Abstract
Rationale
In adult rats, the partial D2-like agonist terguride acts as an antagonist at normosensitive D2-like post-synaptic receptors, while it acts as an agonist at the same receptors during states of low dopaminergic tone.
Objective
The purpose of the present study was to determine whether partial D2-like agonists exhibit both antagonistic and agonistic actions during the preweanling period.
Methods
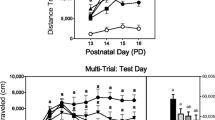
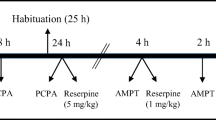
In experiments 1 and 2 (examining the agonistic actions of terguride), preweanling rats were either given an escalating regimen of amphetamine to induce a state of amphetamine withdrawal or pretreated with the tyrosine hydroxylase inhibitor AMPT. Distance traveled was measured after rats were injected with saline, terguride (0.4–1.6 mg/kg), or the full D2-like receptor agonist NPA (0.01 mg/kg). In experiment 3 (examining the antagonistic actions of terguride), preweanling rats were pretreated with terguride 30 min before they were tested with saline, NPA (0.05 mg/kg), or amphetamine (1.5 mg/kg).
Results
NPA had an exaggerated locomotor activating effect when tested under conditions of amphetamine withdrawal, while the partial D2-like agonist did not enhance distance traveled under any circumstance. Similarly, NPA increased and terguride did not affect the distance-traveled scores of AMPT-pretreated rats. In experiment 3, terguride pretreatment significantly reduced the distance traveled of amphetamine-treated and NPA-treated rats.
Conclusions
The behavioral evidence indicates that, during the preweanling period, terguride antagonizes D2-like post-synaptic receptors in a state of high dopaminergic tone; however, there is no evidence that terguride is capable of stimulating D2-like post-synaptic receptors during states of low dopaminergic tone.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arnt J (1983) Differential behavioural effects of dopamine agonists in developing rats: a study of 3-PPP enantiomers. Eur J Pharmacol 91:273–278
Arnt J, Hyttel J (1984) Postsynaptic dopamine agonistic effects of 3-PPP enantiomers revealed by bilateral 6-hydroxy-dopamine lesions and by chronic reserpine treatment in rats. J Neural Transm 60:205–223
Arnt J, Hyttel J (1990) Dopamine D-2 agonists with high and low efficacies: differentiation by behavioural techniques. J Neural Transm 80:33–50
Barr AM, Phillips AG (1999) Withdrawal following repeated exposure to d-amphetamine decreases responding for a sucrose solution as measured by a progressive ratio schedule of reinforcement. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 141:99–106
Burris KD, Molski TF, Xu C, Ryan E, Tottori K, Kikuchi T, Yocca FD, Molinoff PB (2002) Aripiprazole, a novel antipsychotic, is a high-affinity partial agonist at human dopamine D2 receptors. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 302:381–389
Callahan PM, Cunningham KA (1993) Discriminative stimulus properties of cocaine in relation to dopamine D2 receptor function in rats. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 266:585–592
Carlsson A (1983) Dopamine receptor agonists: intrinsic activity vs state of the receptor. J Neural Transm 57:309–315
Clark D, Hjorth S, Carlsson A (1985a) Dopamine-receptor agonists: mechanisms underlying autoreceptor selectivity. I. Review of the evidence. J Neural Transm 62:1–52
Clark D, Hjorth S, Carlsson A (1985b) Dopamine receptor agonists: mechanisms underlying autoreceptor selectivity. II. Theoretical considerations. J Neural Transm 62:171–207
Clark D, Furmidge LJ, Petry N, Tong Z-Y, Ericsson M, Johnson D (1991a) Behavioural profile of partial D2 dopamine receptor agonists. I. Atypical inhibition of d-amphetamine-induced locomotor hyperactivity and stereotypy. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 105:381–392
Clark D, Salah RS, Galloway MP (1991b) Differential agonist profile of the enantiomers of 3-PPP at striatal dopamine autoreceptors: dependence on extracellular dopamine. Synapse 8:169–176
