Heading
Abstract
Rationale. α-2 Noradrenergic agonists improve spatial working memory in animals and in humans. Of the three α-2 receptor subtypes, evidence has suggested that this cognitive improvement may be mediated by the α-2A receptor subtype, but this has not been established. α-2 Agonists are also known to decrease blood pressure significantly. Recent evidence using genetically altered mice indicates that the α-2A receptor subtype mediates this decrease in blood pressure.
Objectives. The present study examined whether the cognitive improvement and hypotension produced by α-2 agonists are mediated by the same receptor subtype in rhesus monkeys. The hypotensive and cognitive-enhancing effects of clonidine and guanfacine were challenged with two α-2 antagonists with differing affinities for the three α-2 receptor subtypes: MK912, a potent antagonist which shows preferential binding to the α-2C receptor subtype, and idazoxan, which slightly prefers the α-2A receptor subtype. If α-2C receptors contribute to the cognitive enhancement, MK912 should reverse the cognitive-enhancing effects of α-2 agonists at lower doses than those needed to reverse the hypotensive effects of these compounds. Conversely, if α-2A receptors contribute to cognitive enhancement, MK912 and idazoxan should reverse the cognitive-enhancing effects of α-2 agonists at the same doses as those needed to reverse the hypotensive effects of these compounds.
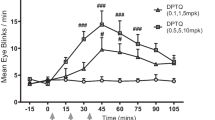
Results. MK-912 and idazoxan dose-dependently reversed both clonidine and guanfacine-induced cognitive improvement and hypotension. Both antagonists were equally potent in reversing either the cognitive enhancement or the hypotension.
Conclusions. The identical pattern of dose-dependent reversal of cognitive improvement and hypotension indicates that, in non-human primates, the same receptor subtype mediates both effects. Previous evidence suggests that the most likely candidate is the α-2A receptor subtype.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Electronic Publication
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Franowicz, J.S., Arnsten, A.F. Actions of α-2 noradrenergic agonists on spatial working memory and blood pressure in rhesus monkeys appear to be mediated by the same receptor subtype. Psychopharmacology 162, 304–312 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-002-1110-6
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-002-1110-6