Abstract
Rationale
Switching patients from one antipsychotic to another can lead to tolerability problems or transient symptom exacerbations. It is important to compare switching strategies to determine which methods produce the best possible patient outcomes.
Objective
To investigate the efficacy, safety and tolerability of three dosing strategies for switching chronic, stable patients with schizophrenia from current oral antipsychotic monotherapy to once-daily oral aripiprazole monotherapy.
Method
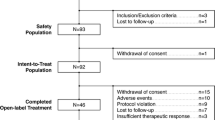
Patients in this 8-week, open-label, outpatient study were randomized to: 1) immediate initiation of 30 mg/day aripiprazole with simultaneous immediate discontinuation of current antipsychotic; 2) immediate initiation of 30 mg/day aripiprazole while tapering off current antipsychotic over 2 weeks; or 3) up-titrating aripiprazole to 30 mg/day over 2 weeks, while simultaneously tapering off current antipsychotic. Efficacy assessments included PANSS, CGI-S, and CGI-I scores. Safety assessments included: adverse events (AEs) recording, evaluation of extrapyramidal symptoms (EPS), vital signs, ECG, and clinical laboratory tests.
Results
Efficacy with aripiprazole was maintained during the study with numerical improvements compared with baseline in all three groups. The overall incidence of AEs was broadly comparable across all groups, and AEs were generally mild to moderate in severity and time-limited. Discontinuations due to AEs were comparable across the groups. No deterioration in EPS occurred in any group. The reduction in body weight and plasma prolactin levels following switch to aripiprazole were comparable across the three groups.
Conclusion
Any of the three strategies evaluated can be used safely for switching patients to aripiprazole from antipsychotic monotherapy. Furthermore, patients' symptoms may continue to improve after switching to aripiprazole.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barnes TRE (1989) A rating scale for drug-induced akathisia. Br J Psychiatry 154:672–676
Bunney WE, Meltzer HY (1995) Schizophrenia—overview. Clin Neurosci 3:55–56
Burris KD, Molski TF, Ryan E, Xu C, Tottori K, Kikuchi T, Yocca FD, Molinoff PB (2000) Aripiprazole is a high affinity partial agonist at human D2 dopamine receptors. Int J Psychopharmacol 3:S129
Carson WH, McQuade RD, Ali M, Saha AR, Dunbar GC, Ingenito GA (2001) A double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of aripiprazole and haloperidol. Schizophrenia Res (Special Issue VIIIth International Congress on Schizophrenia Research, Whistler, British Columbia, Canada) 49:221
Carson WH, Stock E, Saha AR, Ali M, McQuade RD, Kujawa MJ, Ingenito G (2002) Meta-analysis of safety and tolerability with aripiprazole. Abstracts of the XIth Biennial Winter Workshop on Schizophrenia, Davos, Switzerland, February 24–March 1 2002. Schizophr Res 53:1–274
Casey DE (1997) The relationship of pharmacology to side effects. J Clin Psychiatry 58:55–62
Davis JM, Schaffer CB, Killian GA, Kinard C, Chan C (1980) Important issues in the drug treatment of schizophrenia. Schizophr Bull 6:70–87
Dossenbach MRK, Beuzen JN, Avnon M, Belmaker RH, Elizur A, Mark M, Munitz H, Schneidman M, Shoshani D, Kratky P, Grundy SL, Tollefson GD (2000) The effectiveness of olanzapine in treatment-refractory schizophrenia when patients are nonresponsive to or unable to tolerate clozapine. Clin Ther 22:1021–1034
Dossenbach MR, Kratky P, Schneidman M, Grundy SL, Metcalfe S, Tollefson GD, Belmaker RH (2001) Evidence for the effectiveness of olanzapine among patients nonresponsive and/or intolerant to risperidone. J Clin Psychiatry 6:28–34
Fleischhacker WW, Meise U, Gunther V, Kurz M (1994) Compliance with antipsychotic drug treatment: influence of side effects. Acta Psychiatr Scand Suppl 382:11–15
Glennon RA, Dukat M (1995) Serotonin receptor subtypes. In: Bloom FE, Kupfer DJ (eds) Psychopharmacology. The fourth generation of progress. Raven Press, New York, pp 415–430
Goodnick PJ, Kato MM (2001) Antipsychotic medication: effects on regulation of glucose and lipids. Exp Opin Pharmacother 2:1571–1582
Guy W (1976a) Abnormal involuntary movement scale (AIMS). National Institute of Mental Health. In: ECDEU Assessment Manual for Psychopharmacology, Revised 1976. National Institute of Mental Health, Psychopharmacology Research Branch, Division of Basic Brain and Behavioral Sciences, Rockville, Md.