Di Lullo SL, Martin-Iverson MT (1991) Presynaptic dopaminergic neurotransmission mediates amphetamine-induced unconditioned but not amphetamine-conditioned locomotion and defecation in the rat. Brain Res 568:45–54
Drukarch B, Stoof JC (1990) D-2 dopamine autoreceptor selective drugs: do they really exist? Life Sci 47:361–376
Duke MA, O’Neal J, McDougall SA (1997) Ontogeny of dopamine agonist-induced sensitization: role of NMDA receptors. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 129:153–160
Exner M, Furmidge LJ, White FJ, Clark D (1989) Inhibitory effects of partial D2 dopamine receptor agonists on the d-amphetamine discriminative cue. Behav Pharmacol 1:101–111
Finn IB, Iuvone PM, Holtzman SG (1990) Depletion of catecholamines in the brain of rats differentially affects stimulation of locomotor activity by caffeine, d-amphetamine, and methylphenidate. Neuropharmacology 29:625–631
Hoyer D, Boddeke HWGM (1993) Partial agonists, full agonists: dilemmas of definition. Trends Pharmacol Sci 14:270–275
Izzo E, Orsini C, Koob GF, Pulvirenti L (2001) A dopamine partial agonist and antagonist block amphetamine self-administration in a progressive ratio schedule. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 68:701–708
Jung AB, Bennett JP Jr (1996) Development of striatal dopaminergic function. I. Pre- and postnatal development of mRNAs and binding sites for striatal D1 (D1a) and D2 (D2a) receptors. Dev Brain Res 94:109–120
Kehr W (1984) Transdihydrolisuride, a partial dopamine receptor antagonist: effects on monoamine metabolism. Eur J Pharmacol 97:111–119
Kenakin TP (1997) Pharmacological analysis of drug-receptor interactions. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Philadelphia
Kohler WC, Herbster G (1987) Terguride, a mixed dopamine agonist-antagonist, in animal models of Parkinson’s disease. Neurology 37:723–727
Lal S, Sourkes TL (1973) Ontogeny of stereotyped behaviour induced by apomorphine and amphetamine in the rat. Arch Int Pharmacodyn 202:171–182
McDougall SA, Crawford CA, Nonneman AJ (1992) Effects of dopamine receptor inactivation on the locomotor activity and grooming of young and mature rats. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 106:502–510
McDougall SA, Crawford CA, Nonneman (1993) Behavioral effects of selective and nonselective dopamine agonists on young rats after irreversible antagonism of D1 and/or D2 receptors. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 111:225–232
McDougall SA, Garmsen GM, Meier TL, Crawford CA (1997) Kappa opioid mediated locomotor activity in the preweanling rat: role of pre and postsynaptic dopamine receptors. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 133:62–68
Meller E, Bohmaker K, Namba Y, Friedhoff AJ, Goldstein M (1987) Relationship between receptor occupancy and response at striatal autoreceptors. Mol Pharmacol 31:592–598
Meller E, Enz A, Goldstein M (1988) Absence of receptor reserve at striatal dopamine receptors regulating cholinergic neuronal activity. Eur J Pharmacol 155:151–154
Mestlin M, McDougall SA (1993) Ontogenetic differences in the effects of EEDQ on dopamine mediated behaviors. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 45:797–802
Moody CA, Spear LP (1992) Ontogenetic differences in the psychopharmacological responses to separate and combined stimulation of D1 and D2 dopamine receptors during the neonatal to weanling age period. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 106:161–168
Moody CA, Robinson SR, Spear LP, Smotherman WP (1993) Fetal behavior and the dopamine system: activity effects of D1 and D2 receptor manipulations. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 44:843–850
Murrin LC, Zeng W (1990) Ontogeny of dopamine D1 receptors in rat forebrain: a quantitative autoradiographic study. Dev Brain Res 57:7–13
Newman-Tancredi A, Cussac D, Audinot V, Nicolas JP, De Ceuninck F, Boutin J-A, Millan MJ (2002) Differential actions of antiparkinson agents at multiple classes of monoaminergic receptor. II. Agonist and antagonist properties at subtypes of dopamine D2-like receptor and α1/α2-adrenoceptor. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 303:805–814
