Abstract
Rationale
Enhancement of dopamine (DA) release by corticosteroids may be of aetiological importance in substance misuse.
Objectives
To examine the effect of sub-chronic administration of hydrocortisone on the response to amphetamine in healthy male volunteers.
Methods
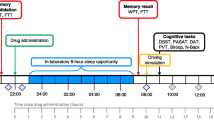
Following baseline assessment, 20 volunteers were pretreated for 7 days with 20 mg of hydrocortisone or placebo at 0800 hours and 2000 hours in a double-blind, random order, cross-over design prior to receiving 0.15 mg/kg metamphetamine intravenously. Blood samples for cortisol and prolactin were taken every 15 min. Subjects also underwent tests of neuropsychological function including sustained attention using the rapid visual information processing test (RVIP), which has been shown to be sensitive to changes in DA function.
Results
Metamphetamine produced a substantial reduction in prolactin levels, and increased subjective mood ratings of "mind-race" and "buzz". Sub-chronic hydrocortisone administration had no effect on these neuroendocrine responses, subjective mood changes or neurocognitive performance on a task of sustained attention (RVIP).
Conclusions
Despite measurable changes in neuroendocrine and affective functioning in response to metamphetamine, pretreatment with hydrocortisone did not significantly affect any of the variables measured. This suggests that this model of DA function is not affected by this regimen of corticosteroid administration.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Battaglia G, Napier TC (1998) The effects of cocaine and the amphetamines on brain and behavior: a conference report. Drug Alcohol Depend 52:41–48
Beck AT, Ward CH, Mendelson M, Mock J, Erbaugh J (1961) An inventory for measuring depression. Arch Gen Psychiatry 4:561–571
Bond A, Lader M (1974) The use of analogue scales in rating subjective feelings. Br J Med Psychol 47:211–218
Cervantes P, Gelber S, Kin F, Nair VNP, Schwartz G (2001) Circadian secretion of cortisol in bipolar disorder. J Psychiatry Neurosci 26:411–416
Creese I (1985) Dopamine and antipsychotic medications. In: Hales RE, Frances AJ (eds) Psychiatry update. American Psychiatric Press, Washington D.C., pp 17–36
de Kloet ER, Joels M, Oitzl M, Sutanto W (1991) Implication of brain corticosteroid receptor diversity for the adaptation syndrome concept. Meth Achiev Exp Pathol 14:104–132
Deuschle M, Schweiger U, Weber B, Gotthardt U, Korner A, Schmider J, Standhardt H, Lammers CH, Heuser I (1997) Diurnal activity and pulsatility of the hypothalamus-pituitary-adrenal system in male depressed patients and healthy controls. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 82:234–238
Dixon RB, Christy NP (1980) On the various forms of corticosteroid withdrawal syndrome. Am J Med 68:224–230
Elliott R, Sahakian BJ, Matthews K, Bannerjea A, Rimmer J, Robbins TW (1997) Effects of methylphenidate on spatial working memory and planning in healthy young adults. Psychopharmacology 131:196–206
Erb S, Shaham Y, Stewart J (1998) The role of corticotropin-releasing factor and corticosterone in stress- and cocaine-induced relapse to cocaine seeking in rats. J Neurosci 18:5529–5536
Goeders NE (2002) Stress and cocaine addiction. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 301:785–789
Grasby PM (2002) Imaging the neurochemical brain in health and disease. Clin Med 2:67–73
Harmer CJ, McTavish SF, Clark L, Goodwin GM, Cowen PJ (2001) Tyrosine depletion attenuates dopamine function in healthy volunteers. Psychopharmacology 154:105–111
Ikemoto S, Panksepp J (1999) The role of nucleus accumbens dopamine in motivated behavior: a unifying interpretation with special reference to reward-seeking. Brain Res Brain Res Rev 31:6–41
King AC, Schluger J, Gunduz M, Borg L, Perret G, Ho A, Kreek MJ (2002) Hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenocortical (HPA) axis response and biotransformation of oral naltrexone: preliminary examination of relationship to family history of alcoholism. Neuropsychopharmacology 26:778–788
Koob GF, Le Moal M (2001) Drug addiction, dysregulation of reward, and allostasis. Neuropsychopharmacology 24:97–129
Koob GF, Caine B, Markou A, Pulvirenti L, Weiss F (1994) Role for the mesocortical dopamine system in the motivating effects of cocaine. NIDA Res Monogr 145:1–18
Kreek MJ, Koob GF (1998) Drug dependence: stress and dysregulation of brain reward pathways. Drug Alcohol Depend 51:23–47
Leitch MM, Ingram CD, Young AH, McQuade R, Gartside SE (2003) Flattening the corticosterone rhythm attenuates 5-HT(1A) autoreceptor function in the rat: relevance for depression. Neuropsychopharmacology 28:119–125
Lieberman HR, Wurtman RJ, Emde GG, Roberts C, Coviella IL (1987) The effects of low doses of caffeine on human performance and mood. Psychopharmacology 92:308–312
Ling MH, Perry PJ, Tsuang MT (1981) Side effects of corticosteroid therapy. Psychiatric aspects. Arch Gen Psychiatry 38:471–477
Marinelli M, Piazza PV (2002) Interaction between glucocorticoid hormones, stress and psychostimulant drugs. Eur J Neurosci 16:387–394