Guy W (1976b) Clinical Global Impressions (CGI). In: ECDEU Assessment Manual for Psychopharmacology. US Department of Health and Human Services, Public Health Service, Alcohol Drug Abuse and Mental Health Administration, NIMH Psychopharmacology Research Branch, Rockville, Md., pp. 218–222
Inoue T, Domae M, Yamada K, Furukawa T (1996) Effects of the novel antipsychotic agent 7-(4-[4-(2,3-dichlorophenyl)-1-piperazinyl]butyloxy)-3,4-dihydro-2(1H)-quinolinone (OPC-14597) on prolactin release from the rat anterior pituitary gland. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 277:137–143
Jan MW (1988) Buspirone: an update on a unique anxiolytic agent. Pharmacotherapy 8:100–116
Jordan S, Koprivica V, Chen R, Tottori K, Kikuchi T, Altar CA (2001) The antipsychotic aripiprazole is a potent, partial agonist at the human 5-HT1A receptor. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol 11:S268
Kane JM (1987) Treatment of schizophrenia. Schizophr Bull 13:133–156
Kane JM, Carson WH, Saha AR, McQuade RD, Ingenito GG, Zimbroff DL, Ali MW (2002) Efficacy and safety of aripiprazole and haloperidol versus placebo in patients with schizophrenia and schizoaffective disorder. J Clin Psychiatry 63:763–771
Kay SR, Opler LA, Fiszbein A (1987) The Positive and Negative Syndrome Scale (PANSS) for schizophrenia. Schizophr Bull 13:261–276
Kikuchi T, Tottori K, Uwahodo Y, Hirose T, Miwa T, Oshiro Y, Morita S (1995) 7-{4-[4-(2,3-Dichlorophenyl)-1-piperazinyl]butoxyl}-3,4-dihydro-2(1H)-quinolone (OPC-14597), a new putative antipsychotic drug with both presynaptic and postsynaptic D2 receptor antagonist activity. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 274:329–336
Kinon BJ, Kane JM, Johns C et al. (1993) Treatment of neuroleptic resistant schizophrenia relapse. Psychopharmacol Bull 29:309–314
Kinon BJ, Basson BR, Gilmore, JA, Malcolm S, Stauffer VL (2000) Strategies for switching from conventional antipsychotic drugs or risperidone to olanzapine. J Clin Psychiatry 61:833–840
Kolakowska T, Williams AO, Arden M et al. (1985) Schizophrenia with good and poor outcome. I: Early clinical features, response to neuroleptics and signs of organic dysfunction. Br J Psychiatry 146:229–239
Kurzthaler I, Fleishhacker WW (2001) The clinical implications of weight gain in schizophrenia. J Clin Psychiatry 62:32–37
Leysen JE, Janssen PMF, Schotte A, Luyten WHML, Mergens AAHP (1993) Interaction of antipsychotic drugs with neurotransmitter receptor sites in vitro and in vivo in relation to pharmacological and clinical role of 5-HT2 receptors. Psychopharmacology 112:S40
Lieberman JA, Johns CA, Kane JM, Rai K, Pisciotta AV, Saltz BL and Howard A (1988) Clozapine-induced agranulocytosis: non-cross-reactivity with other psychotropic drugs. J Clin Psychiatry 49:271–277
Littrell KH, Johnson CG, Hilligoss NM, Peabody CD, Littrell SH (2000) Switching clozapine responders to olanzapine. J Clin Psychiatry 61:912–915
McIntyre RS, Mancini DA, Basile VS (2001) Mechanisms of antipsychotic-induced weight gain. J Clin Psychiatry 62:23–29
Meltzer HY (2001) Putting metabolic side effects into perspective: risks versus benefits of atypical antipsychotics. J Clin Psychiatry 62:35–39
Meyer JM (2001) Effects of atypical antipsychotics on weight and serum lipid levels. J Clin Psychiatry 62:27–34
Millan MJ (2000) Improving the treatment of schizophrenia: focus on serotonin (5-HT)1A receptors. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 295:853–861
Peuskens J (2000) Switching approach in the management of schizophrenia patients. Int Clin Psychopharmacol 15:S15–19
