Abstract
Rationale
Previous studies have strongly implicated a role for GABAB receptors in modulating the reinforcing effects of cocaine.
Objective
The purpose of the present study was to examine the efficacy of two novel positive allosteric modulators of the GABAB receptor, CGP7930 and GS39783, to decrease cocaine self-administration in rats responding under various schedules of reinforcement.
Methods
Rats were trained to self-administer cocaine under progressive ratio (PR), fixed ratio (FR) and discrete trials (DT) schedules of reinforcement, and the ability of CGP7930 and GS39783 to decrease cocaine-maintained responding was examined.
Results
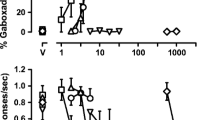
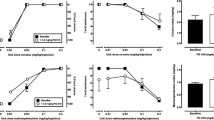
On a PR schedule, CGP7930 markedly decreased break points maintained by 1.5 mg/kg per injection cocaine in a dose-dependent manner. GS39783 produced only modest decreases in cocaine-reinforced break points, with only the highest dose decreasing break points relative to baseline. On an FR1 schedule of reinforcement, both drugs decreased responding for a threshold dose of cocaine, but did not alter responding for higher doses of cocaine. In a DT procedure, 1.5 mg/kg per injection cocaine was made available during three 10-min trials each hour during 24-h sessions (DT3), engendering a circadian pattern of responding characterized by high numbers of infusions during the dark phase and low numbers of infusions during the light phase. Doses of 30 mg/kg CGP7930, 3.0 mg/kg GS39783 and 2.5 mg/kg baclofen significantly decreased cocaine-maintained responding when administered at the beginning of the dark phase of the cycle. Across all schedules, CGP7930 was more effective at decreasing cocaine self-administration than GS39783, a finding that may be due to differences in bioavailability between the two drugs.
Conclusions
These findings suggest that positive allosteric modulators of the GABAB receptor may hold promise as potential pharmacotherapies for cocaine abuse and dependence.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arnold JM, Roberts DCS (1997) A critique of fixed and progressive ratio schedules used to examine the neural substrates of drug reinforcement. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 57:441–447
Ashby CR Jr, Rohatgi R, Ngosuwan J, Borda T, Gerasimov MR, Morgan AE, Kushner S, Brodie JD, Dewey SL (1999) Implication of the GABA(B) receptor in gamma vinyl-GABA’s inhibition of cocaine-induced increases in nucleus accumbens dopamine. Synapse 31:151–153
Bischoff S, Leonhard S, Reymann N, Schuler V, Shigemoto R, Kaupmann K, Bettler B (1999) Spatial distribution of GABA(B)R1 receptor mRNA and binding sites in the rat brain. J Comp Neurol 412:1–16
Brebner K, Froestl, W, Andrews M, Phelan R, Roberts DCS (1999) The GABAB agonist CGP 44532 decreases cocaine self-administration in rats: demonstration using a progressive ratio and a discrete trials procedure. Neuropharmacology 38:1797–1804
Brebner K, Phelan R, Roberts DCS (2000a) Effect of baclofen on cocaine self-administration in rats reinforced under fixed-ratio and progressive-ratio schedules. Psychopharmacology 148:314–321
Brebner K, Phelan R, Roberts DCS (2000b) Intra-VTA baclofen attenuates cocaine self-administration on a progressive ratio schedule of reinforcement. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 66:857–862
Brebner K, Froestl W, Roberts DCS (2002) The GABAB antagonists CGP56433A attenuates the effect of baclofen on cocaine, but not heroin self-administration. Psychopharmacology 160:49–55
Caine SB, Koob GF (1994) Effects of dopamine D-1 and D-2 antagonists on cocaine self-administration under different schedules of reinforcement in the rat. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 270:209–218
Campbell UC, Lac ST, Carroll ME (1999) Effects of baclofen on maintenance and reinstatement of intravenous cocaine self-administration in rats. Psychopharmacology 143:209–214
Fitch T, Roberts DCS (1993) The effects of dose and access restrictions on the periodicity of cocaine self-administration in the rat. Drug Alcohol Depend 33:119–128
Gudeman D, Shoptaw S, Majewska D, Scherf S, Yeats D, Ling W (1996) Preliminary report of baclofen as a cocaine craving medication. NIDA Res Monogr 174:183
Hubner CB, Moreton JE (1991) Effects of selective D1 and D2 dopamine antagonists on cocaine self-administration in the rat. Psychopharmacology 105:151–156
Institute of Laboratory Animal Resources (1996) Guide for the care and use of laboratory animals. National Academy Press, Washington D.C.
Ling W, Shoptaw S, Majewska D (1998) Baclofen as a cocaine anti-craving medication: a preliminary clinical study. Neuropsychopharmacology 18:403–404
Margeta-Mitrovic M, Mitrovic I, Riley RC, Jan LY, Basbaum AI (1999) Immunohistochemical localization of GABA(B) receptors in the rat central nervous system. J Comp Neurol 405:299–321
Richardson NR, Roberts DCS (1996) Progressive ratio schedules in drug self-administration studies in rats: a method to evaluate reinforcing efficacy. J Neurosci Methods 66:1–11
Roberts DCS, Andrews MM (1997) Baclofen suppression of cocaine self-administration: demonstration using a discrete trials procedure. Psychopharmacology 131:271–277
Roberts DCS, Goeders N (1989) Drug self-administration: experimental methods and determinants. In: Boulton AA, Baker GB, Greenshaw AJ (eds) Neuromethods: psychopharmacology (vol 13). Humana Press, Clifton, N.J., pp 349–398
Roberts DCS, Andrews MM, Vickers GJ (1996) Baclofen attenuates the reinforcing effects of cocaine in rats. Neuropsychopharmacology 15:417–423
Roberts DCS, Brebner K, Vincler M, Lynch WJ (2002) Patterns of cocaine self-administration in rats produced by various access conditions under a discrete trials procedure. Drug Alcohol Depend 67:291–299
Shoaib M, Swanner LS, Beyer CE, Goldberg SR, Schindler CW (1998) The GABAB agonist baclofen modifies cocaine self-administration in rats. Behav Pharmacol 9:195–206
Stafford D, LeSage MG, Glowa JR (1998) Progressive-ratio schedules of drug delivery in the analysis of drug self-administration: a review. Psychopharmacology 139:169–184
Urwyler S, Mosbacher J, Lingenhoehl K, Heid J, Hofstetter K, Froestl W, Bettler B, Kaupmann K (2001) Positive allosteric modulation of native and recombinant gamma-aminobutyric acid(B) receptors by 2,6-di-tert-butyl-4-(3-hydroxy-2,2-dimethyl-propyl)-phenol (CGP7930) and its aldehyde analog CGP13501. Mol Pharmacol 60:963–971
Urwyler S, Pozza MF, Lingenhoehl K, Mosbacher J, Lampert C, Froestl W, Koller M, Kaupmann K (2003) GS39783 (N,N’-dicyclopentyl-2-methylsulfanyl-5-nitro-pyrimidine-4,6-diamine) and structurally related compounds: novel allosteric enhancers of {gamma}-aminobutyric acidb receptor function. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 307:322–330
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by US public service grants RO1DA12925 and P50DA06643 from the National Institutes of Health.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Smith, M.A., Yancey, D.L., Morgan, D. et al. Effects of positive allosteric modulators of the GABAB receptor on cocaine self-administration in rats. Psychopharmacology 173, 105–111 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-003-1706-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-003-1706-5