Abstract
Rationale
The possible role of compensatory changes in 5-HT2C receptors in the reduced hypophagic action of d-fenfluramine in 5-HT1B knockout (KO) mice was assessed by comparing their response to d-fenfluramine and the 5-HT2C receptor agonist mCPP. In addition we measured 5-HT2C/A receptor binding in 5-HT1B KO and wild-type (WT) mice and examined the effects of 5-HT1B receptor antagonists on d-fenfluramine-induced hypophagia in WT mice.
Methods
Hypophagic responses to d-fenfluramine (1–30 mg/kg) and mCPP (1–5.6 mg/kg) were measured using a behavioural satiety sequence paradigm. The effects of the 5-HT1B receptor antagonists GR 127,935 and SB 224289 in opposing the hypophagic action of d-fenfluramine were evaluated in WT mice. The binding of [3H]-mesulergine was compared in the brains of both mouse strains.
Results
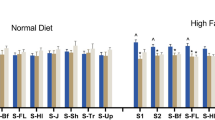
The hypophagic effects of moderate doses of d-fenfluramine and mCPP were attenuated in 5-HT1B KO mice. Pretreatment of WT mice with the 5-HT1B/1D receptor antagonist GR 127,935, or food-deprived WT mice with the 5-HT1B receptor antagonist SB 224289, did not reproduce the reduction in sensitivity to the effects of d-fenfluramine on feeding behaviour observed in 5-HT1B KO mice. Estimates of 5-HT2C receptor binding were similar in 5-HT1B KO and WT mice.
Conclusions
The hypophagic effect of d-fenfluramine in mice is unlikely to be mediated by the 5-HT1B receptor. Instead, the evidence suggests that an adaptive change in 5-HT2C receptor function occurs in 5-HT1B receptor KO mice and contributes to their reduced response to d-fenfluramine.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ase AR, Reader TA, Hen R, Riad M, Descarries L (2001) Regional changes in density of serotonin transporter in the brain of 5-HT1A and 5-HT1B knockout mice, and of serotonin innervation in the 5-HT1B knockout. J Neurochem 78:619–630
Barnes NM, Sharp T (1999) A review of central 5-HT receptors and their function. Neuropharmacology 38:1083–1152
Burns CM, Chu H, Rueter SM, Hutchinson LK, Canton H, Sanders-Bush E, Emeson RB (1997) Regulation of serotonin-2C receptor G-protein coupling by RNA editing. Nature 387:303–308
Caccia S, Ballabio M, Guiso G, Rocchetti M, Garattini S (1982) Species differences in the kinetics and metabolism of fenfluramine isomers. Arch Int Pharmacodyn Ther 258:15–28
Castanon N, Scearce-Levie K, Lucas JJ, Rocha B, Hen R (2000) Modulation of the effects of cocaine by 5-HT1B receptors: a comparison of knockouts and antagonists. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 67:559–566
Clifton PG, Barnfield AM, Philcox L (1989) A behavioural profile of fluoxetine-induced anorexia. Psychopharmacology 97:89–95
Clifton PG, Barnfield AM, Curzon G (1993) Effects of food deprivation and mCPP treatment on the microstructure of ingestive behaviour of male and female rats. J Psychopharmacol 7:257–264
Clifton PG, Lee MD, Dourish CT (2000) Similarities in the action of Ro 60-0175, a 5-HT2C receptor agonist and d-fenfluramine on feeding patterns in the rat. Psychopharmacology 152:256–267
Clifton PG, Lee MD, Somerville EM, Kennett GA, Dourish CT (2003) 5-HT1B receptor knockout mice show a compensatory reduction in 5-HT2C receptor function. Eur J Neurosci 17:185–190
Connolly HM, Crary JL, McGoon MD, Hensrud DD, Edwards BS, Edwards WD, Schaff HV (1997) Valvular heart disease associated with fenfluramine-phentermine. N Engl J Med 337:581–588
Franklin KBJ, Paxinos G (1997) The mouse brain in stereotaxic coordinates. Academic Press, London
Genstat (1987) Genstat 5 reference manual. Clarendon Press, Oxford
Gibson EL, Kennedy AJ, Curzon G (1993) d-Fenfluramine- and d-norfenfluramine-induced hypophagia: differential mechanisms and involvement of postsynaptic 5-HT receptors. Eur J Pharmacol 242:83–90
Gurevich I, Englander MT, Adlersberg M, Siegal NB, Schmauss C (2002) Modulation of serotonin 2C receptor editing by sustained changes in serotonergic neurotransmission. J Neurosci 22:10529–10532
Herrick-Davis K, Grinde E, Niswender CM (1999) Serotonin 5-HT2C receptor RNA editing alters receptor basal activity: implications for serotonergic signal transduction. J Neurochem 73:1711–1717
Hewitt KN, Lee MD, Dourish CT, Clifton PG (2002) Serotonin 2C receptor agonists and the behavioural satiety sequence in mice. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 71:691–700
Howell DC (1995) Fundamental statistics for the behavioral sciences. Duxbury, North Scituate, Mass.
