Abstract
Rationale
Although positive modulators of γ-aminobutyric acidA (GABAA) receptors generally produce similar behavioral effects, regardless of which modulatory site on the GABAA receptor complex mediates these effects, some differences have been observed between the effects of neuroactive steroids and those of other positive GABAA modulators.
Objective
The current study was designed to compare the behavioral effects of a neuroactive steroid to those of other positive GABAA modulators.
Methods
Rats responded under a multiple schedule of repeated acquisition and performance of response chains, with responding maintained under a second-order fixed-ratio 2 schedule of food presentation.
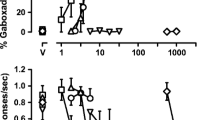
Results
Pregnanolone, flunitrazepam, pentobarbital and ketamine, an antagonist at NMDA receptors, dose-dependently decreased response rates and increased the percentage of errors in both components of the multiple schedule. Although the rate-decreasing and error-increasing effects of pregnanolone, pentobarbital and ketamine were quantitatively similar to each other, flunitrazepam was less effective in decreasing response rates and more effective in increasing errors than the other three drugs. A dose of 3.2 mg/kg pregnanolone potentiated the effects of flunitrazepam and pentobarbital, producing 2- to 3-fold shifts to the left in the dose-effect curves. In contrast, pregnanolone did not alter the ketamine dose-effect curves.
Conclusions
The disruptive effects of the neuroactive steroid pregnanolone are qualitatively similar to those of other positive GABAA modulators as well as ketamine; however, the potentiation of the effects of flunitrazepam and pentobarbital, and not ketamine, emphasizes the importance of GABAA receptors in the behavioral effects of pregnanolone.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arolfo MP, Brioni JD (1991) Diazepam impairs place learning in the Morris water maze. Behav Neural Biol 55:131–136
Baron SP, Moerschbaecher JM (1996) Disruption of learning by excitatory amino acid receptor antagonists. Behav Pharmacol 7:573–584
Baron SP, Wright D, Wenger GR (1998) Effects of drugs of abuse and scopolamine on memory in rats: delayed spatial alternation and matching to position. Psychopharmacology 137:7–14
Beekman M, Ungard JT, Gasior M, Carter RB, Dijkstra D, Goldberg SR, Witkin JM (1998) Reversal of behavioral effects of pentylenetetrazol by the neuroactive steroid ganaxolone. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 284:868–877
Bickel WK, Hughes JR, Higgins ST (1990) Human behavioral pharmacology of benzodiazepines: effects of repeated acquisition and performance of response chains. Drug Dev Res 20:53–65
Bickel WK, Higgins ST, Hughes JR (1991) The effects of diazepam and triazolam on repeated acquisition and performance of response sequences with an observing response. J Exp Anal Behav 56:217–237
Cottrell GA, Lambert JJ, Peters JA (1987) Modulation of GABAA receptor activity by alphaxalone. Br J Pharmacol 90:491–500
Desjardins PJ, Moerschbaecher JM, Thompson DM, Thomas JR (1982) Intravenous diazepam in humans: effects on acquisition and performance of response chains. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 17:1055–1059
Edgar DM, Seidel WF, Gee KW, Lan NC, Field G, Xia H, Hawkinson JE, Wieland S, Carter RB, Wood PL (1997) CCD-3693: an orally bioavailable analog of the endogenous neuroactive steroid, pregnanolone, demonstrates potent sedative hypnotic actions in the rat. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 282:420–429
Frye CA, Sturgis JD (1995) Neurosteroids affect spatial/reference, working, and long-term memory of female rats. Neurobiol Learn Mem 64:83–96
Gasior M, Carter RB, Witkin JM (1999) Neuroactive steroids: potential therapeutic use in neurological and psychiatric disorders. Trends Pharmacol Sci 20:107–112
Hardman JG, Limbird LE, Gilman AG (eds) (2001) Goodman & Gilman’s the pharmacological basis of therapeutics, 10th edn. McGraw-Hill, New York, Chicago, San Francisco, Lisbon, London, Madrid, Mexico City, Milan, New Delhi, San Juan, Seoul, Singapore, Sydney, Toronto
Hattori K, Oomura Y, Akaike N (1986) Diazepam action on gamma-aminobutyric acid-activated chloride currents in internally perfused frog sensory neurons. Cell Mol Neurobiol 6:307–323
Johansson IM, Birzniece V, Lindblad C, Olsson T, Backstrom T (2002) Allopregnanolone inhibits learning in the Morris water maze. Brain Res 934:125–131