Orsini C, Koob GF, Pulvirenti L (2001) Dopamine partial agonist reverses amphetamine withdrawal in rats. Neuropsychopharmacology 25:789–792
Pulvirenti L, Koob GF (1994) Dopamine receptor agonists, partial agonists and psychostimulant addiction. Trends Pharmacol Sci 15:374–379
Pulvirenti L, Balducci C, Piercy M, Koob GF (1998) Characterization of the effects of the partial dopamine agonist terguride on cocaine self-administration in the rat. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 286:1231–1238
Rao PA, Molinoff PB, Joyce JN (1991) Ontogeny of dopamine D1 and D2 receptor subtypes in rat basal ganglia: a quantitative autoradiographic study. Dev Brain Res 60:161–177
Ranaldi R, Wang Z, Woolverton WL (2001) Reinforcing effects of D2 dopamine receptor agonists and partial agonists in rhesus monkeys. Drug Alcohol Depend 64:209–217
Rossetti ZL, Hmaidan Y, Gessa GL (1992) Marked inhibition of mesolimbic dopamine release: a common feature of ethanol, morphine, cocaine and amphetamine abstinence in rats. Eur J Pharmacol 221:227–234
Schambra UB, Duncan GE, Breese GR, Fornaretto MG, Caron MG, Fremeau RT Jr (1994) Ontogeny of D1A and D2 dopamine receptor subtypes in rat brain using in situ hybridization and receptor binding. Neuroscience 62:65–85
Segal DS, Kuczenski R (1997) An escalating dose “binge” model of amphetamine psychosis: behavioral and neurochemical characteristics. J Neurosci 17:2551–2566
Sibole JM, Matea PJ, Krall CM, McDougall SA (2003) Effects of a partial dopamine D2-like agonist on the cocaine-induced behavioral sensitization of preweanling rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 76:27–34
Sobrian SK, Weltman M, Pappas BA (1975) Neonatal locomotor and long-term behavioral effects of d-amphetamine in the rat. Dev Psychobiol 8:241–250
Spealman RD (1995) Discriminative stimulus effects of cocaine in squirrel monkeys: lack of antagonism by the dopamine D2 partial agonists terguride, SDZ 208-911, and SDZ 208-912. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 51:661–665
Spear LP (1979) The use of psychopharmacological procedures to analyse the ontogeny of learning and retention: issues and concerns. In: Spear NE, Campbell BA (eds) Ontogeny of learning and memory. Lawrence Erlbaum Associates, Hillsdale, pp 135–156
Svensson K, Ekman A, Piercey MF, Hoffmann WE, Lum JT, Carlsson A (1991) Effects of the partial dopamine receptor agonists SDZ 208-911, SDZ 208-912 and terguride on central monoamine receptors. A behavioral, biochemical and electrophysiological study. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol 344:263–274
Tirelli E, Laviola G, Adriani W (2003) Ontogenesis of behavioral sensitization and conditioned place reference induced by psychostimulants in laboratory rodents. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 27:163–178
Wachtel H, Dorow R (1983) Dual action on central dopamine function of transdihydrolisuride, a 9,10-dihydrogenated analogue of the ergot dopamine agonist lisuride. Life Sci 32:421–432
Yokoo H, Goldstein M, Meller E (1988) Receptor reserve at striatal dopamine receptors modulating the release of [3H]dopamine. Eur J Pharmacol 155:323–327
Zorrilla EP (1997) Multiparous species present problems (and possibilities) to developmentalists. Dev Psychobiol 30:141–150
Acknowledgements
We thank Dr. Cynthia Crawford for her expertise with the dopamine content assays. This work was partially supported by an ASI research grant (CSUSB) to R.M.H.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
McDougall, S.A., Hernandez, R.M., Reichel, C.M. et al. The partial D2-like dopamine receptor agonist terguride acts as a functional antagonist in states of high and low dopaminergic tone: evidence from preweanling rats. Psychopharmacology 178, 431–439 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-004-2033-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-004-2033-1