Lee MD, Kennett GA, Dourish CT, Clifton PG (2003) Tonic regulation of satiety by 5-HT1B receptors in the mouse: converging evidence from antagonist studies and CP-94,253-induced c-fos immunoreactivity. Appetite 40:334
Lopez-Gimenez JF, Tecott LH, Palacios JM, Mengod G, Vilaro MT (2002) Serotonin 5-HT (2C) receptor knockout mice: autoradiographic analysis of multiple serotonin receptors. J Neurosci Res 67:69–85
Lucas JJ, Yamamoto A, Scearce-Levie K, Saudou F, Hen R (1998) Absence of fenfluramine-induced anorexia and reduced c-Fos induction in the hypothalamus and central amygdaloid complex of serotonin 1B receptor knock-out mice. J Neurosci 18:5537–5544
MacLean MR (1999) Pulmonary hypertension, anorexigens and 5-HT: pharmacological synergism in action? Trends Pharmacol Sci 20:490–495
Marchant NC, Breen MA, Wallace D, Bass S, Taylor AR, Ings RM, Campbell DB, Williams J (1992) Comparative biodisposition and metabolism of 14C-(±)-fenfluramine in mouse, rat, dog and man. Xenobiotica 22:1251–1266
McCann UD, Yuan J, Hatzidimitriou G, Ricaurte GA (1997) Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors dissociate fenfluramine’s anorectic and neurotoxic effects: importance of dose, species and drug. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 281:1487–1498
Mennini T, Bizzi A, Caccia S, Codegoni A, Fracasso C, Frittoli E, Guiso G, Padura IM, Taddei C, Uslenghi A et al (1991) Comparative studies on the anorectic activity of d-fenfluramine in mice, rats, and guinea pigs. Naunyn Schmiedeberg’s Arch Pharmacol 343:483–490
Oluyomi AO, Gibson EL, Barnfield AM, Curzon G (1994) d-Fenfluramine and d-norfenfluramine hypophagias do not require increased hypothalamic 5-hydroxytryptamine release. Eur J Pharmacol 264:111–115
Pazos A, Palacios JM (1985) Quantitative autoradiographic mapping of serotonin receptors in the rat brain. I. Serotonin-1 receptors. Brain Res 346:205–230
Pedrinola F, Sztejnsznajd C, Lima N, Halpern A, Medeiros-Neto G (1996) The addition of dexfenfluramine to fluoxetine in the treatment of obesity: a randomized clinical trial. Obes Res 4:549–554
Porter RH, Benwell KR, Lamb H, Malcolm CS, Allen NH, Revell DF, Adams DR, Sheardown MJ (1999) Functional characterization of agonists at recombinant human 5-HT2A, 5-HT2B and 5-HT2C receptors in CHO-K1 cells. Br J Pharmacol 128:13–20
Quirk K, Lawrence A, Jones J, Misra A, Harvey V, Lamb H, Revell D, Porter RH, Knight AR (2001) Characterisation of agonist binding on human 5-HT2C receptor isoforms. Eur J Pharmacol 419:107–112
Rothman RB, Baumann MH (2002) Serotonin releasing agents. Neurochemical, therapeutic and adverse effects. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 71:825–836
Rowland NE, Carlton J (1986) Neurobiology of an anorectic drug: fenfluramine. Prog Neurobiol 27:13–62
Rowland NE, Lo J, Robertson K (2001) Acute anorectic effect of single and combined drugs in mice using a non-deprivation protocol. Psychopharmacology 157:193–196
Saudou F, Amara DA, Dierich A, LeMeur M, Ramboz S, Segu L, Buhot MC, Hen R (1994) Enhanced aggressive behavior in mice lacking 5-HT1Breceptor. Science 265:1875–1878
Stunkard A, Berkowitz R, Tanrikut C, Reiss E, Young L (1996) d-Fenfluramine treatment of binge eating disorder. Am J Psychiatry 153:1455–1459
Trillat AC, Malagie I, Scearce K, Pons D, Anmella MC, Jacquot C, Hen R, Gardier AM (1997) Regulation of serotonin release in the frontal cortex and ventral hippocampus of homozygous mice lacking 5-HT1B receptors: in vivo microdialysis studies. J Neurochem 69:2019–2025
Vickers SP, Clifton PG, Dourish CT, Tecott LH (1999) Reduced satiating effect of d-fenfluramine in serotonin 5-HT(2C) receptor mutant mice. Psychopharmacology 143:309–314
Vickers SP, Dourish CT, Kennett GA (2001a) Evidence that hypophagia induced by d-fenfluramine and d-norfenfluramine in the rat is mediated by 5-HT2C receptors. Neuropharmacology 41:200–209
Vickers SP, Easton N, Malcolm CS, Allen NH, Porter RH, Bickerdike MJ, Kennett GA (2001b) Modulation of 5-HT(2A) receptor-mediated head-twitch behaviour in the rat by 5-HT(2C) receptor agonists. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 69:643–652
Acknowledgements
M.D.L. was supported by BBSRC (UK) LINK project grant 85/LKD12007. We are very grateful to Professor Rene Hen for providing our initial breeding stocks of 5-HT1B KO and WT mice.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, M.D., Somerville, E.M., Kennett, G.A. et al. Reduced hypophagic effects of d-fenfluramine and the 5-HT2C receptor agonist mCPP in 5-HT1B receptor knockout mice. Psychopharmacology 176, 39–49 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-004-1864-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-004-1864-0