Kokate TG, Svensson BE, Rogawski MA (1994) Anticonvulsant activity of neurosteroids: correlation with gamma-aminobutyric acid-evoked chloride current potentiation. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 270:1223–1229
Kokate TG, Yamaguchi S, Pannell LK, Rajamani U, Carroll DM, Grossman AB, Rogawski MA (1998) Lack of anticonvulsant tolerance to the neuroactive steroid pregnanolone in mice. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 287:553–558
Ladurelle N, Eychenne B, Denton D, Blair-West J, Schumacher M, Robel P, Baulieu E (2000) Prolonged intracerebroventricular infusion of neurosteroids affects cognitive performances in the mouse. Brain Res 858:371–379
Lambert JJ, Belelli D, Hill-Venning C, Peters JA (1995) Neurosteroids and GABAA receptor function. Trends Pharmacol Sci 16:295–303
Lambert JJ, Belelli D, Harney SC, Peters JA, Frenguelli BG (2001) Modulation of native and recombinant GABA(A) receptors by endogenous and synthetic neuroactive steroids. Brain Res Rev 37:68–80
Mayo W, Dellu F, Robel P, Cherkaoui J, Le Moal M, Baulieu EE, Simon H (1993) Infusion of neurosteroids into the nucleus basalis magnocellularis affects cognitive processes in the rat. Brain Res 607:324–328
McMahon LR, France CP (2002) Acute and chronic effects of the neuroactive steroid pregnanolone on schedule-controlled responding in rhesus monkeys. Behav Pharmacol 13:545–555
McNamara RK, Skelton RW (1993) Effects of intracranial infusions of chlordiazepoxide on spatial learning in the Morris water maze. II. Neuropharmacological specificity. Behav Brain Res 59:193–204
McNamara RK, Skelton RW (1997) Tolerance develops to the spatial learning deficit produced by diazepam in rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 56:383–389
Mehta AK, Ticku MK (1999) An update on GABAA receptors. Brain Res Rev 29:196–217
Mennerick S, Zeng CM, Benz A, Shen W, Izumi Y, Evers AS, Covey DF, Zorumski CF (2001) Effects on gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA)(A) receptors of a neuroactive steroid that negatively modulates glutamate neurotransmission and augments GABA neurotransmission. Mol Pharmacol 60:732–741
Paul SM, Purdy RH (1992) Neuroactive steroids. FASEB J 6:2311–2322
Reddy DS, Rogawski MA (2000) Chronic treatment with the neuroactive steroid ganaxolone in the rat induces anticonvulsant tolerance to diazepam but not to itself. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 295:1241–1248
Simmonds MA (1981) Distinction between the effects of barbiturates, benzodiazepines and phenytoin on responses to gamma-aminobutyric acid receptor activation and antagonism by bicuculline and picrotoxin. Br J Pharmacol 73:739–747
Thompson DM (1973) Repeated acquisition as a behavioral base line for studying drug effects. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 184:506–514
Thompson DM, Winsauer PJ, Mastropaolo J (1987) Effects of phencyclidine, ketamine and MDMA on complex operant behavior in monkeys. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 26:401–405
Winsauer PJ, Bixler MA, Mele PC (1995) Differential effects of ionizing radiation on the acquisition and performance of response sequences in rats. Neurotoxicology 16:257–269
Winsauer PJ, Bixler MA, Mele PC (1996) Comparison of the effects of typical and atypical anxiolytics on learning in monkeys and rats. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 276:1111–1127
Winsauer PJ, Rodriguez FH, Cha AE, Moerschbaecher JM (1999) Full and partial 5-HT1A receptor agonists disrupt learning and performance in rats. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 288:335–347
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This study was supported by USPHS Grant DA04775, and submitted as a partial fulfillment of the degree requirements for a PhD in Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics (M.W.S.). Animals used in these studies were maintained in accordance with the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee, Louisiana State University Health Sciences Center, and guidelines of the Committee on Care and Use of Laboratory Animal Resources, National Research Council [Department of Health, Education and Welfare, publication No. (NIH) 85-23, revised 1996].
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gerak, L.R., Stevenson, M.W., Winsauer, P.J. et al. Effects of pregnanolone alone and in combination with other positive GABAA modulators on complex behavior in rats. Psychopharmacology 173, 195–202 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-003-1717-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-003-1717-2