Remington G, Chong S-A (1999) Conventional versus novel antipsychotics: changing concepts and clinical implications. J Psychiatr Neurosci 24:431–441
Saha AR, Carson WH, Ali MW, Dunbar GC, Ingenito G (2001) Efficacy and safety of aripiprazole and risperidone vs placebo in patients with schizophrenia and schizoaffective disorder. W J Biol Psychiatry 2:305S
Simpson GM, Angus JSW (1970) A rating scale for extrapyramidal side effects. Acta Psychiatr Scand 45:11–19
Sovner R, Parner-Sovner N (1989) Use of buspirone in the treatment of schizophrenia. J Clin Psychopharmacol 9:61–61
Sussman N (2001) Review of atypical antipsychotics and weight gain. J Clin Psychiatry 62:5–12
Yeung PP, Carson WH, Saha AR, McQuade RD, Ali MW, Stringfellow JC, Ingenito G (2001) Efficacy of aripiprazole, a novel antipsychotic, in schizophrenia and schizoaffective disorder: results of a placebo-controlled trial with risperidone. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol 11:S241
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by Bristol-Myers Squibb and Otsuka Pharmaceutical Co.
Members of the Aripiprazole Study Group: S. Altinsan, Pharmacology Research Corporation, Reno, Nev., USA; T.M. Antin, PACT Atlanta LLC, Decatur, Ga., USA; M. Banov, Northwest Behavioral Research Center, Marietta, Ga., USA; B. Bastani, North Coast Clinical Trials, Beachwood, Ohio, USA; R. Bielski, Institute for Health Studies, Okemos, Mich., USA; J. Carr, Affiliated Research Institute, Claremont, Calif., USA; S. Cheren, Stanley Cheren, MD, Inc., Brookline, Mass., USA; A. Cutler, Coordinated Research of Florida, Inc., Winter Park, Fla., USA; J.M. Ferguson, Pharmacology Research Clinic, Salt Lake City, Utah, USA; D.L. Fogelson, Pacific Psychopharmacology Research, Santa Monica, Calif., USA; A.M. Freeman, III, Louisiana State University Medical Center, Shreveport, La., USA; H.L. Goldberg, Kauai Community Mental Health Center, Lihue, Hawaii, USA; M.S. Hale, New Britain General Hospital, New Britain, Conn., USA; M.B Hamner, Ralph H. Johnson VA Medical Center, Charleston, S.C., USA; J.T. Hartford, Hartford Research Group, Cincinnati, Ohio, USA; I.S. Kolin, Irving S. Kolin, MD, PA, Winter Park, Fla., USA; G.L. Larson, VA Medical Center, Milwaukee, Wisc., USA; D. Mee-Lee, Hawaii Clinical Research Center, Honolulu, Hawaii, USA; A.L. Miller, University Health Center-Downtown, San Antonio, Tex., USA; J. Miller, Clinical Neuroscience Solutions, West Palm Beach, Fla., USA; J.J. Pahl, Pahl Brain Associates, Inc., Oklahoma City, Okla., USA; R.L. Pearlman, Sisters of Charity Medical Center, Staten Island, N.Y., USA; D.A. Sack, The Institute of Psychopharmacology, Cerritos, Calif., USA; J.S. Simon, Northbrooke Research Center, Brown Deer, Wisc., USA; K. Sokolski, Affiliated Research Institute, Santa Ana, Calif., USA; V. Spratlin, Mercer University, Atlanta, Ga., USA; T.K. Tran-Johnson, California Neuropsychopharmacology, San Diego, Calif., USA; M.M. Viner, Pharmacology Research Corporation, Reno, Nev., USA; S.A. West, Psychiatric Institute of Florida, PA, Orlando, Fla., USA; C. Wronski, Affiliated Research Institute, Santa Ana, Calif., USA; D.L. Zimbroff, Pacific Clinical Research, San Bernardino, Calif., USA.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Consortia
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Casey, D.E., Carson, W.H., Saha, A.R. et al. Switching patients to aripiprazole from other antipsychotic agents: a multicenter randomized study. Psychopharmacology 166, 391–399 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-002-1344-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-002-1344-3