.
Results
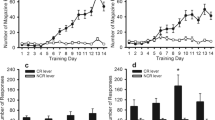
(a) Either cocaine or morphine promoted significant CPP at lower doses in C57 than in DBA mice; (b) only drug-trained C57 mice showed a significant CPP compared with the control group; and (c) only C57 mice showed dose-dependent effects of cocaine on CPP. Moreover, there was no relationship between drug-induced CPP and locomotion.
Conclusions
The results demonstrate that C57 and DBA mice differ in their sensitivity to cocaine- and morphine-induced CPP and suggest that the two strains differ in sensitivity to the positive incentive properties of drugs of abuse.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Badiani A, Cabib S, Puglisi-Allegra S (1992) Chronic stress induces strain-dependent sensitization to the behavioral effects of amphetamine in the mouse. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 43:53–60
Belknap JK, Crabbe JC, Young ER (1993) Voluntary consumption of ethanol in 15 inbred mouse strains. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 112:503–510
Brockwell NT, Ferguson DS, Beninger RJ (1996) A computerized system for the simultaneous monitoring of place conditioning and locomotor activity in rats. J Neurosci Methods 64:227–232
Cabib S, Bonaventura N (1997) Parallel strain-dependent susceptibility to environmentally-induced stereotypies and stress-induced behavioral sensitization in mice. Physiol Behav 61:499–506
Cabib S, Puglisi-Allegra S, Genua C, Simon H, Le Moal M, Piazza PV (1996) Dose-dependent aversive and rewarding effects of amphetamine as revealed by a new place conditioning apparatus. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 125:92–96
Cabib S, Orsini C, Le Moal M, Piazza PV (2000) Abolition and reversal of strain differences in behavioral responses to drugs of abuse after a brief experience. Science 289:463–465
Cardinal RN, Parkinson JA, Hall J, Everitt BJ (2002) Emotion and motivation: the role of the amygdala, ventral striatum, and prefrontal cortex. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 26:321–352
Carney JM, Landrum RW, Cheng MS, Seale TW (1991) Establishment of chronic intravenous drug self-administration in the C57BL/6J mouse. NeuroReport 2:477–480
Cunningham CL, Niehus DR, Malott DH, Prather LK (1992) Genetic differences in the rewarding and activating effects of morphine and ethanol. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 107:385–393
Cunningham CL, Dickinson SD, Grahame NJ, Okorn DM, McMullin CS (1999) Genetic differences in cocaine-induced conditioned place preference in mice depend on conditioning trial duration. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 146:73–80
Ettenberg A, Raven MA, Danluck DA, Necessary BD (1999) Evidence for opponent–process actions of intravenous cocaine. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 64:507–512
Grigson PS (1997) Conditioned taste aversions and drugs of abuse: a reinterpretation. Behav Neurosci 111:129–136
Hunt T, Amit Z (1987) Conditioned taste aversion induced by self-administered drugs: paradox revisited. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 11:107–130
Jones BC, Reed CL, Radcliffe RA, Erwin VG (1993) Pharmacogenetics of cocaine: I. Locomotor activity and self-selection. Pharmacogenetics 3:182–188
Kosten TA, Miserendino MJ (1998) Dissociation of novelty- and cocaine-conditioned locomotor activity from cocaine place conditioning. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 60:785–791
Lett BT (1988) Enhancement of conditioned preference for a place paired with amphetamine produced by blocking the association between place and amphetamine-induced sickness. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 95:390–394
Martin-Iverson MT, Reimer AR (1996) Classically conditioned motor effects do not occur with cocaine in an unbiased conditioned place preferences procedure. Behav Pharmacol 7:303–314
McBride WJ, Murphy JM, Ikemoto S (1999) Localization of brain reinforcement mechanisms: intracranial self-administration and intracranial place-conditioning studies. Behav Brain Res 101:129–152
Meliska CJ, Bartke A, McGlacken G, Jensen RA (1995) Ethanol, nicotine, amphetamine, and aspartame consumption and preferences in C57BL/6 and DBA/2 mice. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 50:619–626
Murphy NP, Lam HA, Maidment NT (2001) A comparison of morphine-induced locomotor activity and mesolimbic dopamine release in C57BL6, 129Sv and DBA2 mice. J Neurochem 79:626–635
O’Dell LE, Khroyan TV, Neisewander JL (1996) Dose-dependent characterization of the rewarding and stimulant properties of cocaine following intraperitoneal and intravenous administration in rats. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 123:144–153
Orsini C, Buchini F, Piazza PV, Puglisi-Allegra S, Cabib S (2004) Susceptibility to amphetamine-induced place preference is predicted by locomotor response to novelty and amphetamine in the mouse. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 172:264–270
Risinger FO, Boyce JM (2002) Conditioning tastant and the acquisition of conditioned taste avoidance to drugs of abuse in DBA/2J mice. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 160:225–232
Risinger FO, Oakes RA (1995) Nicotine-induced conditioned place preference and conditioned place aversion in mice. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 51:457–461
Robinson TE, Berridge KC (1993) The neural basis of drug craving: an incentive-sensitization theory of addiction. Brain Res Brain Res Rev 18:247–291
Seale TW, Carney JM (1991) Genetic determinants of susceptibility to the rewarding and other behavioral actions of cocaine. J Addict Dis 10:141–162
Semenova S, Kuzmin A, Zvartau E (1995) Strain differences in the analgesic and reinforcing action of morphine in mice. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 50:17–21
Shimosato K, Ohkuma S (2000) Simultaneous monitoring of conditioned place preference and locomotor sensitization following repeated administration of cocaine and methamphetamine. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 66:285–292
Tsuang M (2000) Schizophrenia: genes and environment. Biol Psychiatry 47:210–220
Tzschentke TM (1998) Measuring reward with the conditioned place preference paradigm: a comprehensive review of drug effects, recent progress and new issues. Prog Neurobiol 56:613–672
Vanyukov MM, Tarter RE (2000) Genetic studies of substance abuse. Drug Alcohol Depend 59:101–123
Ventura R, Alcaro A, Cabib S, Conversi D, Mandolesi L, Puglisi-Allegra S (2004) Dopamine in the medial prefrontal cortex controls genotype-dependent effects of amphetamine on mesoaccumbens dopamine release and locomotion. Neuropsychopharmacology 29:72–80
Wyvell CL, Berridge KC (2000) Intra-accumbens amphetamine increases the conditioned incentive salience of sucrose reward: enhancement of reward “wanting” without enhanced “liking” or response reinforcement. J Neurosci 20:8122–8130
Zocchi A, Orsini C, Cabib S, Puglisi-Allegra S (1998) Parallel strain-dependent effect of amphetamine on locomotor activity and dopamine release in the nucleus accumbens: an in vivo study in mice. Neuroscience 82:521–528
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by Ministero della Ricerca Scientifica e Tecnologica (COFIN 2003053445), Ateneo 60% (2003), and Facoltà (2000).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Orsini, C., Bonito-Oliva, A., Conversi, D. et al. Susceptibility to conditioned place preference induced by addictive drugs in mice of the C57BL/6 and DBA/2 inbred strains. Psychopharmacology 181, 327–336 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-005-2259-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-005-2259-6