Matthews JN, Altman DG, Campbell MJ, Royston P (1990) Analysis of serial measurements in medical research. BMJ 300:230–235
McTavish SF, McPherson MH, Harmer CJ, Clark L, Sharp T, Goodwin GM, Cowen PJ (2001) Antidopaminergic effects of dietary tyrosine depletion in healthy subjects and patients with manic illness. Br J Psychiatry 179:356–360
Miczek KA, Mutschler NH (1996) Activational effects of social stress on IV cocaine self-administration in rats. Psychopharmacology 128:256–264
Pani L, Porcella A, Gessa GL (2000) The role of stress in the pathophysiology of the dopaminergic system. Mol Psychiatry 5:14–21
Piazza PV, Le Moal ML (1996) Pathophysiological basis of vulnerability to drug abuse: role of an interaction between stress, glucocorticoids, and dopaminergic neurons. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 36:359–378
Piazza PV, Le Moal M (1997) Glucocorticoids as a biological substrate of reward: physiological and pathophysiological implications. Brain Res Brain Res Rev 25:359–372
Piazza PV, Deroche V, Deminiere JM, Maccari S, Le Moal M, Simon H (1993) Corticosterone in the range of stress-induced levels possesses reinforcing properties: implications for sensation-seeking behaviors. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 90:11738–11742
Piazza PV, Rougé-Pont F, Deroche V, Maccari S, Simon H, Le Moal M (1996) Glucocorticoids have state-dependent stimulant effects on the mesencephalic dopaminergic transmission. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 93:8716–8720
Porter RJ, Gallagher P, Watson S, Lunn BS, Young AH (2002) Effects of sub-chronic administration of hydrocortisone on hormonal and psychological responses to l-tryptophan in normal male volunteers. Psychopharmacology 163:68–75
Prasad BM, Sorg BA, Ulibarri C, Kalivas PW (1995) Sensitization to stress and psychostimulants—involvement of dopamine transmission versus the HPA axis. Ann N Y Acad Sci 771:617–625
Roth RH, Wolf ME, Deutch AY (1987) Neurochemistry of midbrain dopamine systems. In: Meltzer HY (ed) Psychopharmacology: the third generation of progress. Raven Press, New York, pp 81–94
Rouge-Pont F, Usiello A, Benoit-Marand M, Gonon F, Piazza PV, Borrelli E (2002) Changes in extracellular dopamine induced by morphine and cocaine: crucial control by D2 receptors. J Neurosci 22:3293–3301
Shaham Y, Stewart J (1994) Exposure to mild stress enhances the reinforcing efficacy of intravenous heroin self-administration in rats. Psychopharmacology 114:523–527
Shaham Y, Funk D, Erb S, Brown TJ, Walker CD, Stewart J (1997) Corticotropin-releasing factor, but not corticosterone, is involved in stress-induced relapse to heroin-seeking in rats. J Neurosci 17:2605–2614
Slattum PW, Venitz J, Barr WH (1996a) Comparison of methods for the assessment of central nervous system stimulant response after dextroamphetamine administration to healthy male volunteers. J Clin Pharmacol 36:1039–1050
Smit HJ, Rogers PJ (2002) Effects of "energy" drinks on mood and mental performance: critical methodology. Food Quality Preference 13:317–326
SPSS (1998) SPSS for Windows version 9. SPSS Inc.
Stewart J (2000) Pathways to relapse: the neurobiology of drug- and stress-induced relapse to drug-taking. J Psychiatr Neurosci 25:125–136
Wachtel SR, Charnot A, de Wit H (2001) Acute hydrocortisone administration does not affect subjective responses to d-amphetamine in humans. Psychopharmacology 153:380–388
Watson S, Porter RJ, Young AH (2000) Effect of hydrocortisone on the pituitary response to growth hormone releasing hormone. Psychopharmacology 152:40–46
Wise RA, Rompre PP (1989) Brain dopamine and reward. Annu Rev Psychol 40:191–225
Wong ML, Kling MA, Munson PJ, Listwak S, Licinio J, Prolo P, Karp B, McCutcheon IE, Geracioti TD, DeBellis MD, Rice KC, Goldstein DS, Veldhuis JD, Chrousos GP, Oldfield EH, McCann SM, Gold PW (2000) Pronounced and sustained central hypernoradrenergic function in major depression with melancholic features: relation to hypercortisolism and corticotropin-releasing hormone. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97:325–330
Yeomans MR, Ripley T, Davies LH, Rusted JM, Rogers PJ (2002) Effects of caffeine on performance and mood depend on the level of caffeine abstinence. Psychopharmacology 164:241–249
Young AH, Sharpley AL, Campling GM, Hockney RA, Cowen PJ (1994) Effects of hydrocortisone on brain 5-HT function and sleep. J Affect Disord 32:139–146
Young AH, Rue J, Odontiadis J, Cowen PJ (1998) Lack of effect of hydrocortisone treatment on d-fenfluramine-mediated prolactin release. Psychopharmacology 136:198–200
Acknowledgements
We thank Mel Leitch and Dorothy Nelson for technical assistance and Anne Maule for assistance with preparation of the manuscript. This work was funded in part by the Mental Health Foundation (North-East branch).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hearn, A.J., Gallagher, P., Owen, B.M. et al. Effect of sub-chronic hydrocortisone on responses to amphetamine in normal male volunteers. Psychopharmacology 171, 458–464 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-003-1609-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-003-1609-5